Top videos
Possible causes are a blocked milk duct or bacteria entering the breast. It usually occurs within the first three months of breast-feeding. Symptoms include breast pain, swelling, warmth, fever, and chills. Antibiotics are required. Mild pain relievers can help with discomfort.
Cytomegalovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Humans and monkeys serve as natural hosts.
Body Restorations will do an “Early Assessment” when you come in for physiotherapy; this allows therapists to identify the more complicated cases quickly and get started with treatment right away. If you are feeling pain now, it is best that you seek treatment as soon as possible. Research has proven that people who seek treatment for their pain immediately have less of a chance of it becoming an issue later own. Early intervention is always the best option. Visit - https://stalbertphysiotherapy.com/contact/
SureViagra.com is an online drug store served generic Viagra pills at best prices.
They might not sound very life threatening, but a blood clot that develops in the deep veins of your leg, if left untreated and unable to dissolve of its own volition, may detach and travel to your lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (or PE). In most cases, a leg blood clot will form due to lengthy periods of travel, for example if you remain immobile in cramped spaces—such as an airplane or bus—with few opportunities to stretch your legs or get up and walk around. Here are ten signs that you may have a dangerous blood clot in your leg
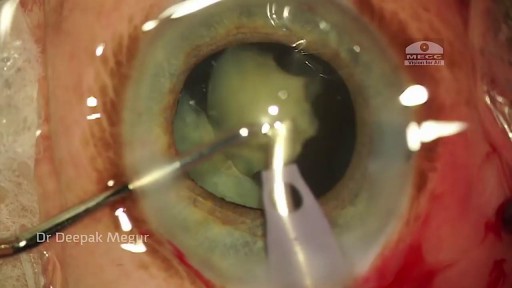
Phacolytic glaucoma usually is associated with a mature or hypermature cataract and typically occurs in elderly patients. Today, phacolytic glaucoma is rare in the United States, found primarily in areas where access to care is poor. Will the increase in the number of under- and uninsured patients lead to an increase in this condition? Evaluation and Diagnosis Signs and symptoms. Patients typically report acute-onset pain, decreased vision, tearing and photophobia. Examination will reveal injection, corneal edema, elevated IOP, anterior chamber reaction with or without pseudohypopyon, particles on the lens capsule and anterior capsule wrinkling. Patient history. The duration of symptoms should be elicited; a delayed presentation of more than five days since onset can result in glaucomatous disc damage and poorer prognosis.¹ The ocular history may reveal that the patient decided against removal of an advanced cataract. Prior intraocular surgery or trauma may have left residual lens material that could cause phacoanaphylactic glaucoma or exacerbate infectious endophthalmitis. Visual acuity and visual potential should be assessed. Exam essentials. A complete ophthalmologic examination should be done. The eye should be inflamed, and the cornea may be edematous due to the high IOP. The anterior chamber will demonstrate massive inflammation and/ or pseudohypopyon. Gonioscopy is essential; it will help rule out angle closure due to phacomorphic glaucoma or neovascularization of the angle. Assess ment of the posterior pole should be performed to rule out vitreous hemorrhage (which can result in ghost-cell glaucoma) or vitritis (which may be associated with infectious endophthalmitis or panuveitis). If the view to the fundus is obstructed, B-scan ultrasonography also should be performed. Differential diagnosis. The differential diagnosis includes infectious endophthalmitis, phacoanaphylactic glaucoma, inflammatory glaucoma, glaucoma secondary to intraocular tumor, phacomorphic glaucoma, acute-angle closure glaucoma and neovascular glaucoma. Management Medication. Medical management is used to temporarily control the glaucoma and inflammation. Initial treatment consists of hyperosmotic agents, aqueous suppressants, anti-inflammatory drugs and cycloplegics. Surgery. Definitive treatment is removal of the lens via extracapsular cataract extraction with or without an IOL. Some ophthalmologists defer placement of an IOL until after the inflammation subsides; however, there is no significant difference in final visual acuity between those patients who did receive an IOL and those who did not.¹ If the phacolytic glaucoma is of long duration (more than seven days), a combined trabeculectomy may be needed to prevent postoperative IOP spikes.² In eyes with hypermature Morgagnian cataracts, one must be especially careful, as the capsule is fragile, the zonules are weak and the view is difficult due to the white, milky cortex. Vision limited to light perception on presentation is not a contraindication to performing cataract extraction. Surgical Tips For a planned extracapsular cataract extraction with a posterior chamber IOL, fashion a superior fornix-based conjunctival flap.