Top videos
If they are damaged, waste and fluids build up in your blood instead of leaving your body. Kidney damage from diabetes is called diabetic nephropathy. It begins long before you have symptoms. An early sign of it is small amounts of protein in your urine.
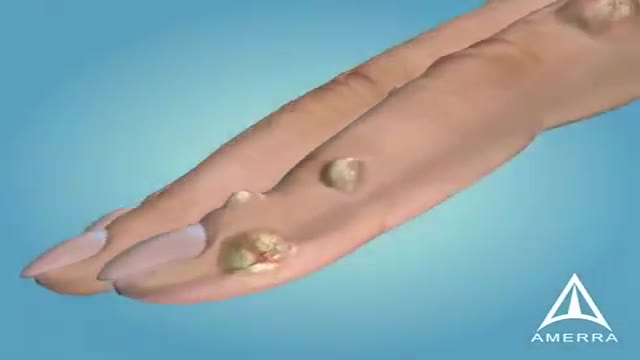
But common warts are actually an infection in the top layer of skin, caused by viruses in the human papillomavirus, or HPV, family. When the virus invades this outer layer of skin, usually through a tiny scratch, it causes rapid growth of cells on the outer layer of skin – creating the wart.
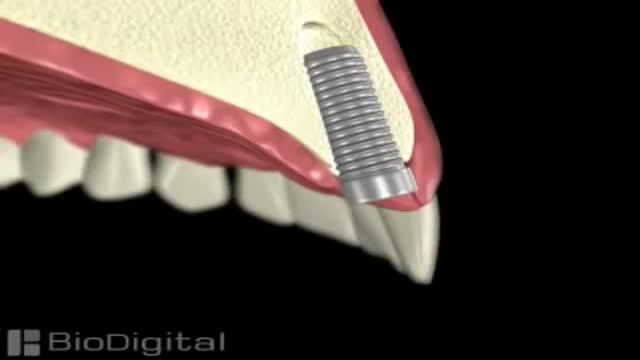
If you are self-conscious because you have missing teeth, wear dentures that are uncomfortable or don't want to have good tooth structure removed to make a bridge, talk to your dentist to see if dental implants are an option for you. Dental implants are a popular and effective way to replace missing teeth and are designed to blend in with your other teeth. They are an excellent long-term option for restoring your smile. In fact, the development and use of implants is one of the biggest advances in dentistry in the past 40 years. Dental implants are made up of titanium and other materials that are compatible with the human body. They are posts that are surgically placed in the upper or lower jaw, where they function as a sturdy anchor for replacement teeth.
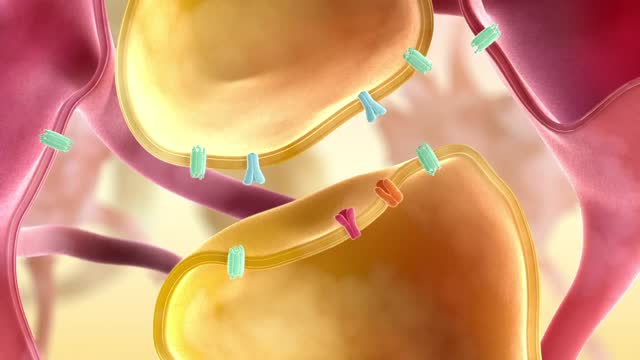
Ca2+ binds with the membrane of the synaptic vesicles, which causes the vesicles to break and release the neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. After the neurotransmitters are released, they diffuse across the synaptic cleft and interact with receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. When the action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal, it provokes the release of a small quantity of neurotransmitter molecules, which bind to chemical receptor molecules located in the membrane of another neuron, the postsynaptic neuron, on the opposite side of the synaptic cleft.
The cause of schizophrenia is still unclear. Some theories about the cause of this disease include: genetics (heredity), biology (abnormalities in the brain’s chemistry or structure); and/or possible viral infections and immune disorders.
