Top videos
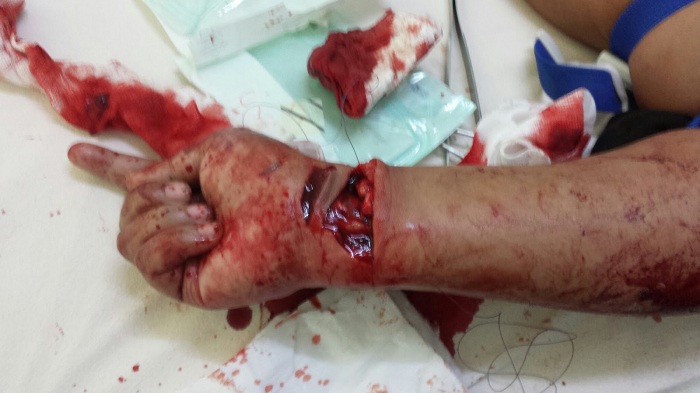
External jugular vein cannulation is an integral part of modern medicine and is practiced in virtually every health care setting. Venous access allows sampling of blood, as well as administration of fluids, medications, parenteral nutrition, chemotherapy, and blood products. [1] This topic describes placement of an intravenous (IV) catheter into the external jugular vein. A similar technique can be used for placement of IV catheters at different anatomic sites.
This video is available for instant download licensing here: https://www.alilamedicalmedia.....com/-/galleries/all-
©Alila Medical Media. All rights reserved.
Support us on Patreon and get FREE downloads and other great rewards: patreon.com/AlilaMedicalMedia
All images/videos by Alila Medical Media are for information purposes ONLY and are NOT intended to replace professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
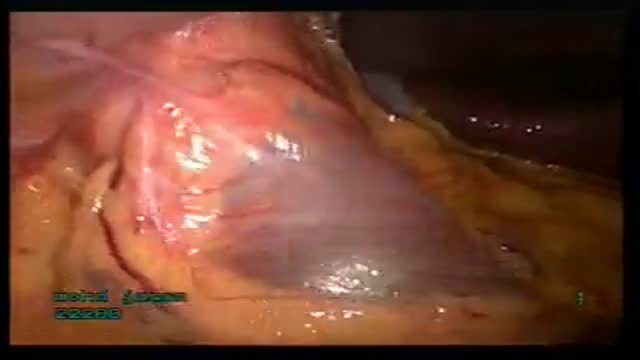
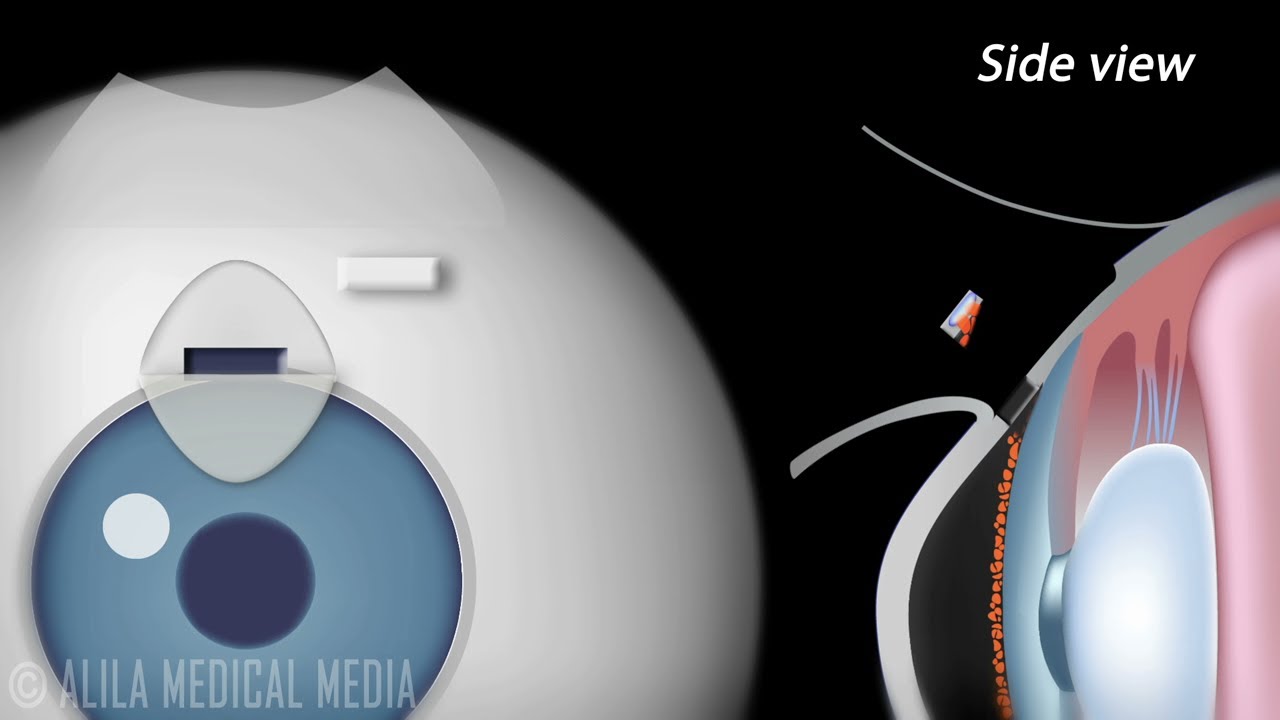
Trabeculectomy, also called Filtration Surgery, is a surgical procedure performed for treatment of glaucoma. The treatment involves removing part of the trabecular meshwork and creating a new escape route for the aqueous humor. When successful, it allows the aqueous fluid to drain from the eye into an area underneath the conjunctiva where it is subsequently absorbed by the body's circulatory system or filtered into tears.
In this procedure:
- A conjunctival pocket is created and maybe treated with Mitomycin or other antimetabolites for a few minutes. These drugs are used to prevent scarring of the operation site. Scarring, if occurs, may clog the new drainage canal, and is therefore the major reason the procedure may fail.
- A half thickness flap is then made in the sclera and is dissected all the way to the clear cornea.
- A block of scleral tissue including part of the trabecular meshwork and Schlemm's canal is then removed to make a hole into the anterior chamber of the eye.
- As the iris may plug up this hole from the inside, a piece of the iris maybe removed at this time. This is called iridectomy.
- The scleral flap is then sutured loosely back in place. These sutures can be released gradually during a couple of weeks after surgery. This allows adjustment of the aqueous flow in order to achieve target pressure and to avoid the complication of having a too low intraocular pressure.
- The conjunctiva is sewn back in place to cover the area.
After surgery, aqueous humor drains into a filtering area called a "bleb" under the conjunctiva. Since the surgery is usually performed near the top of the eye, the bleb can easily be concealed behind the upper eyelid.

