Top videos

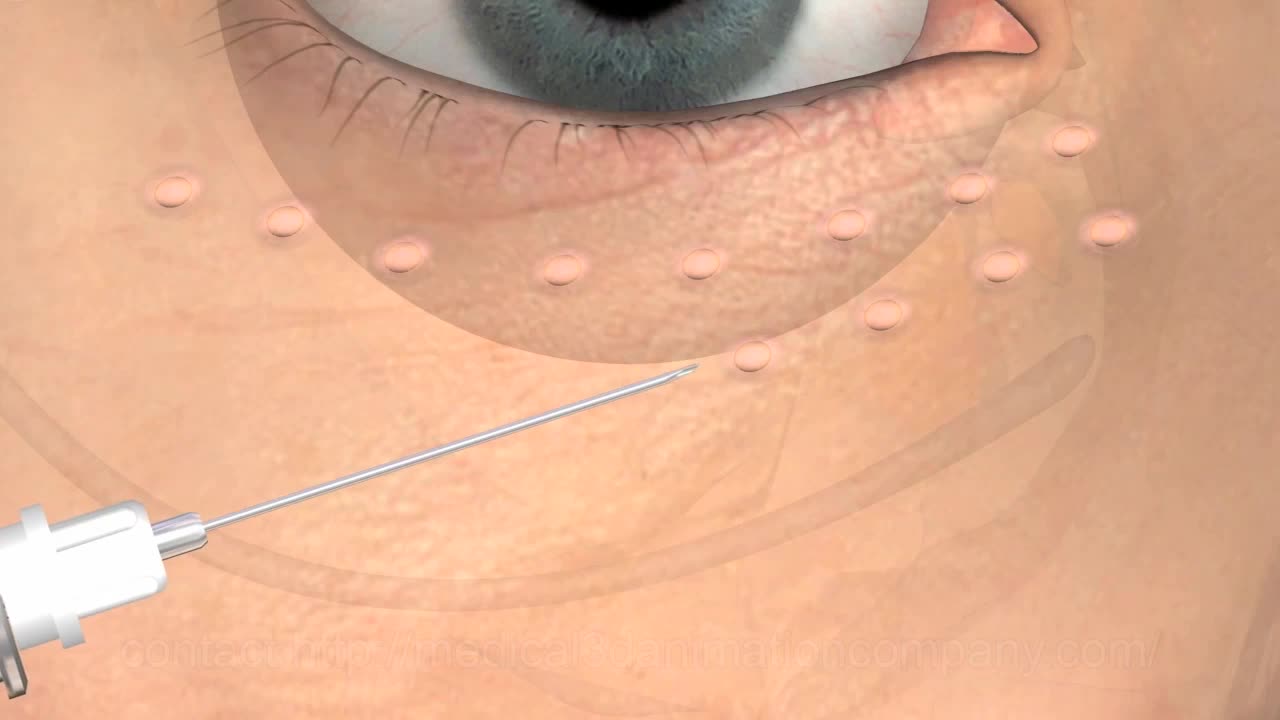
Contact us to find out more http://www.londonvisionclinic.com/contact-us/ Glenn Carp talks about how both distance and some of the reading can be treated via laser eye surgery for hyperopia

Macrobiopsy of breast lesions is a complicated procedure when performed with vacuum assisted biopsy tools. The Spirotome is a hand-held needle set that doesn’t need capital investment, is ready to use and provides tissue samples of high quality in substantial amounts. In this way quantitative molecular biology is possible with one tissue sample. The Coramate is an automated version of this direct and frontal technology

Stomach cancer usually begins in the mucus-producing cells that line the stomach. This type of cancer is called adenocarcinoma. For the past several decades, rates of cancer in the main part of the stomach (stomach body) have been falling worldwide. During the same period, cancer in the area where the top part of the stomach (cardia) meets the lower end of the swallowing tube (esophagus) has become much more common. This area of the stomach is called the gastroesophageal junction.

What is peripheral neuropathy? Your peripheral nervous system connects the nerves from your brain and spinal cord, or central nervous system, to the rest of your body. This includes your: arms hands feet legs internal organs mouth face The job of these nerves is to deliver signals about physical sensations back to your brain.

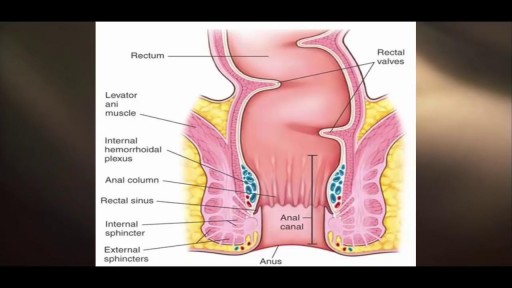
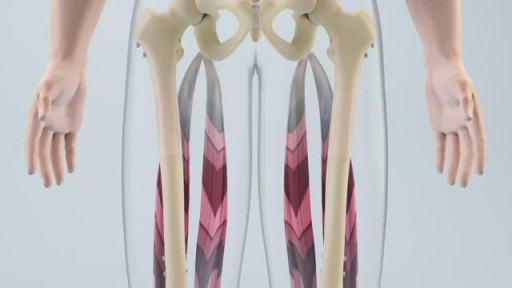
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called a trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditions, including leukemia, multiple myeloma, anemia, and pancytopenia. The bone marrow produces the cellular elements of the blood, including platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. While much information can be gleaned by testing the blood itself (drawn from a vein by phlebotomy), it is sometimes necessary to examine the source of the blood cells in the bone marrow to obtain more information on hematopoiesis; this is the role of bone marrow aspiration and biopsy.