Top videos
Septic arthritis is also known as infectious arthritis, and is usually caused by bacteria, or fungus. The condition is an inflammation of a joint that's caused by infection. Typically, septic arthritis affects one large joint in the body, such as the knee or hip. Less frequently, septic arthritis can affect multiple joints

Traumatic penile injury can be due to multiple factors. Penile fracture, penile amputation, penetrating penile injuries, and penile soft tissue injuries are considered urologic emergencies and typically require surgical intervention. The goals of treatment for penile trauma are universal: preservation of penile length, erectile function, and maintenance of the ability to void while standing. Traumatic injury to the penis may concomitantly involve the urethra.[1, 2] Urethral injury and repair is beyond the scope of this article but details can be found in Urethral Trauma. Penile fracture Penile fracture is the traumatic rupture of the corpus cavernosum. Traumatic rupture of the penis is relatively uncommon and is considered a urologic emergency.[3] Sudden blunt trauma or abrupt lateral bending of the penis in an erect state can break the markedly thinned and stiff tunica albuginea, resulting in a fractured penis. One or both corpora may be involved, and concomitant injury to the penile urethra may occur. Urethral trauma is more common when both corpora cavernosa are injured.[4] Penile rupture can usually be diagnosed based solely on history and physical examination findings; however, in equivocal cases, diagnostic cavernosography or MRI should be performed. Concomitant urethral injury must be considered; therefore, preoperative retrograde urethrographic studies should generally be performed. See the images below.

Please remember that this video is to be used for educational purposes. You must follow your facility or colleges' policies and procedure checklists to ensure you are completing the skill satisfactorily. Thanks for watching!
Music from #Uppbeat (free for Creators!):
https://uppbeat.io/t/swoop/blue-sea
License code: W9DFUQ4II7YVHA59

Brachytherapy or localized radiation treatment can be used in certain patients with breast cancer. Depending on tumor size and other factor, physicians may use APBI or accelerated partial breast irradiation. Dr. Elizabeth Tapen, a radiation oncologist, reviews brachytherapy for breast cancer.

Ellis demonstrates how to insert and then remove an NG tube. This includes drawing gastric residual and checking the pH. After the demonstration, Ellis provides additional tips about clamping the NG tube and using the blue pigtail.
Our Critical Nursing Skills video tutorial series is taught by Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHS and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for your nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN #ClinicalSkills #NGTube #nurseeducator
00:00 What to expect
00:30 Preparing NG tube patient
00:56 Preparing NG tube equipment
1:29 Measuring the NG tube
2:02 Preparing for NG tube insertion
2:28 Inserting the NG tube
3:17 Checking placement with pH
4:23 Anchoring with split-tape
5:32 Connecting to suction
6:05 Disconnecting from suction
6:17 What to do before removal?
7:03 Removing NG tube
7:40 Additional tips on clamping
8:31 The blue pigtail
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Clinical Skills? Check out our flashcards & videos!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.

With ECT, electrodes are placed on the patient's scalp and a finely controlled electric current is applied while the patient is under general anesthesia. The current causes a brief seizure in the brain. ECT is one of the fastest ways to relieve symptoms in severely depressed or suicidal patients.
Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by a buildup of plaque. It’s also called arteriosclerosis or hardening of the arteries. Arteries are the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body. As you get older, fat and cholesterol can collect in your arteries and form plaque. The buildup of plaque makes it difficult for blood to flow through your arteries. This buildup may occur in any artery in your body and can result in a shortage of blood and oxygen in various tissues of your body. Pieces of plaque can also break off, causing a blood clot. Atherosclerosis can lead to heart attack, stroke, or heart failure if left untreated.
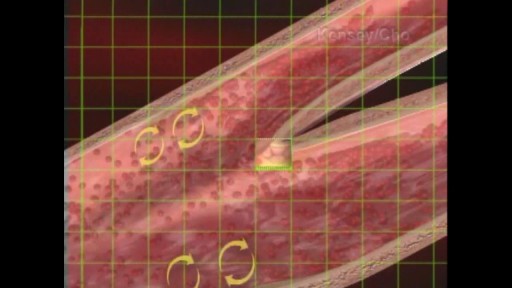
When the hematocrit rises to 60 or 70%, which it often does in polycythemia, the blood viscosity can become as great as 10 times that of water, and its flow through blood vessels is greatly retarded because of increased resistance to flow. This will lead to decreased oxygen delivery.
A tonsillolith lodged in the tonsillar crypt. Specialty. Otorhinolaryngology. Tonsilloliths, also known as tonsil stones, are clusters of calcified material that form in the tonsillar crypts, the crevices of the tonsils. While they occur most commonly in the palatine tonsils, they may also occur in the lingual tonsils.

Bone cancer symptoms. Possible symptoms of bone cancer include: Bone pain: Pain is the most common sign of bone cancer, and may become more noticeable as the tumor grows. Bone pain can cause a dull or deep ache in a bone or bone region (e.g., back, pelvis, legs, ribs, arms).