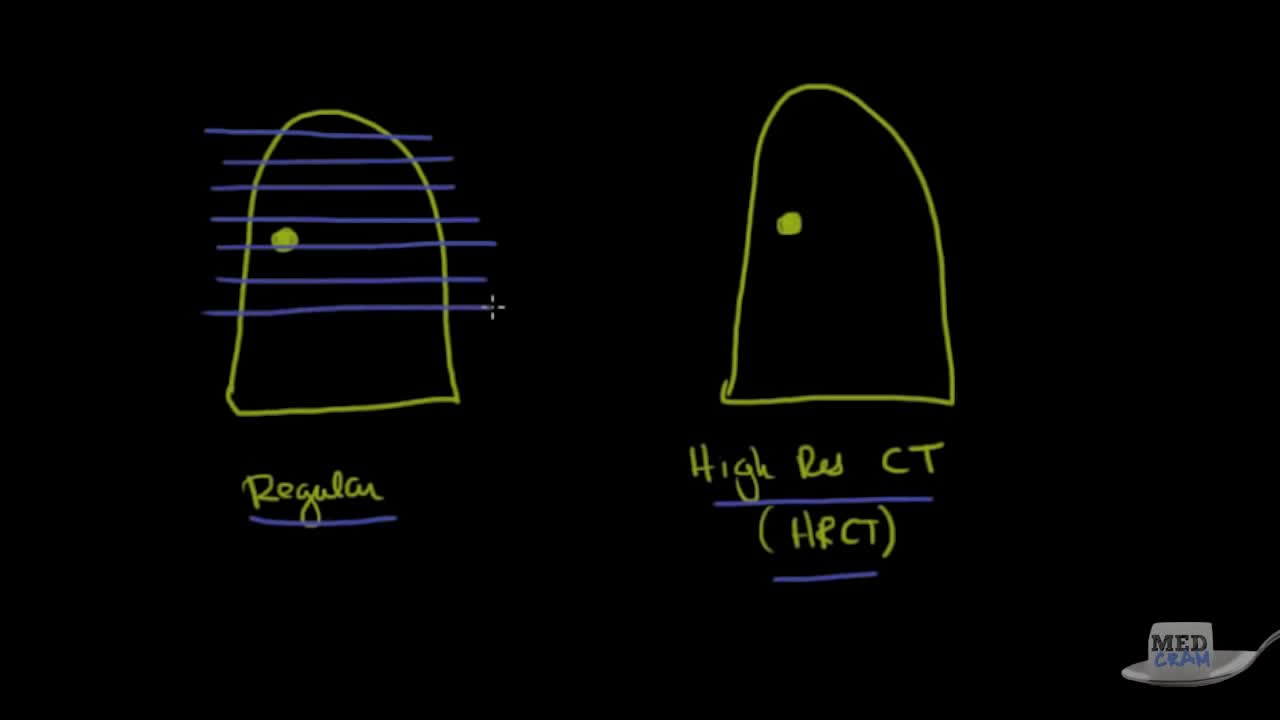
Los mejores videos

James Dunn, MD, PhD is a pediatric surgeon at Stanford Children's Health. He is board certified in General Surgery and Pediatric Surgery.
Learn more at https://www.stanfordchildrens.....org/en/service/gener
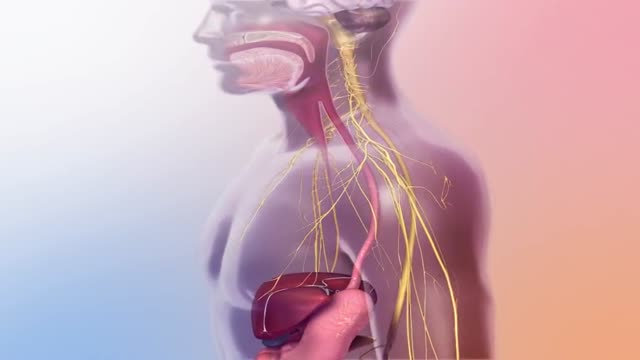
Peristalsis, involuntary movements of the longitudinal and circular muscles, primarily in the digestive tract but occasionally in other hollow tubes of the body, that occur in progressive wavelike contractions. Peristaltic waves occur in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines.

