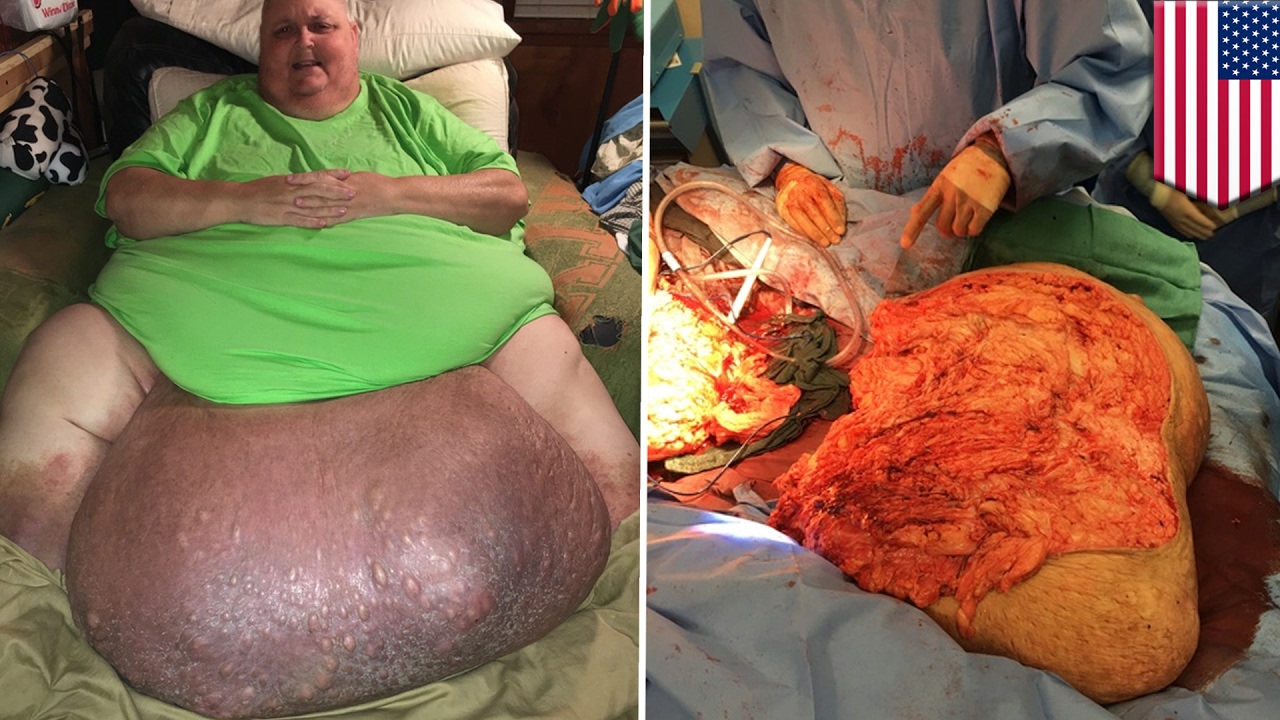
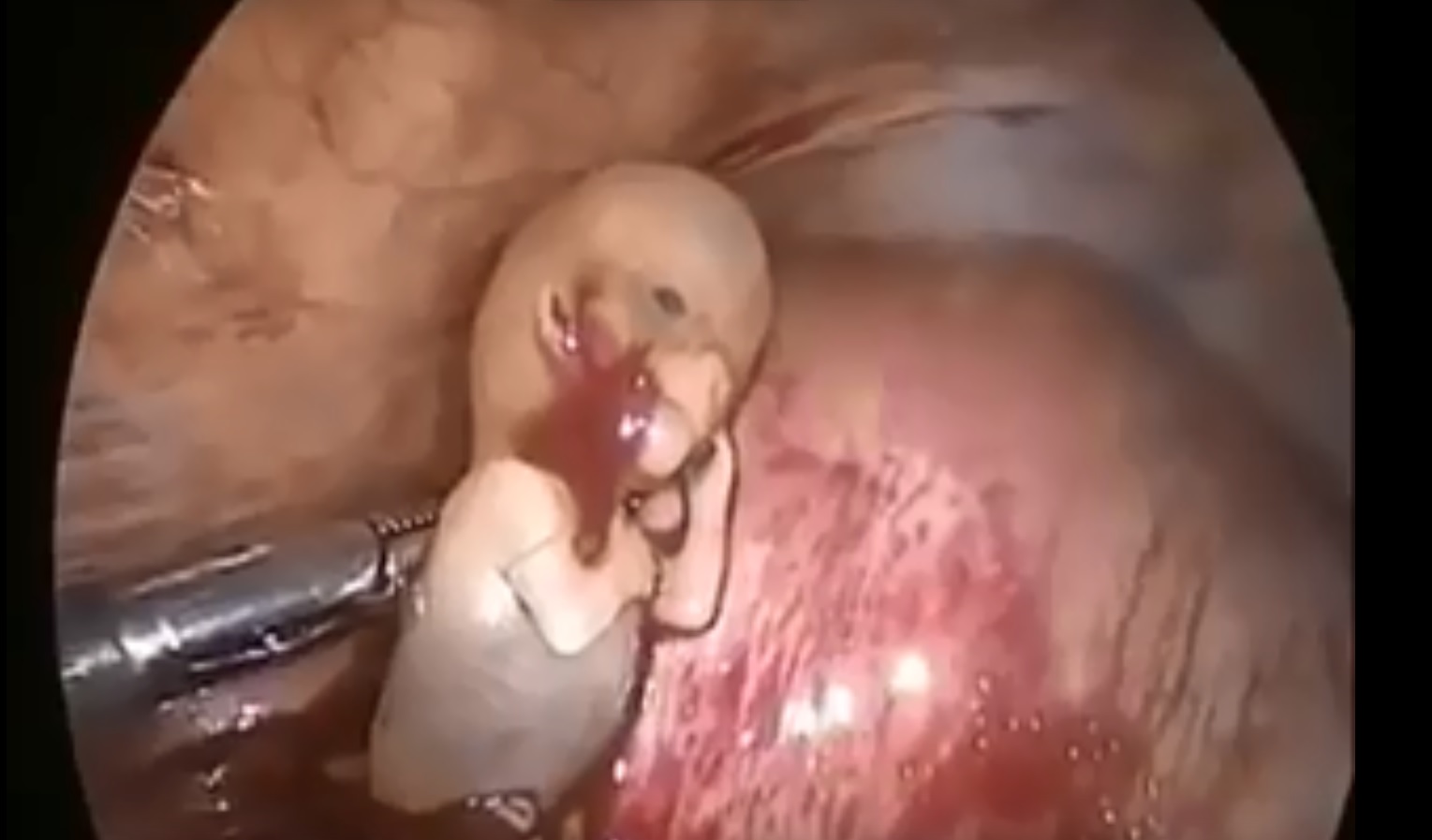
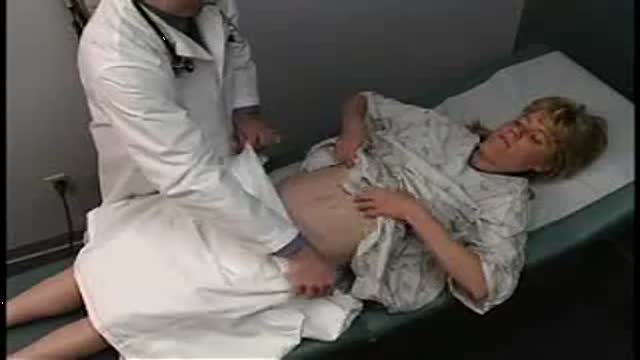
Top videos
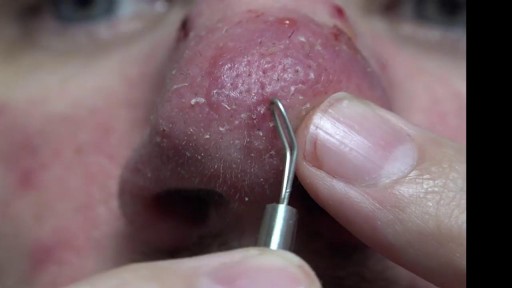
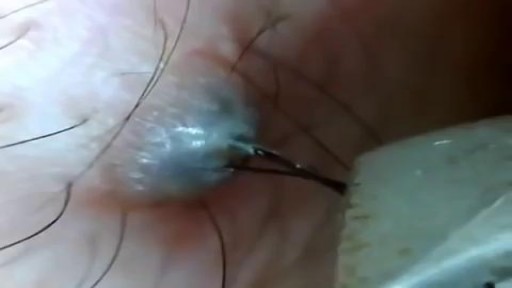
Cystic acne is a severe type of acne in which the pores in the skin become blocked, leading to infection and inflammation. The skin condition mainly affects the face, but also often affects the upper trunk and upper arms. Acne most often affects adolescents and young adults, with an estimated 80 percent of people between 11 and 30 years of age experiencing acne at some point. Cystic acne is the most severe form and affects far fewer people. In 2009, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that acne was the top reason people gave for visiting a dermatologist.

Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain. If you have trigeminal neuralgia, even mild stimulation of your face — such as from brushing your teeth or putting on makeup — may trigger a jolt of excruciating pain. You may initially experience short, mild attacks. But trigeminal neuralgia can progress and cause longer, more-frequent bouts of searing pain. Trigeminal neuralgia affects women more often than men, and it's more likely to occur in people who are older than 50. Because of the variety of treatment options available, having trigeminal neuralgia doesn't necessarily mean you're doomed to a life of pain. Doctors usually can effectively manage trigeminal neuralgia with medications, injections or surgery.
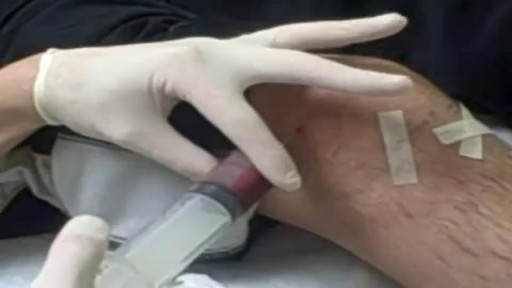
nee joint aspiration and injection are performed to aid in diagnosis and treatment of knee joint diseases. The knee joint is the most common and the easiest joint for the physician to aspirate. One approach involves insertion of a needle 1 cm above and 1 cm lateral to the superior lateral aspect of the patella at a 45-degree angle. Once the needle has been inserted 1 to 1½ inches, aspiration aided by local compression is performed. Local corticosteroid injections can provide significant relief and often ameliorate acute exacerbations of knee osteoarthritis associated with significant effusions. Among the indications for arthrocentesis are crystal-induced arthropathy, hemarthrosis, unexplained joint effusion, and symptomatic relief of a large effusion. Contraindications include bacteremia, inaccessible joints, joint prosthesis, and overlying infection in the soft tissue. Large effusions can recur and may require repeat aspiration. Anti-inflammatory medi

Labia minoraplasty is an elective procedure that can reduce the size and reshape the inner vaginal lips. Large or asymmetrical labia minora can leave you feeling self-conscience in tight clothing or during intimacy. Long labia may result in rubbing, irritation or discomfort during intercourse and exercise. Certain skin conditions can cause increased sensitivity or tearing of the labia minora. In some cases, the labia minora may be fused with tissue in the labia majora and require medical correction.

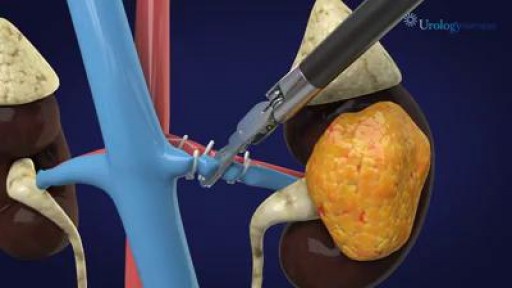
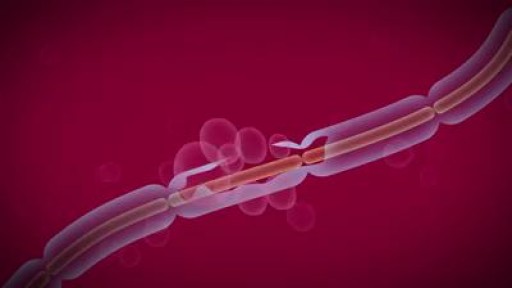
Although techniques of vascular anastomosis after trauma are numerous in type and form, most surgeons will default to the one associated with the greatest comfort and ease. This report offers a rapid and reliable repair using a conceptually and operationally simple technique. Its methodology is appropriate for all repairs, including cases mandating the insertion of vascular conduit. We have employed this technique for the past 15 years in nearly all patients with vascular injuries, regardless of the site and size of the vessel. This has included vessels of the neck, torso, upper and lower extremities. There have been no obvious complications associated with its use. Major advantages include: 1) the operating system is always oriented towards the surgeon, 2) the posterior row of sutures is placed as both ends are readily visualized, avoiding the need for potentially obscuring traction stitches, and 3) flushing is easily performed prior to completing the anterior suture row.