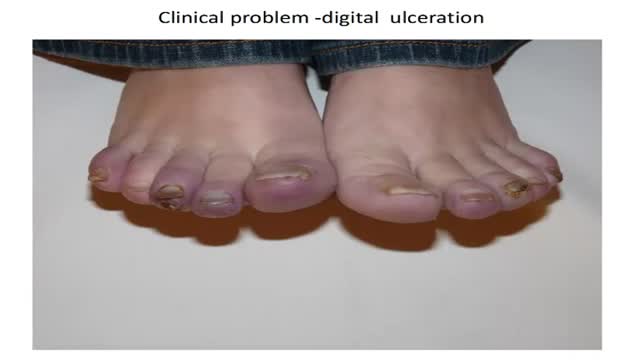
Top videos

Are you seeking sinus, allergy, or nasal congestion relief? Nasal irrigation, also known as nasal rinsining, is your solution! Nasal Care's nasal irrigation system is an all-natural, simple, and easy sinus and allergy treatment that brings gentle and soothing sinus relief. Visit www.nasalcleanse.com to learn more about the safe, simple and all-natural relief you can experience with NasalCare's nasal irrigation system.
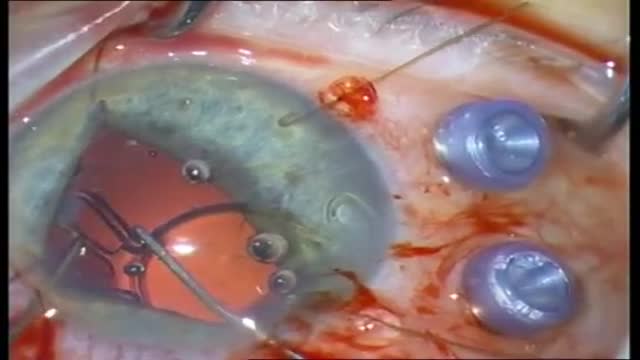
Patients with candida endophthalmitis who have chorioretinitis with vitreal involvement should be treated with vitrectomy and systemic antifungal therapy with amphotericin B (Choice B) and/or fluconazole. An early vitrectomy improves the likelihood of a positive outcome, and intravitreal injection of amphotericin B may be of help. Prompt diagnosis and treatment of candida endophthalmitis is essential, as the condition can worsen quickly.

If a fetal lung lesion is causing heart failure, fetal surgery may be performed to remove the CCAM before birth. http://fetalsurgery.chop.edu
N. Scott Adzick, MD, Mark Johnson, MD, and Holly Hedrick, MD, experts from the Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, explain when fetal intervention for CCAM is recommended, the various approaches that may be used to treat the most complex fetal lung lesions before birth, and how these procedures are performed.
One concern with fetal lung lesions is that they take up space in the chest. If the lung mass grows and pushes the heart and other organs out of place, it can lead to complications such as fetal hydrops (heart failure in the fetus). If this happens, a fetal surgery procedure may be performed to remove the CCAM before birth.
In other cases, an EXIT procedure may be performed to partially deliver the baby, so the team can remove the mass before the baby is fully delivered.
In this video series, parents, nurses and doctors from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia’s Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment talk about the different types of fetal lung lesions like congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) and bronchopulmonary sequestration (BPS), the importance of accurate diagnosis and monitoring, and the most advanced treatment options currently available. They also discuss follow-up care and long-term outcomes for babies diagnosed with fetal lung lesions.

LIS Closed done at 5 O clock position, using Scalpel blade 15. After feeling the groove between internal and external anal sphincter, the blade is passed in and the lower 1/2 of Internal anal sphincter is cut. Remain below dentate line. If anal mucosa is accidently cut suture with 4-0 rapid vicryl. In event of bleeding, pinchcock for 5 minutes.
Porcelain gallbladder is a condition characterized by calcium salt deposits in the wall of a chronically inflamed gallbladder. The calcifications can be thin or faintly visible, or may be amorphous, patchy, and thick. The gallbladder is generally large, but its size can vary considerably. Most porcelain gallbladders are associated with gallstones. A plain radiograph generally detects these, but computed tomography (CT) has a higher specificity; therefore, a CT scan is performed to confirm the diagnosis. Due to their high risk of gallbladder carcinoma, all patients with porcelain gallbladder should have an elective cholecystectomy.
• Define and use related medical terminology.
• Describe and demonstrate techniques for imaging the thyroid gland.
• Discuss functional abnormalities of the thyroid gland.
• Correlate laboratory data relevant to the thyroid and parathyroid glands.
• Describe, and recognize on images, pathologies of the thyroid gland.
• Identify the anatomy of the parathyroid glands on diagrams and sonograms.
• Describe and demonstrate techniques for imaging the parathyroid glands.
• Describe, and recognize on images, pathologies of the parathyroid glands.
• List and describe other neck masses.
• Follow relevant protocols when scanning.
• Differentiate the sonographic appearances of the female reproductive organs in relation to the menstrual cycle, the use of contraceptives and hormone replacement, and following chemotherapy.
• Explain the Patient Privacy Rule (HIPAA) and Patient Safety Act (see reference).

