Top videos
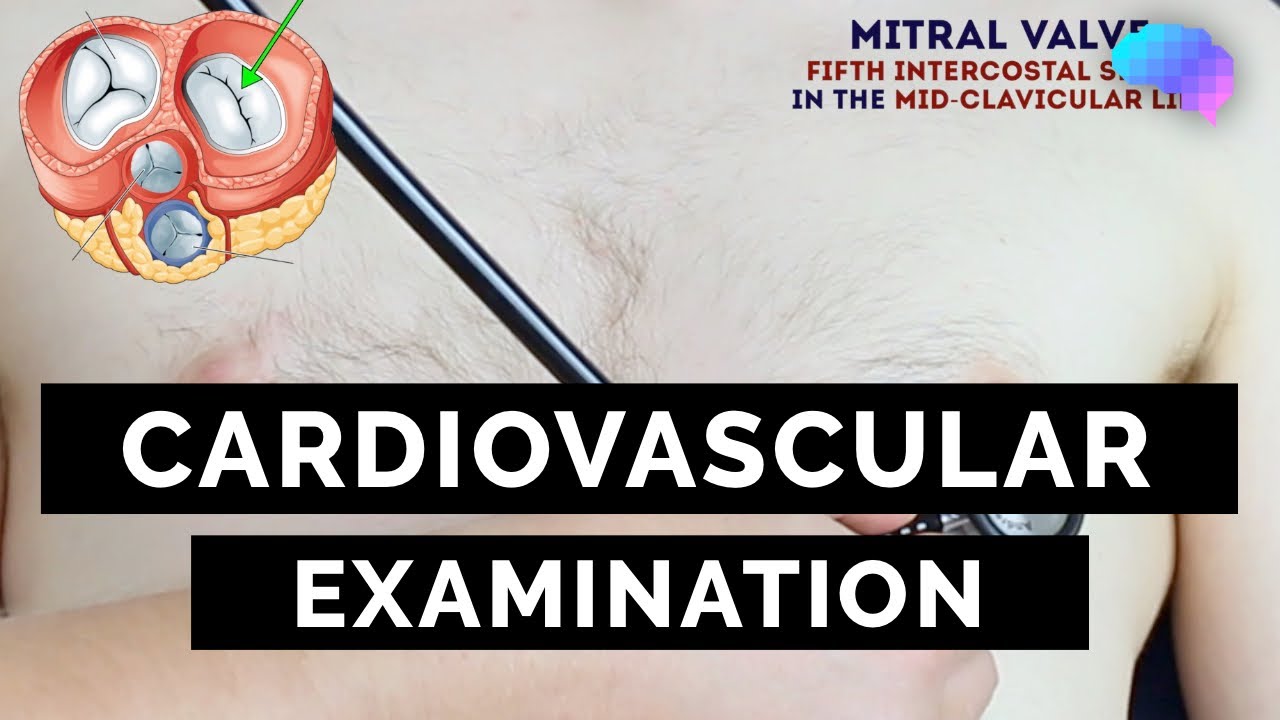
This video demonstrates how to perform a cardiovascular examination in an OSCE station.
