Top videos

As you consider Fort HealthCare and our Pediatric Surgical Services, here is a quick tour to give you and your child an idea of what to expect.
We look forward to helping you.
To find out more information, please visit forthealthcare.com/PediatricSurgery
Video production by Highlights Media, LLC

World-renowned surgeons at Shriners Hospitals for Children – Northern California provide complex pediatric surgery for children one-year and older with congenital and acquired conditions. Children from throughout the Western United States with chest wall malformations, gastro-intestinal disease, ano-rectal disorders, urologic conditions and other complex surgical needs benefit from the expert care. The pediatric surgery team is devoted to the development of innovative and minimally invasive surgical techniques.
There are three main types of lung cancer. Knowing which type you have is important because it affects your treatment options and your outlook (prognosis). If you aren’t sure which type of lung cancer you have, ask your doctor so you can get the right information.

Watch this video to learn how and when to change a dressing for a child with a hemodialysis catheter. You should change your child's dressing if it becomes soiled with water or blood or if it comes off at home. Keeping a clean dressing on your child will limit risk of infection.
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In humans, this event occurs when the follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm

Multiple sclerosis causes many different symptoms, including vision loss, pain, fatigue, and impaired coordination. The symptoms, severity, and duration can vary from person to person. Some people may be symptom free most of their lives, while others can have severe chronic symptoms that never go away.
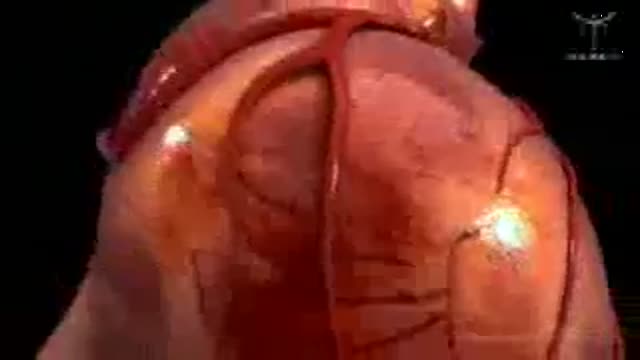
This video is really sad. You can literally watch this man dying. He was shot in the chest and rushed to the emergency room. His heart has stopped beating or has arrested. As a last resort, surgeons did an extreme procedure called an open thoracotomy which is that crazy tool you see there that basically splits the ribs open and allows easy open access to the heart. They did this so they could give him a cardiac massage. A cardiac massage is when surgeons are manually trying to pump the heart after it has stopped working on its own (cardiac arrest). Unfortunately he lost so much blood from his gun shot wound and he was pronounced dead. There are cases of patients surviving after having this kind of invasive resuscitation but it is rare.

Learn with Dr. Wahdan 2
You can download the lecture from this link
https://docdro.id/5ni1FFZ

Scientists have found that every baby has genius potential, a child's education must begin early in order to develop the potential it has. Pregnancy is not too early to start, as evidence indicating that the developing fetus can learn is ever mounting.
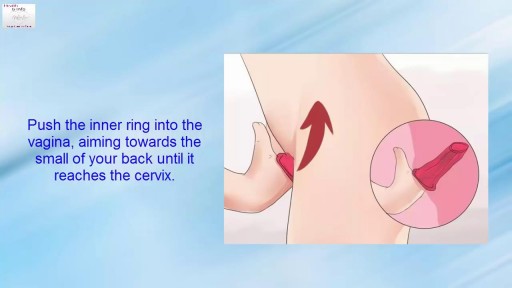
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into a woman's uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversible birth control (LARC).

It may be reassuring to know spotting or bleeding after sex is common and can come from the vagina, cervix, or urinary tract. It occurs most commonly in women 20 to 40 years old. Cervical Cancer: A very rare cause of spotting. ... Vaginal Dryness: Often caused by inadequate foreplay or vaginal lubrication.