What is systemic lupus erythematosus? The immune system normally fights off dangerous infections and bacteria to keep the body healthy. An autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system attacks the body because it confuses it for something foreign. There are many autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The term lupus has been used to identify a number of immune diseases that have similar clinical presentations and laboratory features, but SLE is the most common type of lupus. People are often referring to SLE when they say lupus.
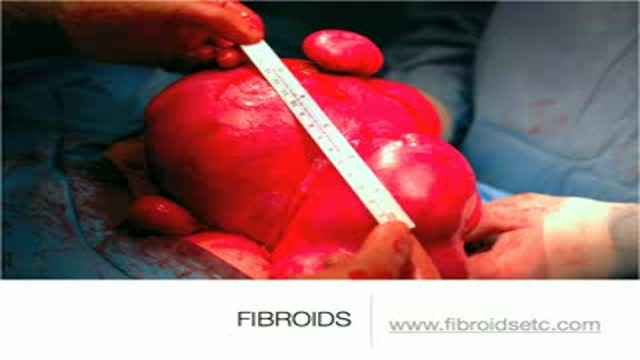
A uterine fibroid (also uterine leiomyoma, myoma, fibromyoma, leiofibromyoma, fibroleiomyoma, and fibroma) (plural of ... myoma is ...myomas or ...myomata) is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that originates from the smooth muscle layer (myometrium) and the accompanying connective tissue of the uterus. Fibroids are the most common benign tumors in females and typically found during the middle and later reproductive years. While most fibroids are asymptomatic, they can grow and cause heavy and painful menstruation, painful sexual intercourse, and urinary frequency and urgency. Uterine fibroids is the major indication for hysterectomy in the US.[2] Fibroids are often multiple and if the uterus contains too many leiomyomatas to count, it is referred to as uterine leiomyomatosis. The malignant version of a fibroid is uncommon and termed a leiomyosarcoma.
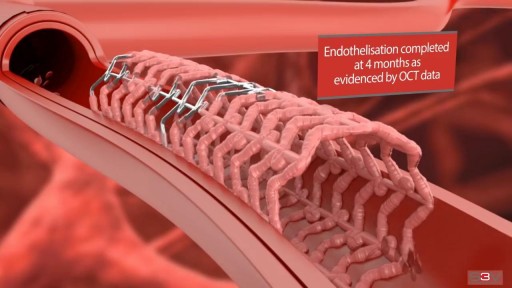
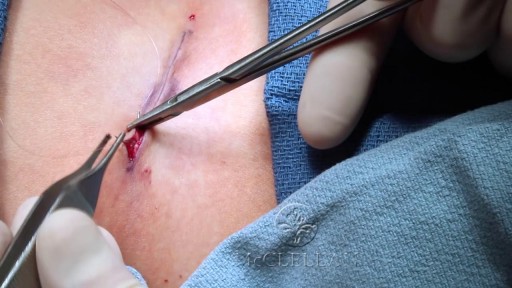
Angioplasty is a procedure to restore blood flow through the artery. You have angioplasty in a hospital. The doctor threads a thin tube through a blood vessel in the arm or groin up to the involved site in the artery. The tube has a tiny balloon on the end.

Macrobiopsy of breast lesions is a complicated procedure when performed with vacuum assisted biopsy tools. The Spirotome is a hand-held needle set that doesn’t need capital investment, is ready to use and provides tissue samples of high quality in substantial amounts. In this way quantitative molecular biology is possible with one tissue sample. The Coramate is an automated version of this direct and frontal technology

Watch this video to learn how and when to change a dressing for a child with a hemodialysis catheter. You should change your child's dressing if it becomes soiled with water or blood or if it comes off at home. Keeping a clean dressing on your child will limit risk of infection.

An excellent video demonstrating how a laparoscopy is performed to evaluate the uterus (note a small fibroid appearing as a bulge in the uterus), fallopian tubes and ovaries. Blue dye is injected into the uterus, entering the fallopian tubes and spilling from the end of the tubes into the abdominal cavity, confirming that both tubes are open