You can access our step-by-step OSCE guide to accompany this video here: https://geekymedics.com/cardio....vascular-examination
Check out our other awesome clinical skills resources including:
• 🔥 Geeky Medics Bundles (discounted products): https://app.geekymedics.com/purchase/bundles/
• ✨ 1000+ OSCE Stations: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/osce-stations
• 🏥 Geeky Medics OSCE Revision Book: https://app.geekymedics.com/purchase/book/
• 📝 150+ PDF OSCE Checklists: https://geekymedics.com/pdf-osce-checklists/
• 🗂️ 3000+ OSCE Flashcards: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/flashcard-col
• 📱 Geeky Medics OSCE App: https://geekymedics.com/geeky-medics-app/
• 🩺 Medical Finals SBA Question Pack: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/medical-stude
• 💊 PSA Question Pack: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/prescribing-s
Chapters:
- Introduction 00:00
- General inspection 00:35
- Hands 00:46
- Schamroth's window test 01:07
- Capillary refill 01:27
- Pulses 01:35
- Carotid auscultation 02:21
- Carotid pulse 02:43
- Jugular venous pressure 02:55
- Hepatojugular reflux 03:09
- Inspection of the face 03:21
- Inspection of the chest 03:49
- Apex beat 04:12
- Heaves and thrills 04:28
- Heart valve ausculation 04:49
- Accentuation manoeuvres 05:45
- Lung base auscultation 06:23
- Sacral and pedal oedema 06:43
- Summary 07:10
Subscribe to our newsletter to be the first to know about our latest content: https://geekymedics.com/newsletter/ ✉️
Join the Geeky Medics community: 👩👩👧👧
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/geekymedics
Instagram: https://instagram.com/geekymedics
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/geekymedics
Always adhere to your medical school/local hospital guidelines when performing examinations or clinical procedures. DO NOT perform any examination or procedure on patients based purely upon the content of these videos. Geeky Medics accepts no liability for loss of any kind incurred as a result of reliance upon the information provided in this video.
Normal heart sounds and aortic regurgitation/stenosis sounds
Recorded on a Thinklabs Digital Stethoscope (https://www.thinklabs.com)
Some people have found this video useful for ASMR purposes.

Transgender Man Gives Birth to Healthy Baby, Talks Navigating Pregnancy as a Man Trystan Reese is a transgender man who just gave birth to a healthy baby boy. He told us about his pregnancy—and why his story isn't so out of the ordinary.

Surgeons in London removed a woman's brain tumor during a very unusual procedure. CBS News' Tina Kraus reports, the patient's love of music helped guide the surgery.
Subscribe to the CBS News Channel HERE: http://youtube.com/cbsnews
Watch CBSN live HERE: http://cbsn.ws/1PlLpZ7
Follow CBS News on Instagram HERE: https://www.instagram.com/cbsnews/
Like CBS News on Facebook HERE: http://facebook.com/cbsnews
Follow CBS News on Twitter HERE: http://twitter.com/cbsnews
Get the latest news and best in original reporting from CBS News delivered to your inbox. Subscribe to newsletters HERE: http://cbsn.ws/1RqHw7T
Get your news on the go! Download CBS News mobile apps HERE: http://cbsn.ws/1Xb1WC8
Get new episodes of shows you love across devices the next day, stream CBSN and local news live, and watch full seasons of CBS fan favorites like Star Trek Discovery anytime, anywhere with CBS All Access. Try it free! http://bit.ly/1OQA29B
---
CBSN is the first digital streaming news network that will allow Internet-connected consumers to watch live, anchored news coverage on their connected TV and other devices. At launch, the network is available 24/7 and makes all of the resources of CBS News available directly on digital platforms with live, anchored coverage 15 hours each weekday. CBSN. Always On.

Patient Greg Grindley communicates with host Bryant Gumbel and his wife for the first time while undergoing deep brain stimulation surgery at University Hospital's Case Medical Center in Cleveland, Ohio.
➡ Subscribe: http://bit.ly/NatGeoSubscribe
About National Geographic:
National Geographic is the world's premium destination for science, exploration, and adventure. Through their world-class scientists, photographers, journalists, and filmmakers, Nat Geo gets you closer to the stories that matter and past the edge of what's possible.
Get More National Geographic:
Official Site: http://bit.ly/NatGeoOfficialSite
Facebook: http://bit.ly/FBNatGeo
Twitter: http://bit.ly/NatGeoTwitter
Instagram: http://bit.ly/NatGeoInsta
Greg's First In-Surgery Conversation | Brain Surgery Live
https://youtu.be/zvqV_2zncNU
National Geographic
https://www.youtube.com/natgeo
![Female Foley Insertion (Urinary Catheter) [How to Insert Nursing Skills]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Mq4Yh0-iozY/maxresdefault.jpg)
Pass your tests and improve your grades with the below FREE resources:
1) A FREE 140 Must Know Meds book
Click here to get your FREE copy of the 140 Must Know Meds Book: https://bit.ly/41rxSt0
2) A FREE test-taking tips webinar
Join us for our free test-taking tips webinar to boost your exam scores: https://bit.ly/nursingtesttaking
You can now test your knowledge with a free lesson quiz on NURSING.com!
