Top videos

For more than 25 years, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia — the first Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center in Pennsylvania — has provided unparalleled medical and surgical care for all injured children, including those with the most severe injuries.
Learn what makes the Trauma Center at CHOP a Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center, and how our work toward trauma prevention, research advances and overall trauma awareness provides hope for reduced injuries in the future.
Learn more about the Trauma Center at CHOP: http://www.chop.edu/trauma.

UPMC liver surgeons are among the most experienced in the world in performing minimally invasive liver surgery. Most patients benefit from less trauma and pain, minimal scarring, a shorter hospital stay, and faster recovery than from traditional surgery.
To learn more, please visit https://www.upmc.com/services/....liver-cancer/treatme

Dr. Fizan Abdullah is head of the Division of Pediatric Surgery and vice chair of the Department of Surgery at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago. His special interests include Chest wall deformities, pectus excavatum, abdominal wall defects, neonatal surgery, pulmonary and upper airway malformations, congenital diaphragmatic hernia, esophageal and gastrointestinal anomalies, hernia repair, tissue engineering, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), surgical safety protocols and surgical infections.
Learn more at www.luriechildrens.org

ormal sperm densities range from 15 million to greater than 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen. You are considered to have a low sperm count if you have fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter or less than 39 million sperm total per ejaculate.

Ankle fusion (arthrodesis) This is a surgical procedure which joins together the main bones of the ankle joint (the tibia and the talus). However, depending on the technique your surgeon will use, occasionally the fibula will be included in this procedure. The two joint surfaces which generate the pain are removed.
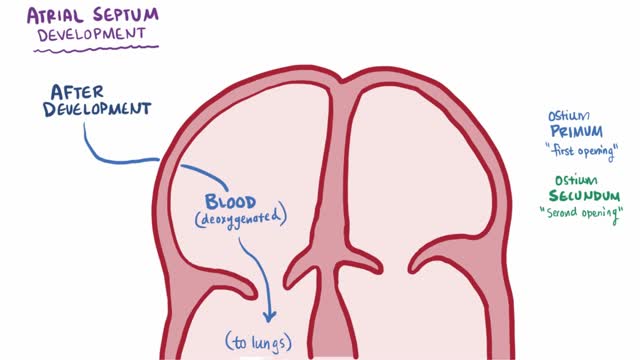
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present from birth (congenital). Small atrial septal defects may close on their own during infancy or early childhood. Large and long-standing atrial septal defects can damage your heart and lungs. Small defects may never cause a problem and may be found incidentally. An adult who has had an undetected atrial septal defect for decades may have a shortened life span from heart failure or high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Surgery may be necessary to repair atrial septal defects to prevent complications.
Nasal polyps are linked to allergic rhinitis, asthma, aspirin allergy, sinus infections, acute and chronic infections, something stuck in the nose, and cystic fibrosis. But many times the cause is unknown. Sometimes, people get them before they develop asthma or sinusitis

Bell's palsy is a form of facial paralysis resulting from damage or trauma to the facial nerves. The facial nerve-also called the 7th cranial nerve-travels through a narrow, bony canal (called the Fallopian canal) in the skull, beneath the ear, to the muscles on each side of the face. For most of its journey, the nerve is encased in this bony shell. Each facial nerve directs the muscles on one side of the face, including those that control eye blinking and closing, and facial expressions such as smiling and frowning. Additionally, the facial nerve carries nerve impulses to the lacrimal or tear glands, the saliva glands, and the muscles of a small bone in the middle of the ear called the stapes. The facial nerve also transmits taste sensations from the tongue. When Bell's palsy occurs, the function of the facial nerve is disrupted, causing an interruption in the messages the brain sends to the facial muscles. This interruption results in facial weakness or paralysis. Bell's palsy is named for Sir Charles Bell, a 19th century Scottish surgeon who described the facial nerve and its connection to the condition. The disorder, which is not related to stroke, is the most common cause of facial paralysis. Generally, Bell's palsy affects only one of the paired facial nerves and one side of the face, however, in rare cases, it can affect both sides.

Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain. If you have trigeminal neuralgia, even mild stimulation of your face — such as from brushing your teeth or putting on makeup — may trigger a jolt of excruciating pain. You may initially experience short, mild attacks. But trigeminal neuralgia can progress and cause longer, more-frequent bouts of searing pain. Trigeminal neuralgia affects women more often than men, and it's more likely to occur in people who are older than 50. Because of the variety of treatment options available, having trigeminal neuralgia doesn't necessarily mean you're doomed to a life of pain. Doctors usually can effectively manage trigeminal neuralgia with medications, injections or surgery.