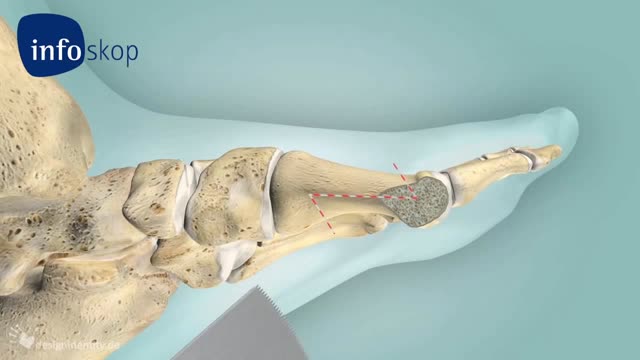
Knee osteotomy is commonly used to realign your knee structure if you have arthritic damage on only one side of your knee. The goal is to shift your body weight off the damaged area to the other side of your knee, where the cartilage is still healthy. When surgeons remove a wedge of your shinbone from underneath the healthy side of your knee, the shinbone and thighbone can bend away from the damaged cartilage. Imagine the hinges on a door. When the door is shut, the hinges are flush against the wall. As the door swings open, one side of the door remains pressed against the wall as space opens up on the other side. Removing just a small wedge of bone can "swing" your knee open, pressing the healthy tissue together as space opens up between the thighbone and shinbone on the damaged side so that the arthritic surfaces do not rub against each other. Osteotomy is also used as an alternative treatment to total knee replacement in younger and active patients. Because prosthetic knees may wear out over time, an osteotomy procedure can enable younger, active osteoarthritis patients to continue using the healthy portion of their knee. The procedure can delay the need for a total knee replacement for up to ten years.
Alzheimer's worsens over time. Alzheimer's is a progressive disease, where dementia symptoms gradually worsen over a number of years. In its early stages, memory loss is mild, but with late-stage Alzheimer's, individuals lose the ability to carry on a conversation and respond to their environment. Alzheimer's is the sixth leading cause of death in the United States. Those with Alzheimer's live an average of eight years after their symptoms become noticeable to others, but survival can range from four to 20 years, depending on age and other health conditions. Alzheimer's has no current cure, but treatments for symptoms are available and research continues. Although current Alzheimer's treatments cannot stop Alzheimer's from progressing, they can temporarily slow the worsening of dementia symptoms and improve quality of life for those with Alzheimer's and their caregivers. Today, there is a worldwide effort under way to find better ways to treat the disease, delay its onset, and prevent it from developing. Alzheimer's has no current cure, but treatments for symptoms are available and research continues. Although current Alzheimer's treatments cannot stop Alzheimer's from progressing, they can temporarily slow the worsening of dementia symptoms and improve quality of life for those with Alzheimer's and their caregivers. Today, there is a worldwide effort under way to find better ways to treat the disease, delay its onset, and prevent it from developing.
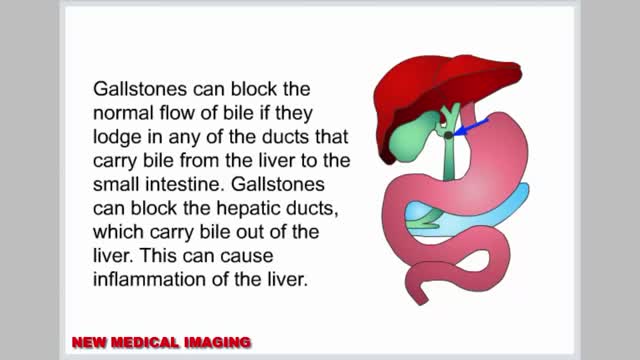
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid that can form in your gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into your small intestine. Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people develop just one gallstone, while others develop many gallstones at the same time. Gallstones are common in the United States. People who experience symptoms from their gallstones usually require gallbladder removal surgery. Gallstones that don't cause any signs and symptoms typically don't need treatment.