Click here to take a free quiz: https://bit.ly/3HwJr8t
FREE Nursing School Cheat Sheets at: http://www.NURSING.com
Get the full lesson on Female Foley Insertion here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-03-01-inserting-
Get the Male Foley Insertion lesson here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-03-02-inserting-
Get the Sterile glove application lesson here:
https://nursing.com/lesson/ski....lls-01-04-sterile-gl
Check out our new Nurse Care Plan Lessons here:
https://bit.ly/3BPRfPL
Get Access to Thousands of Lessons here:
https://nursing.com/courses/
Welcome to the NURSING Family, we call it the most supportive nursing cohort on the planet.
At NURSING.com, we want to help you remove the stress and overwhelm of nursing school so that you can focus on becoming an amazing nurse.
Check out our freebies and learn more at: (http://www.nursing.com)
Female Foley Insertion (Urinary Catheter)- Nursing Skills
In this video, we’re going to look at inserting a Foley catheter in a female. Of course make sure you’ve verified your order and told the patient what’s happening. You’ll also typically want to perform perineal care before you start. Then, you’ll want to assist the patient into the appropriate position. For females, that’s supine with their knees bent and feet close to their hips – allowing their knees to fall to the side. You may need a helper to help hold the patient in this position. We love you guys! Go out and be your best selves today! And, as always, happy nursing!
Bookmarks:
0.05 Female Foley insertion introduction
0.15 Patient positioning
0.27 Opening the sterile kit
1.41 Setting up the sterile field
2.25 Prepping the remaining Foley kit items
2.34 Catheter lubrication
3.00 Saline syringe attachment
3.10 Iodine, swabs and cleansing the area
3.52 Catheter insertion (into urethra)
4.06 Balloon inflation
4.25 Final catheter setting
4.31 Securing the catheter and bag
4.48 Discarding your supplies
5.00 Documentation
5.08 Foley insertion outro
Visit us at https://nursing.com/medical-disclaimer/ for disclaimer information.
NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, INC. and hold no affiliation with NURSING.com.
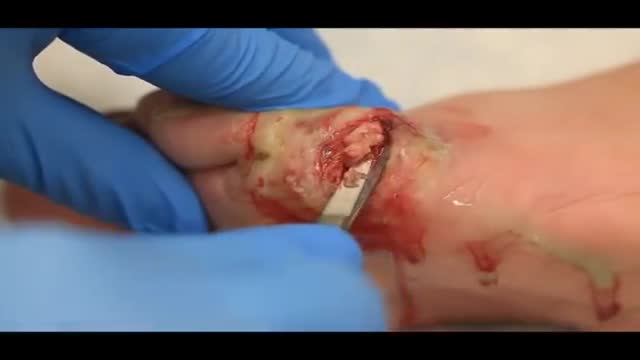
Treatment may not be needed for an eschar if it is part of the natural healing process. However, if an eschar looks like it may have a wound infection – symptoms can include oozing fluid such as pus or blood, your clinician will likely recommend topical treatment or debridement to help control and remove the infection.
An aortic dissection is a serious condition in which the inner layer of the aorta, the large blood vessel branching off the heart, tears. Blood surges through the tear, causing the inner and middle layers of the aorta to separate (dissect). If the blood-filled channel ruptures through the outside aortic wall, aortic dissection is often fatal. Aortic dissection is relatively uncommon. The condition most frequently occurs in men in their 60s and 70s. Symptoms of aortic dissection may mimic those of other diseases, often leading to delays in diagnosis. However, when an aortic dissection is detected early and treated promptly, the chance of survival greatly improves.
External cephalic version, or version, is a procedure used to turn a fetus from a breech position or side-lying (transverse) position into a head-down (vertex) position before labor begins. When successful, version makes it possible for you to try a vaginal birth.
