Top videos
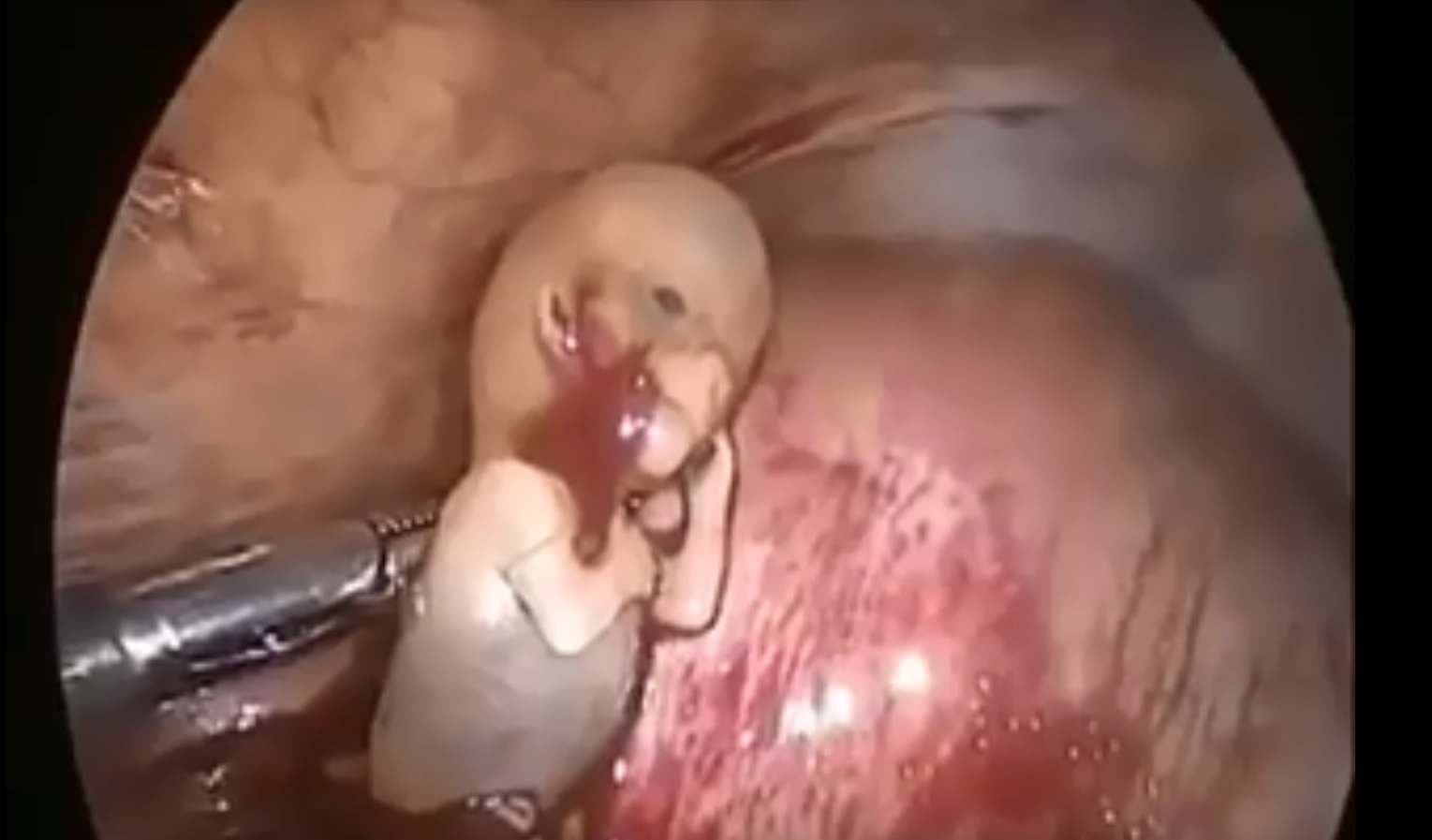
Watch that Ectopic Pregnancy Abortion Surgery
Sepsis occurs when chemicals released in the bloodstream to fight an infection trigger inflammation throughout the body. This can cause a cascade of changes that damage multiple organ systems, leading them to fail, sometimes even resulting in death. Symptoms include fever, difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, fast heart rate, and mental confusion. Treatment includes antibiotics and intravenous fluids.
