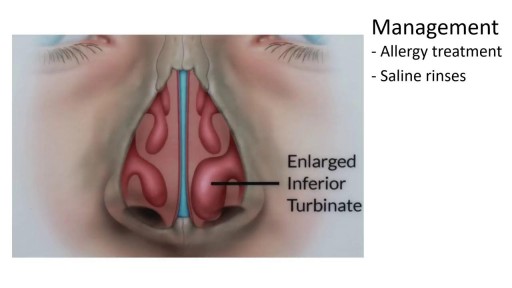
Top videos
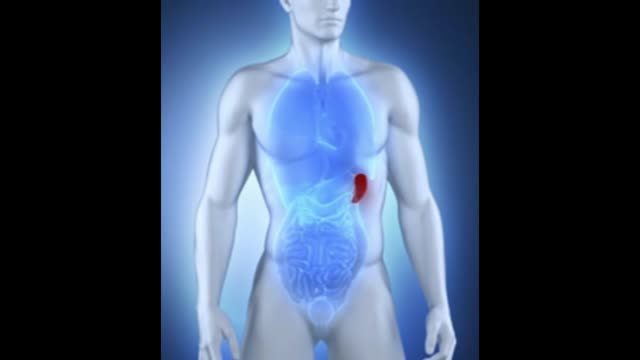
What is the spleen and what causes an enlarged spleen (splenomegaly)? The spleen sits under your rib cage in the upper left part of your abdomen toward your back. It is an organ that is part of the lymph system and works as a drainage network that defends your body against infection. White blood cells produced in the spleen engulf bacteria, dead tissue, and foreign matter, removing them from the blood as blood passes through it. The spleen also maintains healthy red and white blood cells and platelets; platelets help your blood clot. The spleen filters blood, removing abnormal blood cells from the bloodstream. A spleen is normally about the size of your fist. A doctor usually can't feel it during an exam. But diseases can cause it to swell and become many times its normal size. Because the spleen is involved in many functions, many conditions may affect it.
A breech birth occurs when a baby is born bottom first instead of head first. Around 3-5% of pregnant women at term (37–40 weeks pregnant) will have a breech baby. Most babies in the breech position are born by a caesarean section because it is seen as safer than being born vaginally.

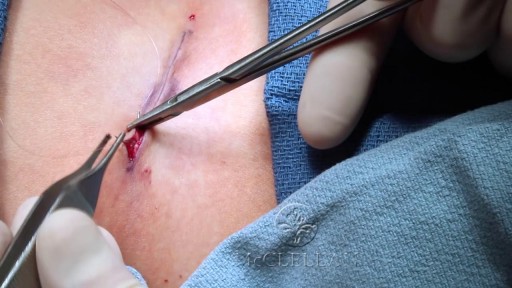
Patients are generally placed in a supine position with the head in an extended position. As noted above, Gardner-Wells tongs can be used for additional cervical traction. The hands can also be tied downward to increase the operative exposure. Once the surgical site is properly prepared with cleansing material, the appropriate surgical level is identified with intraoperative radiographs. A scalpel is used to make a linear longitudinal incision just medial to the body of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The incision is made long enough to include at least 2 vertebral levels if a 1-level discectomy is being performed. Alternatively, transverse skin incisions over the targeted vertebral level can also be performed. The platysmal muscle is identified and incised. The platysmal incision can be extended if a multilevel decompression is the surgical aim. Extensive subplatysmal dissection is performed to reduce retraction injury.

Candida Albicans is more than just yeast- for most people, it's already mutated into a more aggressive fungal form that eats holes through the intestinal tract causing many of todays health problems like food allergies, autoimmune disorders, Crohn's disease, IBS, low energy and many more aggressive diseases. People need to know what it is and what to do about it.

A parasitic twin (also known as an asymmetrical or unequal conjoined twin) is the result of the processes that produce vanishing twins and conjoined twins, and may represent a continuum between the two. Parasitic twins occur when a twin embryo begins developing in utero, but the pair does not fully separate, and one embryo maintains dominant development at the expense of the other. Unlike conjoined twins, one ceases development during gestation and is vestigial to a mostly fully-formed, otherwise healthy individual twin. The undeveloped twin is defined as parasitic, rather than conjoined, because it is incompletely formed or wholly dependent on the body functions of the complete fetus. The independent twin is called the autosite.
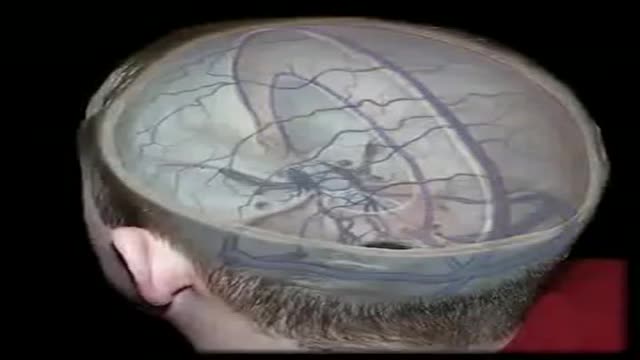
The dural venous sinuses are spaces between the endosteal and meningeal layers of the dura. They contain venous blood that originates for the most part from the brain or cranial cavity. The sinuses contain an endothelial lining that is continuous into the veins that are connected to them.