Ettore Vulcano, MD, Foot and Ankle Orthopedic Surgeon at Mount Sinai West, discusses a new minimally invasive bunion surgery that has patients walking immediately after surgery, and getting back to an active lifestyle much quicker than with the traditional surgery.

Neurotransmitter 3D Animation
on Tuesday, December 21, 2010
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals which transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to receptors in the membrane on the postsynaptic side of the synapse. Release of neurotransmitters usually follows arrival of an action potential at the synapse, but may also follow graded electrical potentials. Low level "baseline" release also occurs without electrical stimulation. Neurotransmitters are synthesized from plentiful and simple precursors, such as amino acids, which are readily available from the diet and which require only a small number of biosynthetic steps to convert. The chemical identity of neurotransmitters is often difficult to determine experimentally. For example, it is easy using an electron microscope to recognize vesicles on the presynaptic side of a synapse, but it may not be easy to determine directly what chemical is packed into them. The difficulties led to many historical controversies over whether a given chemical was or was not clearly established as a transmitter. In an effort to give some structure to the arguments, neurochemists worked out a set of experimentally tractable rules. According to the prevailing beliefs of the 1960s, a chemical can be classified as a neurotransmitter if it meets the following conditions: * There are precursors and/or synthesis enzymes located in the presynaptic side of the synapse. * The chemical is present in the presynaptic element. * It is available in sufficient quantity in the presynaptic neuron to affect the postsynaptic neuron; * There are postsynaptic receptors and the chemical is able to bind to them. * A biochemical mechanism for inactivation is present. There are many different ways to classify neurotransmitters. Dividing them into amino acids, peptides, and monoamines is sufficient for some classification purposes. Major neurotransmitters: * Amino acids: glutamate, aspartate, D-serine, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine * Monoamines and other biogenic amines: dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (noradrenaline; NE, NA), epinephrine (adrenaline), histamine, serotonin (SE, 5-HT), melatonin * Others: acetylcholine (ACh), adenosine, anandamide, nitric oxide, etc. In addition, over 50 neuroactive peptides have been found, and new ones are discovered regularly. Many of these are "co-released" along with a small-molecule transmitter, but in some cases a peptide is the primary transmitter at a synapse. β-endorphin is a relatively well known example of a peptide neurotransmitter; it engages in highly specific interactions with opioid receptors in the central nervous system. Single ions, such as synaptically released zinc, are also considered neurotransmitters by some[by whom?], as are some gaseous molecules such as nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO). These are not classical neurotransmitters by the strictest definition, however, because although they have all been shown experimentally to be released by presynaptic terminals in an activity-dependent way, they are not packaged into vesicles. By far the most prevalent transmitter is glutamate, which is excitatory at well over 90% of the synapses in the human brain. The next most prevalent is GABA, which is inhibitory at more than 90% of the synapses that do not use glutamate. Even though other transmitters are used in far fewer synapses, they may be very important functionally—the great majority of psychoactive drugs exert their effects by altering the actions of some neurotransmitter systems, often acting through transmitters other than glutamate or GABA. Addictive drugs such as cocaine and amphetamine exert their effects primarily on the dop
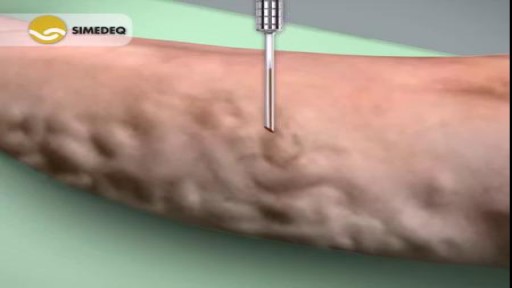
Varicose veins are generally benign. The cause of this condition is not known. For many people, there are no symptoms and varicose veins are simply a cosmetic concern. In some cases, they cause aching pain and discomfort or signal an underlying circulatory problem. Treatment involves compression stockings, exercise, or procedures to close or remove the veins.

Liposuction surgery is used to reduce the extra fat from your body with the very safe surgical process but you must consult with your Surgeon first when deciding about using this surgery to meet your body fat needs.
Vaser Lipo was Rs. 65000 per region. Now at Rs. 50,000 per Region
Offer valid till 31st March only
Vaser Liposuction technology helps to reduce the healing time and increase effective skin contraction, giving you smooth, slim results. With Liposuction there are no stitches, only a single 1cm small incision giving you permanent large result.
For further information, are available visit our website:
http://www.imageclinic.org/liposuction.html
Your Query for Chat and call +91-9818369662, 9958221983 (WhatsApp)