ABGs Made Easy | Arterial Blood Gas | Acid Base Balance: Everything You Need To Know!
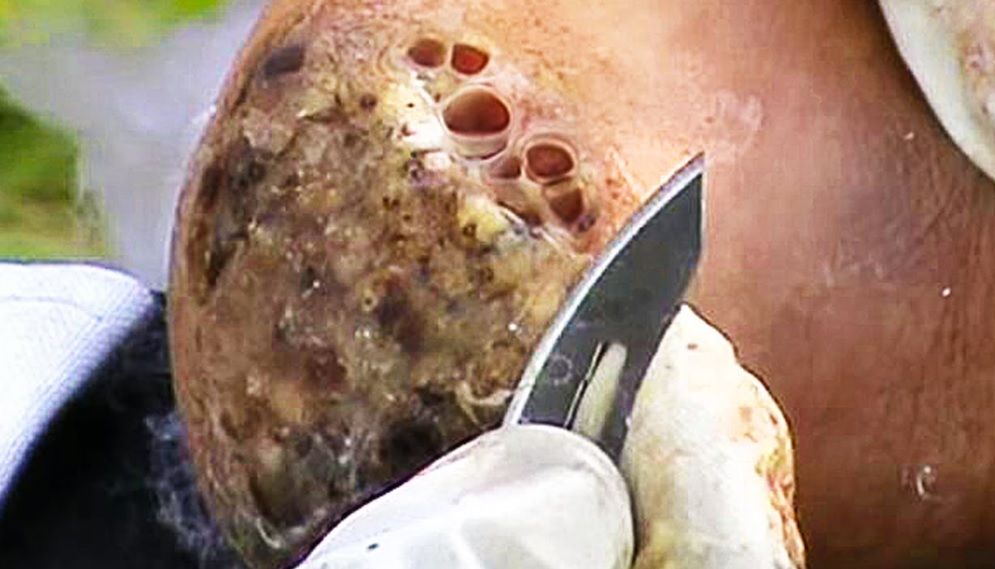
Watch that video of The Worst skin Jiggers Removals
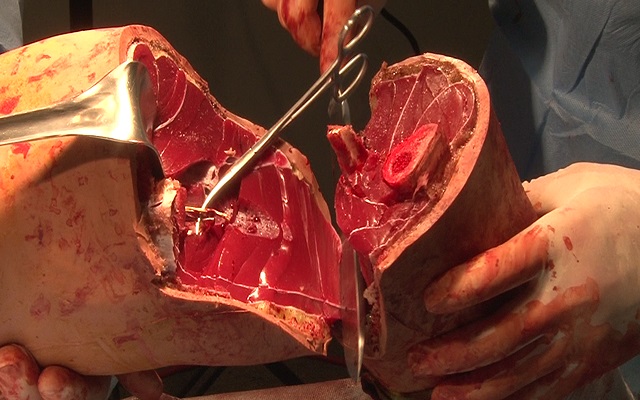
Watch that Above Knee Leg Amputation Surgery
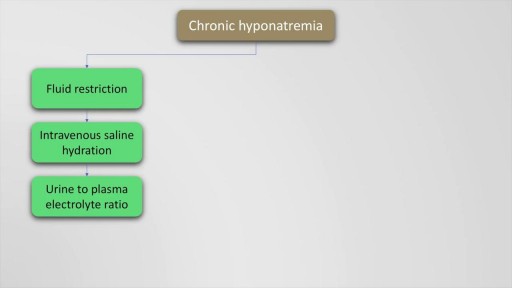
Hyponatremia is defined as a serum sodium of less than 135 Meq per litre and occurs in upto 22 % of hospitalised patients. The causes of hyponatremia may be understood based on the pre-existing volume status of the patient which may either be hypovolemic, euvolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia. This presentation discusses in detail, the causes of these underlying conditions. Also mentioned are the clinical features and management options and therapeutic sodium targets in patients with hyponatremia. Drugs such as demeclocycline and vaptans (Tolvaptan, Conivaptan) are also mentioned as management options which may be used on a case to case basis. Finally, the all important targets of sodium correction over 24 hours are also mentioned, along with a practical formula for calculation of sodium deficit which is explained with an example.
