Top videos

Eric knew he needed help when an old knee injury began worsening over the course of time and was significantly affecting his quality of life. That’s when he turned to his hometown orthopedic experts at Mayo Clinic Health System in Mankato, who recommended a total knee replacement. After overcoming some initial fears, Eric decided it was time to have the operation — a fuller and more active life with his family depended on it.
This video: Blisters caused by friction or minor burns do not require a doctor's care. New skin will form underneath the affected area and the fluid is simply absorbed. Do not puncture a blister unless it is large, painful, or likely to be further irritated. The fluid-filled blister keeps the underlying skin clean, which prevents infection and promotes healing.

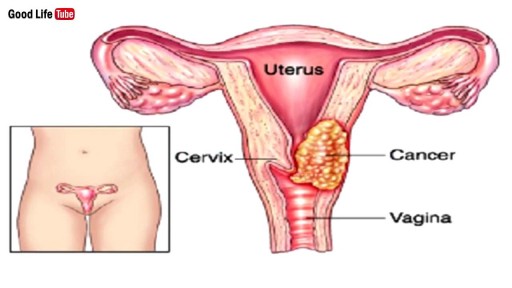
TV interview with Adina Nack, Ph.D. about her own cervical HPV experiences, STD research, her new book (Damaged Goods? Women Living with Incurable Sexually Transmitted Diseases), and women's lives after genital warts, HPV and herpes infections. More info is available on STDdatings.com, which is the official STD dating & support site.

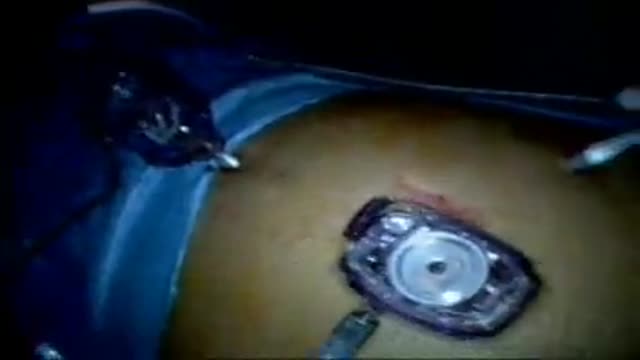
New York Plastic Surgeon, Carlin Vickery, MD (http://www.5thavesurgery.com) performs a CoolSculpting by Zeltiq procedure.
A NYC patient in this video explains her interest in the CoolSculpting procedure and discusses her experience on camera while receiving this Zeltiq treatment.

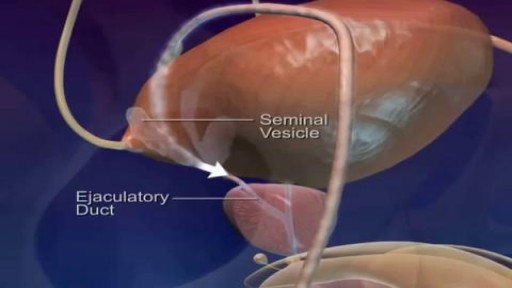
Most times, a pulmonary embolism is caused by blood clots that travel from the legs or, rarely, other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis, or DVT). Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, and cough. Prompt treatment to break up the clot greatly reduces the risk of death. This can be done with blood thinners and drugs or procedures. Compression stockings and physical activity can help prevent clots from forming in the first place.

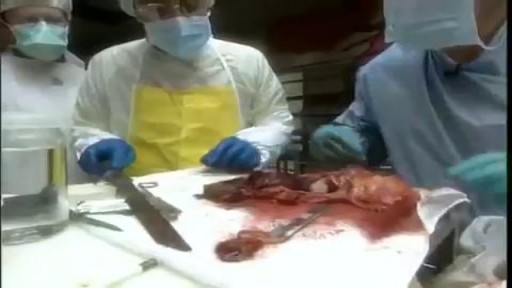
The type of operation performed for removal of pancreatic cancer is based on the location of the tumor. For tumors of the head and neck of the pancreas a Whipple procedure, (also called a pancreaticoduodenectomy) is performed. This is a complex operation perfected at Johns Hopkins. This video will explain the surgery and what patients can expect.
Learn more about the Whipple procedure at Johns Hopkins:
http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org..../pancreatic_cancer_c