Initially, lead poisoning can be hard to detect — even people who seem healthy can have high blood levels of lead. Signs and symptoms usually don't appear until dangerous amounts have accumulated. Lead poisoning symptoms in children Signs and symptoms of lead poisoning in children include: Developmental delay Learning difficulties Irritability Loss of appetite Weight loss Sluggishness and fatigue Abdominal pain Vomiting Constipation Hearing loss Seizures Eating things, such as paint chips, that aren't food (pica) Lead poisoning symptoms in newborns Babies exposed to lead before birth might: Be born prematurely Have lower birth weight Have slowed growth Lead poisoning symptoms in adults Although children are primarily at risk, lead poisoning is also dangerous for adults. Signs and symptoms in adults might include: High blood pressure Joint and muscle pain Difficulties with memory or concentration Headache Abdominal pain Mood disorders Reduced sperm count and abnormal sperm Miscarriage, stillbirth or premature birth in pregnant women Causes Lead is a metal that occurs naturally in the earth's crust, but human activity — mining, burning fossil fuels and manufacturing — has caused it to become more widespread. Lead was also once used in paint and gasoline and is still used in batteries, solder, pipes, pottery, roofing materials and some cosmetics. Lead in paint Lead-based paints for homes, children's toys and household furniture have been banned in the United States since 1978. But lead-based paint is still on walls and woodwork in many older homes and apartments. Most lead poisoning in children results from eating chips of deteriorating lead-based paint. Water pipes and imported canned goods Lead pipes, brass plumbing fixtures and copper pipes soldered with lead can release lead particles into tap water. Lead solder in food cans, banned in the United States, is still used in some countries. Other sources of lead exposure Lead sometimes can also be found in: Soil. Lead particles from leaded gasoline or paint settle on soil and can last years. Lead-contaminated soil is still a major problem around highways and in some urban settings. Some soil close to walls of older houses contains lead. Household dust. Household dust can contain lead from lead paint chips or from contaminated soil brought in from outside. Pottery. Glazes found on some ceramics, china and porcelain can contain lead that can leach into food served or stored in the pottery. Toys. Lead is sometimes found in toys and other products produced abroad. Cosmetics. Tiro, an eye cosmetic from Nigeria, has been linked to lead poisoning. Herbal or folk remedies. Lead poisoning has been linked to greta and azarcon, traditional Hispanic medicines, as well as some from India, China and other countries. Mexican candy. Tamarind, an ingredient used in some candies made in Mexico, might contain lead. Lead bullets. Time spent at firing ranges can lead to exposure. Occupations. People are exposed to lead and can bring it home on their clothes when they work in auto repair, mining, pipe fitting, battery manufacturing, painting, construction and certain other fields

Osgood-Schlatter disease can cause a painful lump below the kneecap in children and adolescents experiencing growth spurts during puberty. Osgood-Schlatter disease occurs most often in children who participate in sports that involve running, jumping and swift changes of direction — such as soccer, basketball, figure skating and ballet. While Osgood-Schlatter disease is more common in boys, the gender gap is narrowing as more girls become involved with sports. Age ranges differ by sex because girls experience puberty earlier than do boys. Osgood-Schlatter disease typically occurs in boys ages 13 to 14 and girls ages 11 to 12. The condition usually resolves on its own, once the child's bones stop growing.

The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, keeping the head of your upper arm bone firmly within the shallow socket of the shoulder. A rotator cuff injury can cause a dull ache in the shoulder, which often worsens when you try to sleep on the involved side. Rotator cuff injuries occur most often in people who repeatedly perform overhead motions in their jobs or sports. Examples include painters, carpenters, and people who play baseball or tennis. The risk of rotator cuff injury also increases with age. Many people recover from rotator cuff disease with physical therapy exercises that improve flexibility and strength of the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. Sometimes, rotator cuff tears may occur as a result of a single injury. In those circumstances, medical care should be provided as soon as possible. Extensive rotator cuff tears may require surgical repair, transfer of alternative tendons or joint replacement.
You're sneezing, coughing, and all stuffed up. It sounds and feels like a cold, alright. But as time goes on, you start to wonder. Is it turning into a sinus infection? They've got some things in common, but there are ways to tell them apart. The right ID lets your doctor get you the best treatment. What Is a Common Cold? It's an infection caused by a virus, a tiny living thing. You can't miss the symptoms: Nasal congestion Runny nose Post-nasal drip (drop-by-drop release of fluid from your nose into the back of the throat) Headache Fatigue You may also get a cough and a mild fever. The symptoms usually build, peak, and slowly disappear. Some medications can ease symptoms. For example, decongestants may decrease drainage and open the nasal passages. Pain relievers may help with fever and headache. Cough medicine may help, as well. Colds typically last from a few days to about a week or longer. Sometimes, a cold may cause swelling in the sinuses, hollow spaces in your skull that are connected to each other. The swelling can prevent the flow of mucus.