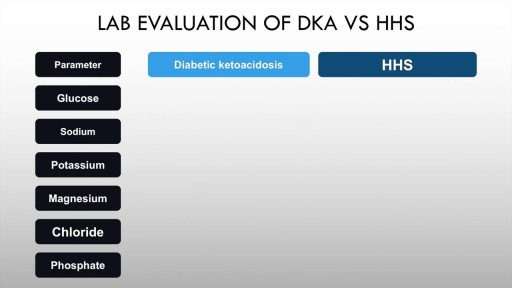
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute complication of uncontrolled hyperglycaemia characterised by high anion gap metabolic acidosis, dehydration and other metabolic abnormalities. Upto half of patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus may have DKA. The incidence in T2DM is also rising. Precipitants include acute illness such as myocardial infarction, trauma and infection. Paitents of diabetic ketoacidosis may present with vomiting, pain abdomen and lethargy. Mental obtundation may also be present. Management of diabetic ketoacidosis revolves around administration of IV normal saline, insulin, replacement of potassium with frequent monitoring of sugars and electrolytes.
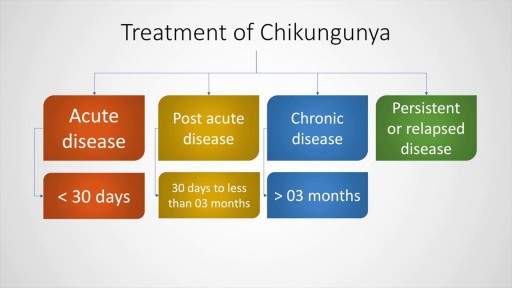
A decade ago we thought that Chikungunya was a tropical disease restricted to the rain forests. However, after the 2007 epidemic in Italy and later in the Reunion islands, this dreaded condition has now spread to the Carribean and the Americas. Its an arthropod borne alpha virus which causes fever, polyarthralgia and arthritis. There could be serious complications in the adult such as meningoencephalitis or GBS as well as in neonates. This presentation discusses in detail the clinical features, diagnosis and management of Chikungunya fever. A detailed discussion of its complications is also included. Check out our other videos
A brief description of the pathophysiology, clinical features, warning signs, diagnosis and management of Dengue fever. This description is based on the World Health Organisation guidelines of the management of Dengue fever.
A detailed description of Adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease) including basic physiology of the HPA axis, causes of primary and secondary insufficiency, clinical features of acute and chronic adrenal insufficiency. Lab testing for Addison's disease is also dealt with in detail. The management, both short term and long term are discussed in detail.
A detailed description of the Hepato-pulmonary syndrome including its definition, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. The pathophysiology includes nitric oxide in the pulmonary vasculature which results in intrapulmonary vasodilatation. This causes the classical and unique symptom of platypnea and orthodeoxia.
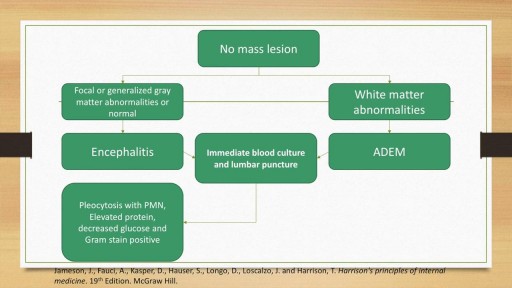
A detailed discussion of the causes, diagnosis and management of the causes of Meningitis and Encephalitis. Includes bacterial, viral, fungal and autoimmune conditions as well as treatment of these conditions. Includes antivirals such as Aciclovir and Ganciclovir as well as IVIG and plasma exchange for autoimmune encephalitis.