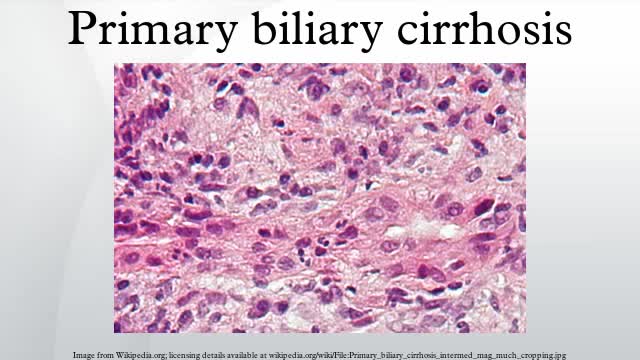
Primary biliary cirrhosis, sometimes called PBC, is a disease in which the bile ducts in your liver are slowly destroyed. Bile, a fluid produced in your liver, plays a role in digesting food and helps rid your body of worn-out red blood cells, cholesterol and toxins. When bile ducts are damaged, as in primary biliary cirrhosis, harmful substances can build up in your liver and sometimes lead to irreversible scarring of liver tissue (cirrhosis). Primary biliary cirrhosis is considered an autoimmune disease, in which the body turns against its own cells. Researchers think it is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Primary biliary cirrhosis usually develops slowly and medication can slow its progression, especially if treatment begins early.

Morning erections have colloquially been termed as “morning wood” while scientifically it is called nocturnal penile tumescence. It is a normal and healthy physiological reaction and response that most men experience in their lives. Morning erections are really the ending of a series of erections that happen to men during the night. Healthy men can, on average, have anywhere between three to five erections in a full night of sleep, each of which lasts from 25-35 minutes.
Best and 100% Successful Hymen Repair Surgery in Delhi with Latest Ultrafine Hymen repair Technology. 100% successful , Secure and Private. for more information visit: http://www.olmeccosmeticsurgery.com/best-hymenoplasty-surgery-india-delhi/

Cannula are often introduced into blood vessels in 80% of patients in the hospital for treatment. This can be a daunting experience to patients and stressful to doctors as multiple attempts are used. This may result in introducing spreading MRSA, E Coli & Chlostredium living on your skin into blood and results in Invasive MRSA infection.
Skin is often not adequatly cleaned during subsequent atempts as doctors/nurses do not wait for 1 min after applying cleaning solution on the skin before they puncture your skin.
Multiple punctured sites allow CA-MRSA to enter blood stream resulting in bacteremia and death.
Our mission is to reduce spreading invasive CA-MRSA in the hospitals by developing alternative technique to introduce cannulae.
Medifix was created by doctors with a mission to reduce the threat of spreading antibiotic resustant bacteria to mankind.
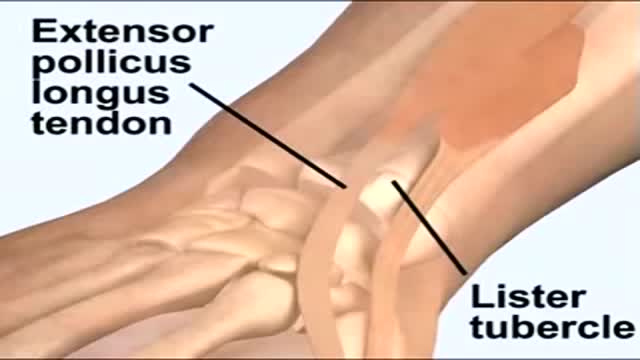
A needle is inserted into a joint for two main indications: aspiration of fluid (arthrocentesis) for diagnosis or for relief of pressure, or injection of medications. In practical terms, most injections into joints consist of a glucocorticoid, a local anesthetic, or a combination of the two. Occasionally saline is injected into the joint to diagnose a joint injury. This topic will review the basic technique of inserting a needle into a joint and the main indications for intraarticular steroid injections. The same techniques apply for injection of the less commonly used hyaluronate viscosupplementation agents into knees, hips, and perhaps shoulders.








