Top videos
Hardware removals are among the most commonly performed surgical procedures worldwide. Current literature offers little data concerning postoperative patient satisfaction. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the patients’ point of view on implant removal. watch to learn more.

Choking occurs when a foreign object becomes lodged in the throat or windpipe, blocking the flow of air. In adults, a piece of food often is the culprit. Young children often swallow small objects. Because choking cuts off oxygen to the brain, administer first aid as quickly as possible. The universal sign for choking is hands clutched to the throat. If the person doesn't give the signal, look for these indications: Inability to talk Difficulty breathing or noisy breathing Inability to cough forcefully Skin, lips and nails turning blue or dusky Loss of consciousness

A water birth means at least part of your labor, delivery, or both happen while you’re in a birth pool filled with warm water. It can take place in a hospital, a birthing center, or at home. A doctor, nurse-midwife, or midwife helps you through it. In the U.S., some birthing centers and hospitals offer water births. Birthing centers are medical facilities that offer a more homelike setting than a hospital and more natural options for women having babies. The use of a birthing pool during the first stage of labor might: Help ease pain Keep you from needing anesthesia Speed up your labor The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), which sets guidelines for pregnancy and childbirth care in the U.S., says a water birth during the first stage of labor may have some benefits but delivering your baby underwater should be considered an experimental procedure with risks. The first stage is from when contractions start until your cervix is fully dilated.

Testicular torsion occurs when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum. The reduced blood flow causes sudden and often severe pain and swelling. Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 16, but it can occur at any age, even before birth. Testicular torsion usually requires emergency surgery. If treated quickly, the testicle can usually be saved. But when blood flow has been cut off for too long, a testicle might become so badly damaged that it has to be removed.
Myelomeningocele remains the most complex congenital malformation of the central nervous system that is compatible with life. This lesion results when the neural tube fails to fold normally during postovulatory Days 21 to 27.[6] The exact cause of disorders remains under some historical debate and is not within the scope of this paper. Myelomeningocele within the context of this discussion refers only to lesions that involve an open caudal neural tube defect on the surface of the skin

nkylosing spondylitis (pronounced ank-kih-low-sing spon-dill-eye-tiss), or AS, is a form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, although other joints can become involved. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort
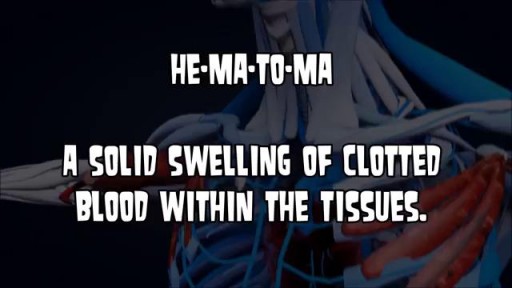
A subdural hematoma is most often the result of a severe head injury. This type of subdural hematoma is among the deadliest of all head injuries. The bleeding fills the brain area very rapidly, compressing brain tissue. This often results in brain injury and may lead to death. Subdural hematomas can also occur after a minor head injury. The amount of bleeding is smaller and occurs more slowly. This type of subdural hematoma is often seen in older adults. These may go unnoticed for many days to weeks, and are called chronic subdural hematomas. With any subdural hematoma, tiny veins between the surface of the brain and its outer covering (the dura) stretch and tear, allowing blood to collect. In older adults, the veins are often already stretched because of brain shrinkage (atrophy) and are more easily injured.
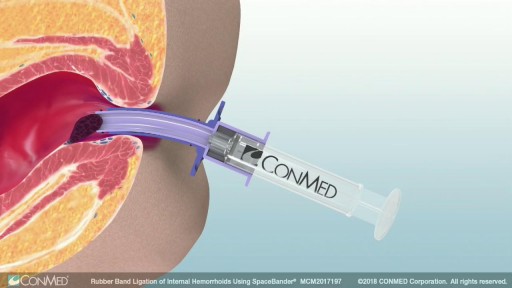
Rubber band ligation is a procedure in which the hemorrhoid is tied off at its base with rubber bands, cutting off the blood flow to the hemorrhoid. This treatment is only for internal hemorrhoids. To do this procedure, a doctor inserts a viewing instrument (anoscope) into the anus. The hemorrhoid is grasped with an instrument, and a device places a rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid. The hemorrhoid then shrinks and dies and, in about a week, falls off. A scar will form in place of the hemorrhoid, holding nearby veins so they don't bulge into the anal canal. The procedure is done in a doctor's office. You will be asked whether the rubber bands feel too tight. If the bands are extremely painful, a medicine may be injected into the banded hemorrhoids to numb them. After the procedure, you may feel pain and have a sensation of fullness in the lower abdomen. Or you may feel as if you need to have a bowel movement. Treatment is limited to 1 to 2 hemorrhoids at a time if done in the doctor's office. Several hemorrhoids may be treated at one time if the person has general anesthesia. Additional areas may be treated at 4- to 6-week intervals.