With keratoconus, the clear, dome-shaped tissue that covers the eye (cornea) thins and bulges outward into a cone shape. Its cause is unknown. Symptoms first appear during puberty or the late teens and include blurred vision and sensitivity to light and glare. Vision can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses early on. Advanced cases may require a cornea transplant.
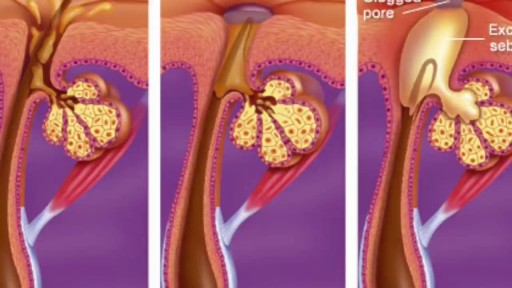
Acne can form several types of skin blemish, each with a distinct appearance and symptoms. Most minor acne blemishes respond to at-home care and over-the-counter medications. However, people with severe or long-term acne should speak with a doctor or dermatologist. Acne affects around 80 percent of adolescents and young adults. About 40–50 million Americans have acne at any given time. The following are common types of blemish associated with acne: whiteheads blackheads pustules, which are commonly called pimples papules cysts nodules Each type of acne lesion requires a different treatment. Receiving prompt, correct treatment can reduce the risk of long-term skin complications, such as dark spots and scarring. Acne blemishes fall into two categories, depending on whether or not they cause inflammation of the surrounding skin. Whiteheads Whiteheads Blackheads blackheads are pockets of oxidized melanin on the surface of the skin Papules Papules Pustules (pimples) Pustules (pimples) Nodules Nodules Cysts pus in a cyst 1of6 Noninflammatory acne types Whiteheads and blackheads are types of noninflammatory acne lesion. They are the least severe forms of acne. Noninflammatory blemishes usually do not cause swelling and are not very painful. Whiteheads The medical term for whiteheads is closed comedones. These are small, whitish or flesh-colored spots or bumps. They usually have a white, circular center surrounded by a red halo. A hair will sometimes emerge from the center of a whitehead, or it may appear to be trapped within the blemish. The skin around a whitehead may appear to be tight or wrinkled, especially when the whitehead is large or especially raised. ADVERTISEMENT Approved NSCLC Treatment - HCP Info & Resources Request A Rep & Discover A Therapy For Stage III NSCLC. www.stage-iii-nsclc-therapy.com Whiteheads typically do not cause scarring. Blackheads Blackheads are also called open comedones. They are small, black or dark-colored spots that may appear as slightly raised bumps. The skin around a blackhead usually appears normal, while the center of the blackhead is darker than the surrounding area. The coloration is not a result of trapped dirt. Blackheads are simply whiteheads that have opened and widened. When the contents of a whitehead are exposed to air, they darken. Treatment options Many over-the-counter rinses, moisturizers, gels, toners, and creams can treat noninflammatory acne blemishes. They often contain a mix of active ingredients. The following ingredients in over-the-counter treatments can help to break down whiteheads and blackheads: benzoyl peroxide salicylic acid sulfur resorcinol Also, several home remedies and lifestyle changes can help to reduce most minor-to-mild forms of noninflammatory acne. It may help to try: washing the face with lukewarm water and soap twice daily washing the whole body every 2 days reducing stress eating a healthful, balanced diet staying hydrated avoiding over-washing or irritating the skin limiting exposure to the sun always wearing sunscreen when outdoors People should never pop acne blemishes. Doing so can lead to complications, such as: nodules cysts scarring dark spots pitting Inflammatory acne types Inflammatory acne blemishes include: papules pustules nodules cysts Inflammatory acne is more severe than noninflammatory acne, and this type is more likely to cause complications, such as scarring or pitting. Blemishes or lesions that are inflamed, or red, swollen, and warm to the touch can result from inflammatory acne. Minor-to-mild forms Papules Papules are bumps under the skin's surface. They are solid, tender, pink, and raised, and the skin around a papule is usually slightly swollen and red. Unlike whiteheads, papules have no visible center. Unlike blackheads, the pores of a papule