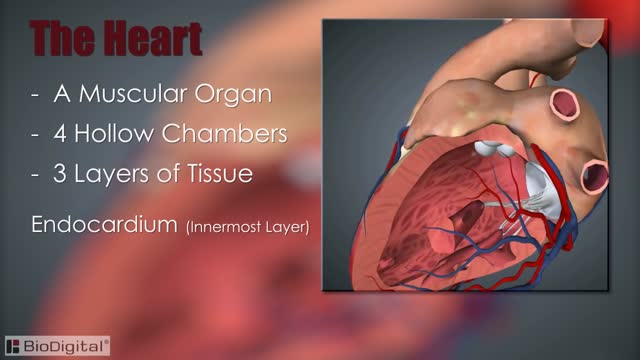
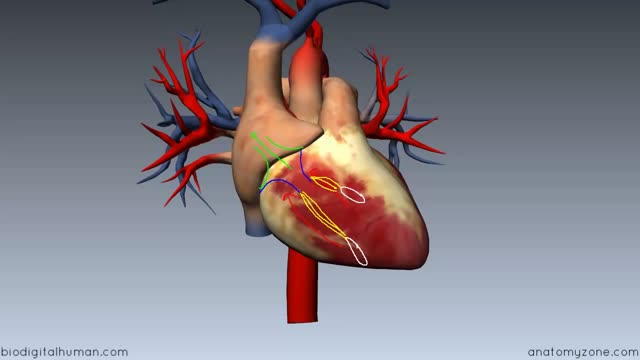
The heart, blood vessels, and blood are the parts that make up the circulatory system, which is defined as a closed system of blood vessels for the transport of gasses and nutrients. The heart is the key organ in the circulatory system. As a hollow, muscular pump, its main function is to propel blood throughout the body.

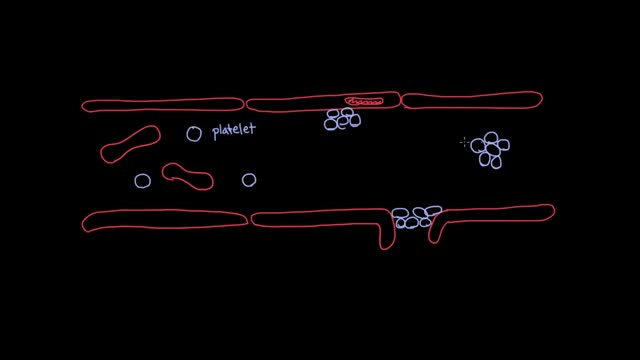
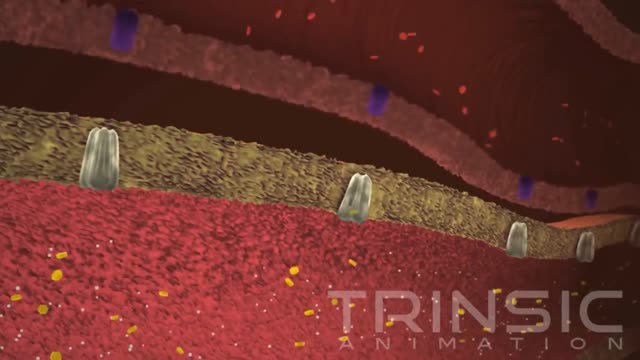
Hemophilia A, also called factor VIII (FVIII) deficiency or classic hemophilia, is a genetic disorder caused by missing or defective factor VIII, a clotting protein. Although it is passed down from parents to children, about 1/3 of cases are caused by a spontaneous mutation, a change in a gene. According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, hemophilia occurs in approximately 1 in 5,000 live births. There are about 20,000 people with hemophilia in the US. All races and ethnic groups are affected. Hemophilia A is four times as common as hemophilia B while more than half of patients with hemophilia A have the severe form of hemophilia.

Cancer starts when cells in a part of the body begins to grow out of control and can spread to other areas of the body. There are many kinds of cancer. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer. To learn more about how cancers start and spread, see What Is Cancer? Leukemias are cancers that start in cells that would normally develop into different types of blood cells. Here we will talk about acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) has many other names, including acute myelocytic leukemia, acute myelogenous leukemia, acute granulocytic leukemia, and acute non-lymphocytic leukemia. “Acute” means that this leukemia can progress quickly if not treated, and would probably be fatal in a few months. “Myeloid” refers to the type of cell this leukemia starts from. Most cases of AML develop from cells that would turn into white blood cells (other than lymphocytes), but some cases of AML develop in other types of blood-forming cells. The different types of AML are listed in “ How is acute myeloid leukemia classified?” AML starts in the bone marrow (the soft inner part of certain bones, where new blood cells are made), but in most cases it quickly moves into the blood. It can sometimes spread to other parts of the body including the lymph nodes, liver, spleen, central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), and testicles. Other types of cancer can start in these organs and then spread to the bone marrow. But these cancers that start elsewhere and then spread to the bone marrow are not leukemias. Normal bone marrow, blood, and lymphoid tissue To understand the different types of leukemia, it helps to know about the blood and lymph systems.