Top videos

The MINI tummy-tuck is a lesser variant of the classic tummy tuck. The MINI tummy-tuck always involved skin excision (often a scar revision and skin excision of the flabby skin over a C-section scar or hysterectomy or laparotomy scar) but may also involve liposuction, umbilical floating, etc. Commonly it will not include any muscle repair otherwise it it now a classic tummy tuck (aka abdominoplasty). Cost varies depending on the components involved. Here, Toronto Aesthetic Plastic Surgeon Dr Marc DuPéré describes a MINI tummy-tuck done on a patient who had a Brazilian Butt Lift before (and skin harvesting from abdomen) and a recent 20 lbs weight loss, a patient who wants more liposuction to abdomen and flanks and whose skin has now lost elasticity, hence the requirement for this small skin excision. Dr DuPéré also explains what UMBILICAL floating means. Dr DuPéré performs more than 5 different techniques of tummy-tucks in Toronto and the technique chosen reflects the patient’s expectations and anatomy. Call us if interested in learning about YOUR options for a flatter tummy! 📱 416-929-9800
Patient consent obtained. Thank you to my patient.
Visage Clinic Toronto
https://www.visageclinic.com/
(416) 929-9800
101-133 Hazelton Avenue, Toronto, ON M5R 0A6
https://www.facebook.com/VisageClinic/
https://www.instagram.com/VisageClinicDrDuPere/

Business Insider's Michelle Yan has been nearsighted since she was 9 years old. After laser eye surgery, she has 20/20. She walks us through the pre-surgery steps, the actual surgery, as well as the recovery process.
MORE MEDICAL TECH:
8 Medical Procedures That Are Improving Lives
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kTMMrAP6DNI
13 Medical Procedures Changing The Health World
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VAR44vnxWis
Lifelike Medical Robot Actually Bleeds
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IjnhmcCQLsc
------------------------------------------------------
#Lasik #Surgery #TechInsider
Tech Insider tells you all you need to know about tech: gadgets, how-to's, gaming, science, digital culture, and more.
Visit us at: https://www.businessinsider.com
TI on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/techinsider
TI on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/tech_insider/
TI on Twitter: https://twitter.com/techinsider
TI on Amazon Prime: http://read.bi/PrimeVideo
INSIDER on Snapchat: https://insder.co/2KJLtVo
------------------------------------------------------
What It's Like To Get Laser Eye Surgery

When diving into a Breast Reduction procedure, there are many things to consider. Even as a patient, being aware of any concerns and how the procedure works is important. Therefore, when a plastic surgeon operates on a patient, the results are clear. Dr. Linder, a Breast surgeon specialist in Beverly Hills, helps explain what goes into a Breast Reduction Procedure.
Before Dr. Benjamin Carson became the first person to successfully separate twins conjoined at the head, before he had a TV movie made about his life, before he became known for his "gifted hands" and before he became head of pediatric neurosurgery at Johns Hopkins, Ben Carson was headed down the wrong path in life.

As you consider Fort HealthCare and our Pediatric Surgical Services, here is a quick tour to give you and your child an idea of what to expect.
We look forward to helping you.
To find out more information, please visit forthealthcare.com/PediatricSurgery
Video production by Highlights Media, LLC

Surgeons at St Mary's Hospital, part of Imperial College Healthcare have come up with a new surgical procedure that cures heartburn with a device called RefluxStop.
Mr Ahmed Ahmed, a consultant surgeon, says surgery should now be seen as an alternative to life-long drug treatment - as Sky's Thomas Moore reports.
Read more: https://news.sky.com/story/new....-nhs-heartburn-surge
#heartburncure #surgery #skynews
SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube channel for more videos: http://www.youtube.com/skynews
Follow us on Twitter: https://twitter.com/skynews
Like us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/skynews
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/skynews
Follow us on TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@skynews
For more content go to http://news.sky.com and download our apps: Apple https://itunes.apple.com/gb/ap....p/sky-news/id3163919 Android https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.bskyb.skynews.android&hl=en_GB
Sky News Daily podcast is available for free here: https://podfollow.com/skynewsdaily/
Sky News videos are now available in Spanish here/Los video de Sky News están disponibles en español aquí: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCzG5BnqHO8oNlrPDW
To enquire about licensing Sky News content, you can find more information here: https://news.sky.com/info/library-sales
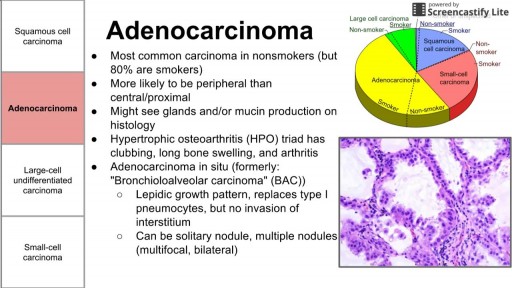
There are three main types of lung cancer. Knowing which type you have is important because it affects your treatment options and your outlook (prognosis). If you aren’t sure which type of lung cancer you have, ask your doctor so you can get the right information.