³ Make a partial-thickness incision along the sclerolimbal junction superiorly for 120 degrees with a No. 69 blade. Forty-five degrees away, a paracentesis should be done to decompress the eye. The anterior chamber fluid can be withdrawn for analysis, to look for macrophages and high molecular-weight proteins. Inject balanced salt solution in a cannula to wash out any residual particulate matter, then inject Healon or viscoelastic into the anterior chamber. Make an incision entering the anterior chamber at the 12 o’clock position with a keratome. A 26-gauge cystotome mounted on a syringe is then introduced through the 12 o’clock incision and used to puncture the capsular bag. The milky cortex should be aspirated as much as possible, until the nucleus is visible. Withdraw the needle through the keratome incision, then inject Healon through the 12 o’clock incision into the capsular bag. Next, enlarge the corneoscleral keratome incision with curved Westcott scissors to 120 degrees. Perform a partial V-shaped capsulotomy; this can be done either with the cystotome or with an angled Vannas scissors. Place viscoelastic under the nucleus to float the nucleus and sever any adhesions between the nucleus and the capsule. The nuclear portion of the lens can then be removed with an irrigating vectis (lens loop) with or without gentle pressure at the inferior limbus (6 o’clock). Irrigate and aspirate the residual cortex with the Simcoe cannula. Inspect the capsular bag; if it is intact, place a posterior chamber IOL into the bag. Close the incision with several interrupted 10-0 monofilament nylon sutures and reattach the conjunctival flap. Potential Sequelae and Prognosis Postoperatively, the patient should be managed with topical steroids and/or aqueous suppressants and hyperosmotics if necessary. Vitreous opacification behind the posterior capsule occurs in a small percentage of eyes. These vitreous opacities are typically absorbed by one to two weeks postoperatively. IOP usually is controlled without antiglaucoma medications after the cataract removal. A detailed glaucoma evaluation (including repeat gonioscopy to assess for peripheral anterior synechiae, visual field and optic nerve status) should be done to assess the extent of glaucomatous damage. The prognosis is dependent on the duration of elevated IOP, PAS and optic nerve damage. In one study, patients who were older than 60 and whose glaucoma was present for more than five days did significantly worse than a comparison group of younger individuals with shorter disease duration.
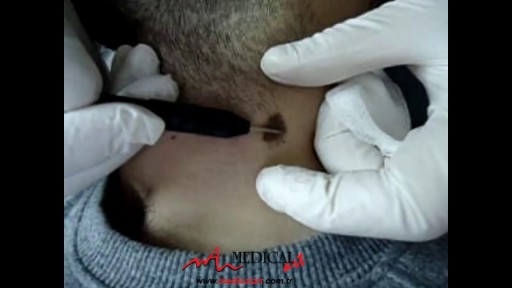
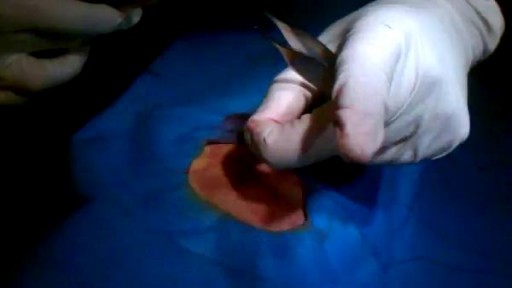
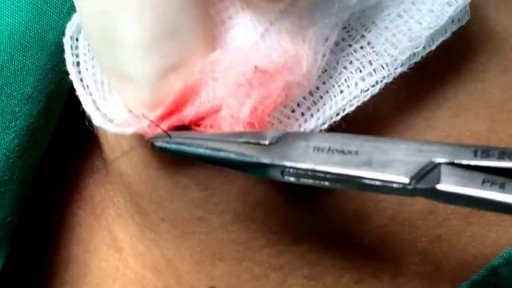
Most people develop several moles (nevi) throughout adulthood. Moles can be found anywhere on the body, usually in sun-exposed areas, and are usually brown, smooth, and slightly raised. In most cases, a nevus is benign and doesn't require treatment. Rarely, they turn into melanoma or other skin cancers. A nevus that changes shape, grows bigger, or darkens should be evaluated for removal.
Most people develop several moles (nevi) throughout adulthood. Moles can be found anywhere on the body, usually in sun-exposed areas, and are usually brown, smooth, and slightly raised. In most cases, a nevus is benign and doesn't require treatment. Rarely, they turn into melanoma or other skin cancers. A nevus that changes shape, grows bigger, or darkens should be evaluated for removal.
The condition is caused by a blockage in the lymphatic system, part of the immune and circulatory systems. Lymphedema is most commonly caused by lymph node removal or damage due to cancer treatment. The main symptom is swelling in an arm or leg that may be accompanied by pain or discomfort. Exercise, wrapping, massage, and compression can help.
Treating Lymphedema -
Alcoholic hepatitis is inflammation of the liver caused by drinking alcohol. Alcoholic hepatitis is most likely to occur in people who drink heavily over many years. However, the relationship between drinking and alcoholic hepatitis is complex. Not all heavy drinkers develop alcoholic hepatitis, and the disease can occur in people who drink only moderately. If you're diagnosed with alcoholic hepatitis, you must stop drinking alcohol. People who continue to drink alcohol face a high risk of serious liver damage and death.