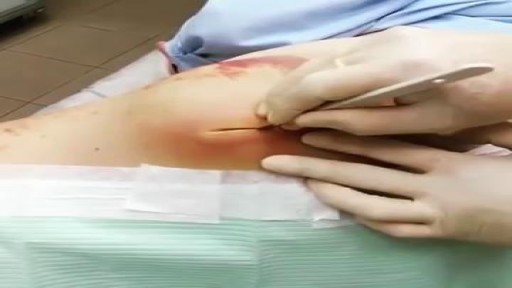
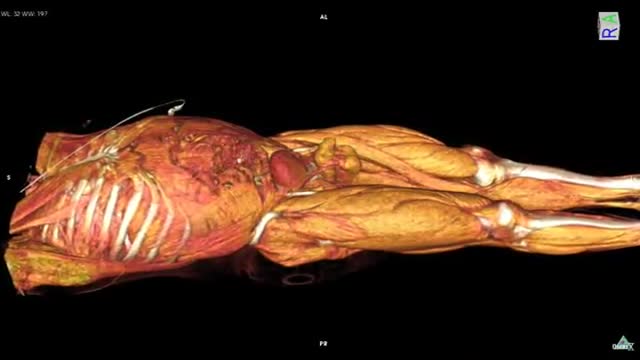
Ellis demonstrates how to clean a reusable inner cannula, care for a tracheostomy site, and suction a tracheostomy.
Our Critical Nursing Skills video tutorial series is taught by Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHS and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for your nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#ClinicalSkills #NCLEX #tracheostomy #patientcare #ATI #Kaplan #LVN #PN #RN #nurseeducator #nurse #nursingstudent #murse #clinicals #clinicalnursingskills
00:00 What to expect Tracheostomy Care and Suctioning
0:33 Explaining the process Tracheostomy Care and Suctioning
1:10 Positioning patient for a Tracheostomy Care and Suctioning
1:33 Opening tray
1:46 Pouring saline
1:58 Removing inner cannula
2:14 Removing clean gloves
2:25 Donning sterile gloves
3:16 Showing tray contents
3:53 Removing previous dressing
4:06 Pouring saline
4:27 Cleaning stoma
5:10 Cleaning faceplate
5:20 Drying site
5:30 Cleaning inner cannula
6:00 Drying inner cannula
6:20 Reinserting inner cannula
6:40 Placing new gauze
7:00 Replacing ties
8:00 Replacing oxygen
8:13 Preparing for suction
8:58 Checking suction
9:30 Opening saline
9:42 Opening kit
9:58 Donning sterile gloves
11:04 Setting up saline container
11:20 Pouring saline
11:52 Connecting catheter to suction
12:46 Inserting catheter
13:10 Removing catheter
13:24 Rinsing catheter
13:40 Reoxyginating
14:05 Reinserting catheter
14:17 Removing catheter
14:29 Rinsing catheter
14:44 Reoxyginating
14:55 Cleaning up
15:09 Chatting about sterility
17:00 Checking a tie
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Clinical Skills? Check out our flashcards & videos!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.

In this episode of Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology, Hank gives you a brief history of histology and introduces you to the different types and functions of your body's tissues.
Pssst... we made flashcards to help you review the content in this episode! Find them on the free Crash Course App!
Download it here for Apple Devices: https://apple.co/3d4eyZo
Download it here for Android Devices: https://bit.ly/2SrDulJ
Chapters:
Introduction 00:00
Nervous, Muscle, Epithelial & Connective Tissues 1:23
History of Histology 2:07
Nervous Tissue Forms the Nervous System 5:17
Muscle Tissue Facilitates All Your Movements 7:00
Identifying Samples 9:03
Review 9:48
Credits 10:22
Crash Course is on Patreon! You can support us directly by signing up at http://www.patreon.com/crashcourse
Want to find Crash Course elsewhere on the internet?
Facebook - http://www.facebook.com/YouTubeCrashCourse
Twitter - http://www.twitter.com/TheCrashCourse
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/thecrashcourse/
CC Kids: http://www.youtube.com/crashcoursekids

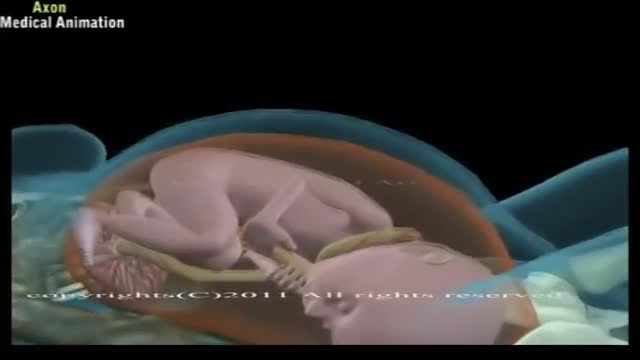
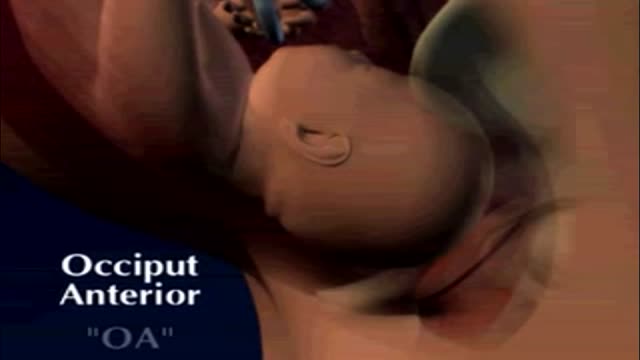
External cephalic version is a process by which a breech baby can sometimes be turned from buttocks or foot first to head first. External cephalic version (ECV) is a manual procedure that is advocated by national guidelines for breech presentation singleton pregnancy, in order to enable vaginal delivery.

