Los mejores videos

Lattrell Wells was a perfect candidate for the MACI procedure. Dr. Michael O'Malley is a sports medicine surgeon at Carilion Clinic, "It’s a two stage procedure. So what we do is we actually harvest a small portion of the patient's cartilage and bone cells and we send it to a lab where the lab then that grows additional cartilage cells. It comes back to us in a little sheet and six weeks after that initial surgery, we re-implant the cartilage in a second surgery where we implant that sheet depending on the size of lesion right where his defect. This the only option where there’s virtually no risk of any kind of graft rejection or anything of that nature.
Small cell lung cancer, which occurs almost exclusively in smokers, is a malignancy characterised by rapid doubling time, high growth fraction and widespread metastasis at presentation. In this presentation, we will briefly discuss the classification of pulmonary Neuro-endocrine tumours by the World Health Organisation followed by a detailed discussion of the clinical features, lab evaluation and management of SCLC, both limited and extended stage. The frontline therapy in small cell lung cancer is etoposide and cisplatin along with thoracic radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation in patients who have a good response to therapy. Hyperfractionation of radiotherapy may provide some benefit but is also associated with increase incidence of complications. Newer agents for SCLC include Vandetanib and immunotherapy molecules, such as Iplimumab and nivolumab.
If you have a lung disease, a type of surgery called a lobectomy is one treatment option your doctor may suggest. Your lungs are made up of five sections called lobes. You have three in your right lung and two in your left. A lobectomy removes one of these lobes. After the surgery, your healthy tissue makes up for the missing section, so your lungs should work as well or better than they did before.

Contact us to find out more http://www.londonvisionclinic.com/contact-us/ Glenn Carp talks about how both distance and some of the reading can be treated via laser eye surgery for hyperopia
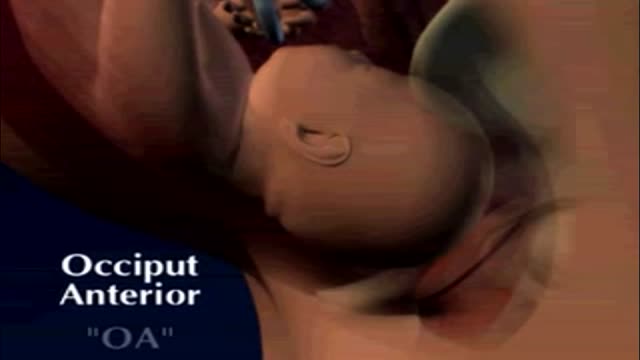
fetal position in womb at 34 weeks fetal position in womb week by week fetal position in womb at 19 weeksUnborn babies toss and turn and hold many different positions within the womb during the gestation period; pregnant women everywhere will attest to the fact that their children always start up the gymnastics at bedtime.

Linen Changes (with Patient in Bed)- Nursing Skills
FREE Nursing School Cheat Sheets at: http://www.NURSING.com
Get the full lesson on Patient Linen Changes here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-01-02-linen-chan
Get the full lesson on Bed Baths here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/skills-01-01-bed-bath/
Check out our new Nurse Care Plan Lessons here:
https://bit.ly/3BPRfPL
Get Access to Thousands of Lessons here:
https://nursing.com/courses/
Welcome to the NURSING Family, we call it the most supportive nursing cohort on the planet.
At NURSING.com, we want to help you remove the stress and overwhelm of nursing school so that you can focus on becoming an amazing nurse.
Check out our freebies and learn more at: (http://www.nursing.com)
Linen Changes (with Patient in Bed)- Nursing Skills
In this video, we’re going to show you how to change the linens with a patient in the bed. This might be after a bed bath or during incontinence care. So check out the bed bath video to see what got us up to this point. We love you guys! Go out and be your best selves today! And, as always, happy nursing!
Bookmarks:
0.05 Linen change introduction
0.16 Linen change supplies
0.30 Adjusting the patient/ sheet removal
1.00 Secure new fitted sheet
1.12 Pro tip
1.40 Roll patient back over
1.50 Repeat linen removal
2.02 Linen disposal
2.20 Wrinkle check
2.31 Reposition the patient for comfort
2.40 Covering the patient/ tuck-in
2.48 Pillowcase change (trick)
3.30 Making the patient comfortable
3.40 Linen change outro
Visit us at https://nursing.com/medical-disclaimer/ for disclaimer information.
NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, INC. and hold no affiliation with NURSING.com.

#dialysis #uvahealth
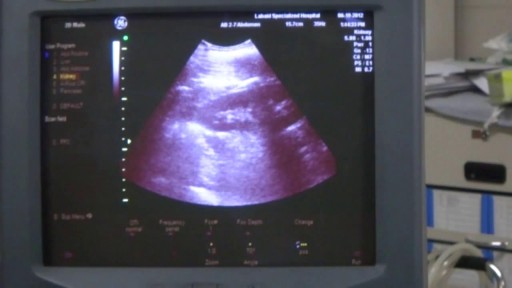
If your kidney function is declining and medications and other treatments aren’t working, dialysis can offer life-saving care. UVA has one of the largest dialysis programs in the country. Nephrologist Daphne Knicely, MD, explains the types of home dialysis and how they can work to fit your life.
Find out more at: https://uvahealth.com/services/dialysis
Transcript
Dialysis is just a way to replace the kidneys when they're not working anymore. So when the kidneys stop working, they stop getting rid of water, stop balancing the chemistry, stop getting rid of the toxins. Then dialysis does its job by balancing the chemistries, getting rid of the toxins, and help remove fluid. It doesn't fix the kidneys. It just replaces them.
I usually think of dialysis as two components. There's hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. So peritoneal dialysis can only be done at home. Hemodialysis can be done in a center, or it can be done at home.
Hemodialysis is where you have some sort of access to the blood. Either some sort of shunt in the arm that connects an artery and vein, or a catheter. And it allows for blood to leave you, go through a machine, get cleaned, chemistries balanced, and then comes back to you.
For home hemodialysis, the patient actually learns how to do that treatment. It's a very simple machine, very user-friendly. Training is usually about anywhere from four weeks up to eight weeks, and you work one-on-one with a nurse. You still see the physician. You come in about once a month, maybe twice a month, to get labs. You'll see a social worker, and a nutritionist at the same time.
Peritoneal dialysis takes place by putting a tube into your abdomen. And we take dialysis fluid that's chemically balanced. When we put it into the abdomen, it uses those little blood vessels to pull toxins out, to balance chemistries, kind of like little filters. Now, after it sits in there for several hours, we drain it out.
Anyone that needs dialysis is a candidate for home dialysis. There's not one type of dialysis that's going to make you live longer. They're all equal. The goal is to pick the type of dialysis that fits with your life.