Top videos
A renal biopsy is a procedure used to extract kidney tissue for laboratory analysis. The word “renal” describes the kidneys. A renal biopsy is also called a kidney biopsy. The test helps your doctor identify the type of kidney disease you have, how severe it is, and the best treatment for it.

Symptoms of depression in women include: Persistent sad, anxious, or "empty" mood. Loss of interest or pleasure in activities, including sex. Restlessness, irritability, or excessive crying. Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, helplessness, hopelessness, pessimism. Sleeping too much or too little, early-morning awakening.

This case study video from www.5thavesurgery.com shows a 19 year old patient getting breast reduction surgery in NYC. This surgery made a tremendous difference in the life of this young woman, see how it can do the same for you.
Most babies will move into delivery position a few weeks prior to birth, with the head moving closer to the birth canal. When this fails to happen, the baby’s buttocks and/or feet will be positioned to be delivered first. This is referred to as “breech presentation.” Breech births occur in approximately 1 out of 25 full-term births.
ow does a perforation of the eardrum occur? There are many ways an eardrum perforation can occur. An infection behind the eardrum in the middle ear may cause a rupture of the eardrum. Trauma to the ear may result from an object entering the ear canal and puncturing the eardrum. A traumatic blow to the ear with a cupped hand can rupture the eardrum. Hot welding slag can burn a hole through the eardrum. After a ventilation tube has been extruded or is removed, the opening usually closes; in some cases a permanent opening of the eardrum may occur. Chronic ear problems such as deep retraction pockets and cholesteatoma can weaken and erode the eardrum, resulting in a defect or perforation.
Carpal tunnel release (part 1). Skin incision and retraction. Procedure performed by Deepak Kapila, MD, Broward Health, Fort Lauderdale, FL. Courtesy of BroadcastMed (http://ortho.broadcastmed.com/....4229/videos/carpal-t
There are hundreds more procedural videos as well as news, features, resources and references on Medscape.com. Join today for free.
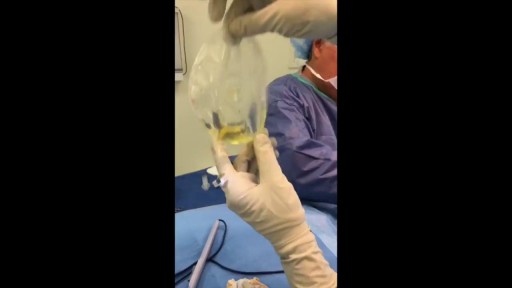
As you can see I access the left implant from the periareolar incisions which I made at the lower portion of the areola. As I entered the capsule and begin to remove the implant I noticed a lot of fluid surrounding the implant. Right away I know this is a rupture and that the mammogram was incorrect. Mammograms are very helpful in detecting cancer but often not ruptures. When implants rupture, it is important to have them replaced as soon as possible to avoid excessive scarring in the breasts. If too much scar tissue has accumulated around the deflated implant, it becomes difficult to create a normal breast shape in the future. Therefor know the signs of a ruptured implant such as, painful to touch, visible asymmetry or loss of integrity to the bag. For more information please visit: www.drlinder.com
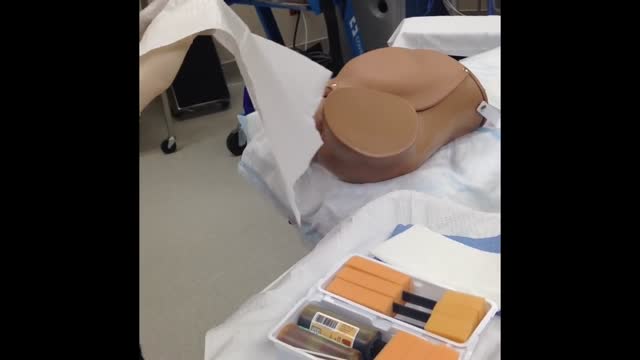
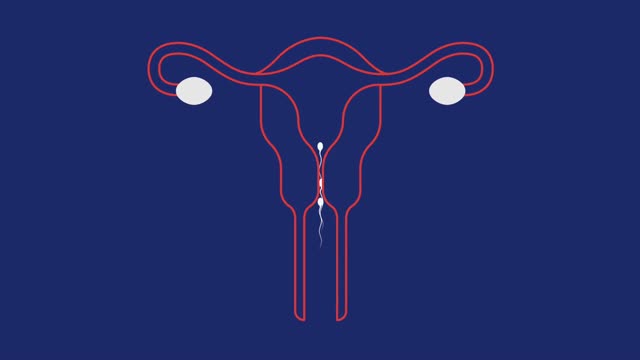
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure to remove tissue from inside your uterus. Doctors perform dilation and curettage to diagnose and treat certain uterine conditions — such as heavy bleeding — or to clear the uterine lining after a miscarriage or abortion.
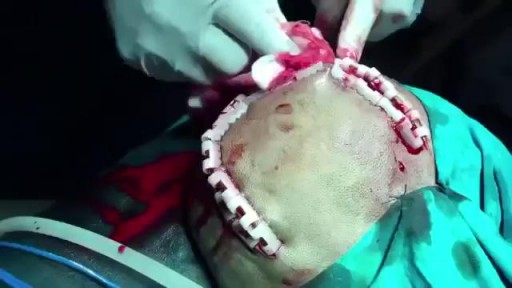
Epidural hematoma (EDH) is a traumatic accumulation of blood between the inner table of the skull and the stripped-off dural membrane. EDH results from traumatic head injury, usually with an associated skull fracture and arterial laceration.The inciting event often is a focused blow to the head, such as that produced by a hammer or baseball bat. In 85-95% of patients, this type of trauma results in an overlying fracture of the skull. Blood vessels in close proximity to the fracture are the sources of the hemorrhage in the formation of an epidural hematoma. Because the underlying brain has usually been minimally injured, prognosis is excellent if treated aggressively. Outcome from surgical decompression and repair is related directly to patient's preoperative neurologic condition. [1]

Watch to learn more about what happens during a stent procedure.
More information about this procedure and other heart care at BJC: https://www.bjc.org/Services/M....edical-Services/angi
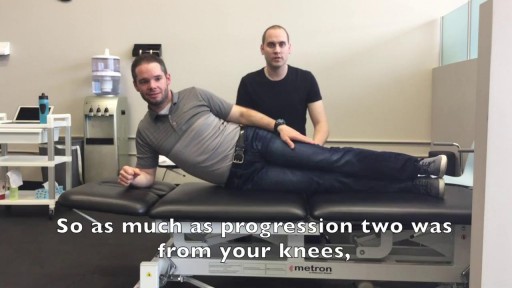
We get excited when people graduate! May it be graduating from physiotherapy or even graduating onto a new progression of an exercise! Today you move onto new challenges as Mike & Tyler demonstrate the final side plank progression. Kitchener Massage Therapy - http://www.strivept.ca/massage-therapy-kitchener.html