do not appear to be widened. Papules develop when whiteheads or blackheads cause so much irritation that they damage some of the surrounding skin. The damage leads to inflammation. Pustules (pimples) Pustules are larger, tender bumps with a defined circular center. The center is filled with whitish or yellowish pus, and the bump has a pink or red base. Immune cells and bacterial cells collect to form this pus. Pustules typically look like much larger and more inflamed whiteheads. Treatment options Several home remedies and over-the-counter medications can treat minor-to-mild papules and pustules. The following tips can help: washing the affected area with cool water and soap using clean hands or a clean, gentle facecloth twice a day applying a warm compress or cloth to the affected area for 10–15 minutes to encourage trapped debris to rise to the surface using products with benzoyl peroxide to combat bacteria using products with salicylic acid to remove dead skin cells and other debris How do you prevent pimples? How do you prevent pimples? How can you prevent pimples from forming? Learn 15 methods of prevention here, including home remedies, lifestyle changes, and diet tips. READ NOW Moderate-to-severe forms Nodules Nodules are hard, painful, inflamed lumps located deep within the skin. They look like larger, deeper papules and have no visible center or head. This type of acne lesion develops when clogged pores damage tissues and cells deep beneath the skin's surface. Nodules are a severe form of acne blemish, and they can cause skin complications such as dark spots or scarring. Cysts Cysts are very large, soft, painful, red or white lumps situated deep in the skin. They are filled with pus. Cysts form deeper within the skin than nodules, and they are the most severe type of acne blemish. Cysts can also cause skin complications, such as scarring. Treatment options People cannot treat moderate-to-severe inflammatory blemishes at home. These lesions require care from a doctor or dermatologist. The doctor can use many products and procedures to treat nodules and cysts. These include: antibiotics, such as tetracycline, doxycycline, and amoxicillin topical corticosteroids oral contraceptives for hormonal-related acne systematic retinoids, such as isotretinoin steroid injections chemical peels photodynamic therapy to combat bacteria drainage and extraction to remove large cysts What causes acne? young woman with forehead acne When a pore becomes clogged, acne can develop. Normally, dead cells collect in the skin's pores, then slowly rise to the surface of the openings and eventually fall away from the skin. A natural body oil called sebum helps to prevent skin cells from drying out. The glands that produce this oil are attached to the pores. When excess sebum builds up, it can cause dead cells to stick together, forming a mixture that becomes trapped in the pores. Acne occurs when a pore becomes clogged with dead skin cells, natural body oils, and a type of bacteria. These bacteria live on the skin and are called Propionibacterium acnes. If they enter and infect clogged pores, this causes acne blemishes to form. When to see a doctor In cases of minor-to-moderate acne, a person will generally have to use home and over-the-counter remedies consistently for 4–8 weeks before they see results. More severe inflammatory types of acne tend to take much longer to clear up. Speak to a doctor or dermatologist if whiteheads, blackheads, papules, or pustules: are severe do not respond to over-the-counter medications are very painful are very large bleed a lot release a lot of pus cover a significant portion of the face or body cause emotional distress develop very close to sensitive areas, such as the eyes or lips Most active ingredients in over-the-counter products are available in prescription-strength treatments. Dermatologists can also remove lesions that are very large or persistent. They can also remove those that do not respond to other forms of treatment. Always see a doctor or dermatologist about nodules and cysts, because these require medical care. Untreated nodules and cysts and those that have been picked or popped can cause scarring.
Benefits of Breast Feeding