http://angularcheilitis-end.cbwin1.com Corner Of Mouth Cracked, Angular Cheilitis, Home Remedies For Angular Cheilitis, Angular Cheilitis How to Treat Angular Cheilitis Effectively Thousands or even millions of people are searching every year for an effective treatment that will get them rid for good of Angular Cheilitis. Some manage to relieve themselves from the pains this skin conditions causes, while others continue to struggle for months with this terrible skin condition. For those who are still trying to get rid of Angular Cheilitis but still have not yet found a good result, here are some tips which may make your fight easier. As you probably know, the first thing you have to do when the first signs of Angular Cheilitis appear is to discover the cause which determined the apparition of this skin condition. You can make an examination of the area and see if there have been folds where moisture could be retained. If you have had some teeth pulled out or if you are wearing dentures, such folds may appear in time. If this is the issue, you should fix that by making an appointment to your dentist. Also, some blood tests will show you if your body has all the nutrients and vitamins it needs to function properly. In most of the cases, the Angular Cheilitis is triggered by malnutrition and anemia, thus making these tests will help you see whether this is your case, too. Once you know the results of the blood tests you should know if you should take vitamin supplements or your Angular Cheilitis was only a surface problem, caused by excessive moisture in the corners of your mouth. Apart from addressing the problem from the interior to the exterior, you will also have to apply some creams or ointments which will alleviate your suffering and at the same time will actively work on the sores. What most Angular Cheilitis treatments do is create a dry environment in which the bacteria cannot develop and trap them between the layer of cream and the layer of skin, thus killing them. Hydrocortisone, Mycolog II cream (which contains triamcinolone acetonide and nystatin) and Miconazole are the most popular medications prescribed by dermatologists in such conditions.

Ettore Vulcano, MD, Foot and Ankle Orthopedic Surgeon at Mount Sinai West, discusses a new minimally invasive bunion surgery that has patients walking immediately after surgery, and getting back to an active lifestyle much quicker than with the traditional surgery.

Strep throat is a bacterial infection that can make your throat feel sore and scratchy. Strep throat accounts for only a small portion of sore throats. If untreated, strep throat can cause complications, such as kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever can lead to painful and inflamed joints, a specific type of rash or heart valve damage. Strep throat is most common in children, but it affects people of all ages. If you or your child has signs or symptoms of strep throat, see your doctor for prompt testing and treatment.

Colorectal surgeon Conor Delaney, MD, explains laparoscopic surgery for colon cancer, including how it works and what patients can typically expect before, during, and after the procedure.
Learn more about colon cancer at http://cancer.org/coloncancer
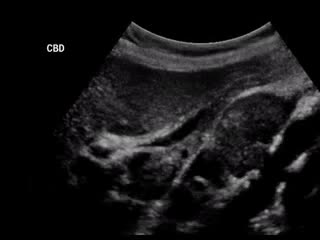
Gallbladder cancer is cancer that begins in the gallbladder. Your gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just beneath your liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a digestive fluid produced by your liver. Gallbladder cancer is uncommon. When gallbladder cancer is discovered at its earliest stages, the chance for a cure is very good. But most gallbladder cancers are discovered at a late stage, when the prognosis is often very poor. Gallbladder cancer is difficult to diagnose because it often causes no specific signs or symptoms. Also, the relatively hidden nature of the gallbladder makes it easier for gallbladder cancer to grow without being detected. Symptoms ShareTweet Aug. 07, 2014 References Products and Services Book: Mayo Clinic on Digestive Health Give today to find cancer cures for tomorrow See also Abdominal pain Can you recommend a diet after gallbladder removal? Chemo Targets Chemotherapy Chemotherapy and hair loss: What to expect during treatment Chemotherapy and sex: Is sexual activity OK during treatment? Chemotherapy nausea and vomiting: Prevention is best defense Show more Advertisement Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Advertising & Sponsorship PolicyOpportunitiesAd Choices Mayo Clinic Store Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic. NEW! – The Mayo Clinic Diet, Second Edition Relief for America's epidemic of indigestion Keeping your bones healthy and strong Manage blood pressure for better health The Mayo Clinic Diet Online