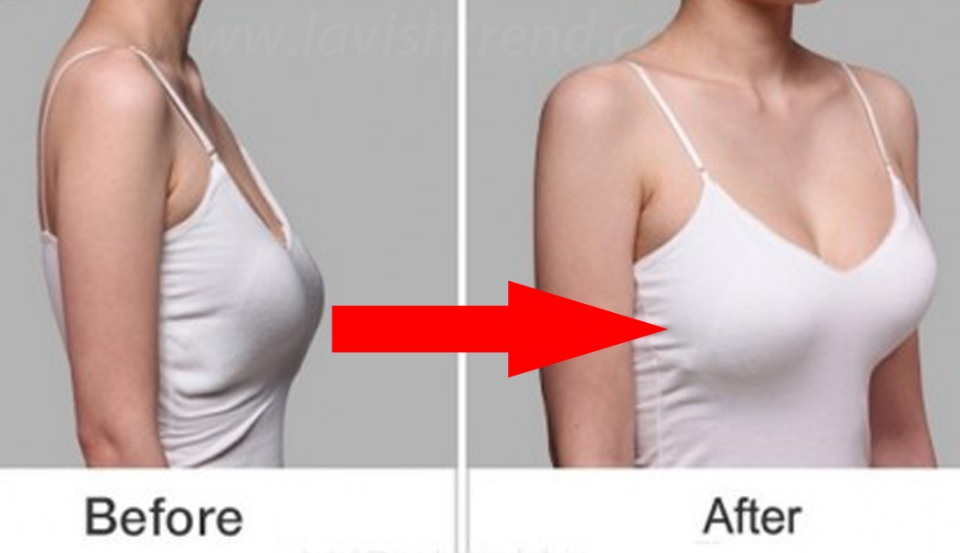
How to Improve Sexual Health or Stamina part 4 All Solution of Male Disorder Male Infertility Diagnostic and Treatment Re-Slim Care Latest Technology in Pakistan Dr. Aslam Naveed is a well known sexologist in Pakistan. He has treated more than 1 Lac patients since last 30 years of clinical Practice in sexology, he knows how to help the people facing sexual disorders. Contact: 02134965050, 03432821919 www.sexologistpakistan.com https://www.facebook.com/menssexcareclinic/ https://youtu.be/_fRbtwWtLoE Part 1 https://youtu.be/S17bCnwCLuI Part 2 https://youtu.be/CPAXxkdz7mM Part 3 https://youtu.be/YlsdBZJ4prg Part 4 https://youtu.be/fylxbK4azvs Part 5 https://youtu.be/Zb8TcdgJ7Io Part 6 https://youtu.be/0wbDDNAwsmo Part 7 https://youtu.be/gHDmwfsMgTw Part 8 https://youtu.be/IasXoRKUlV4 Part 9 ADDRESS: Men’s Care Modern Hospital, Opposite, Safari Park, University Road, Karachi, Pakistan.
fetal position in womb at 34 weeks fetal position in womb week by week fetal position in womb at 19 weeksUnborn babies toss and turn and hold many different positions within the womb during the gestation period; pregnant women everywhere will attest to the fact that their children always start up the gymnastics at bedtime.

UPDATE 1/30/15: Watch the updated version of this animation: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LVP6JngpgEE
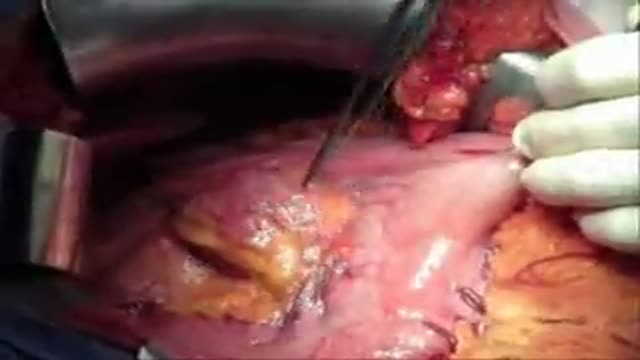
This 3D medical animation shows how adhesions in the abdomen may cause complications. These problems may include obstruction, twisting, and dislocating areas of the small intestine. Adhesions can be separated with laparoscopic instruments.
ANH00037