Top videos

I talk about 5 Essential Skills you need as a nurse. These skills are timeless in the fat that you will always need to use them at some level. Of course specific skills are good to have as well but these skills are universal and can help you in other areas of life as well.
NURSING SCHOOL STUDY RESOURCES: https://sellfy.com/nursingschoolstudyNURSING
PHARMACOLOGY: https://sellfy.com/p/fnoy/
INSTAGRAM:https://www.instagram.com/your_mentor_rn/?hl=en
PERSONAL INSTAGRAM: https://www.instagram.com/crosby_steen/
MEDIUM ARTICLES: https://medium.com/@rnacademy1..../7-tips-for-nursing-
AMAZON PRIME STUDENT DISCOUNT: https://amzn.to/2OIleAe
VIDEO GEAR
Camera: G7X Markii - https://amzn.to/2na3OR8
Phone: Galaxy Note 8- https://amzn.to/2nboHM3
Audio: Zoom H4NPro Audio Recorder- https://amzn.to/2vktlf8
Computer: 13 inch Macbook Pro- https://amzn.to/2ndhISw
INSTAGRAM TV https://www.instagram.com/crosby_steen/
Hi Guys! My name is Crosby Steen. I am a Nursing Educator, and ER Travel Nurse. I do videos on daily science based news and travel, with the goal of providing value for you in science based education and travel nursing. Any questions hit me up in the comments or Email below.....
PRIVATE TUTORING OR VIDEO REQUESTS CONTACT:
crosby.steen@gmail.com
MUSIC BY: https://andrewapplepie.com/ and copyrighted by Epidemic Sound
Music by Joakim Karud http://youtube.com/joakimkarud
Music by DJ Quads
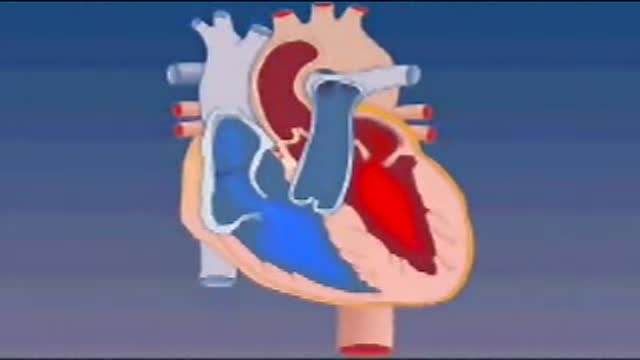
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.

Shingles is a viral infection that causes a painful rash. Although shingles can occur anywhere on your body, it most often appears as a single stripe of blisters that wraps around either the left or the right side of your torso. Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus — the same virus that causes chickenpox. After you've had chickenpox, the virus lies inactive in nerve tissue near your spinal cord and brain. Years later, the virus may reactivate as shingles. While it isn't a life-threatening condition, shingles can be very painful. Vaccines can help reduce the risk of shingles, while early treatment can help shorten a shingles infection and lessen the chance of complications.

A young patient undergoes state of the art robotic surgery for Ovarian Cancer and Endometrial Cancer in Chicago, IL. The surgery is performed by noted gynecologic oncologist and expert robotic surgeon M. Patrick Lowe MD. Dr Lowe has been performing robotic surgery since 2006 and is one of a few gynecologic oncologist in the United States who utilizes robotics for ovarian cancer.
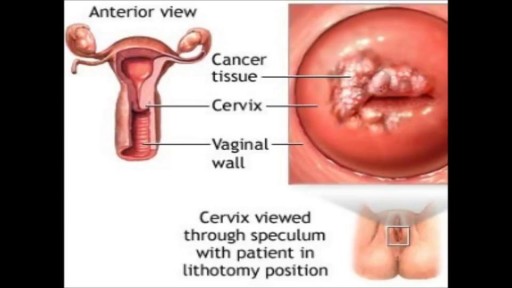
Menorrhagia is the medical term for menstrual periods with abnormally heavy or prolonged bleeding. Although heavy menstrual bleeding is a common concern, most women don't experience blood loss severe enough to be defined as menorrhagia. With menorrhagia, you can't maintain your usual activities when you have your period because you have so much blood loss and cramping. If you dread your period because you have such heavy menstrual bleeding, talk with your doctor. There are many effective treatments for menorrhagia.

Bone cancer symptoms. Possible symptoms of bone cancer include: Bone pain: Pain is the most common sign of bone cancer, and may become more noticeable as the tumor grows. Bone pain can cause a dull or deep ache in a bone or bone region (e.g., back, pelvis, legs, ribs, arms).

Scientists don't know what causes canker sores. Most believe that there is a problem with the body's immune system. Emotional stress, menstruation or injury to the mouth are common triggers for simple canker sores. Certain foods such as citrus or acidic foods may trigger a canker sore or make one more uncomfortable.

The purpose of the organs of the male reproductive system is to perform the following functions: To produce, maintain, and transport sperm (the male reproductive cells) and protective fluid (semen) To discharge sperm within the female reproductive tract during sex To produce and secrete male sex hormones responsible for maintaining the male reproductive system

Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from your face to your brain. If you have trigeminal neuralgia, even mild stimulation of your face — such as from brushing your teeth or putting on makeup — may trigger a jolt of excruciating pain. You may initially experience short, mild attacks. But trigeminal neuralgia can progress and cause longer, more-frequent bouts of searing pain. Trigeminal neuralgia affects women more often than men, and it's more likely to occur in people who are older than 50. Because of the variety of treatment options available, having trigeminal neuralgia doesn't necessarily mean you're doomed to a life of pain. Doctors usually can effectively manage trigeminal neuralgia with medications, injections or surgery.
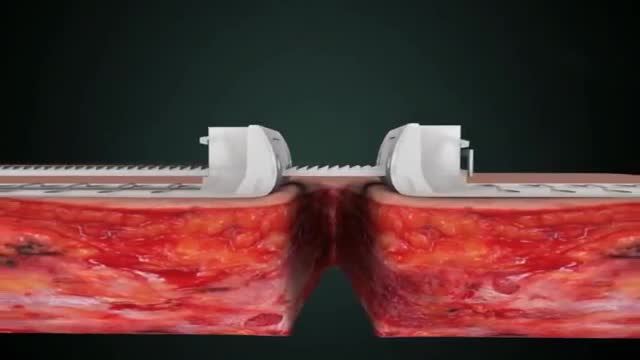
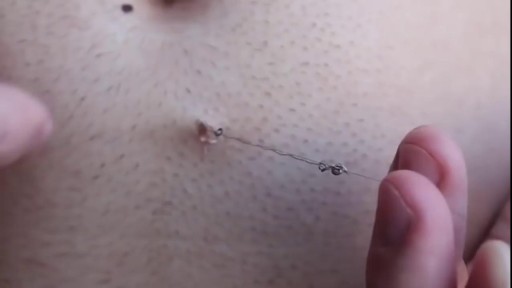
Wound closure techniques have evolved from the earliest development of suturing materials to comprise resources that include synthetic sutures, absorbables, staples, tapes, and adhesive compounds. The engineering of sutures in synthetic material along with standardization of traditional materials (eg, catgut, silk) has made for superior aesthetic results. Similarly, the creation of topical skin adhesives (the monomer 2-octyl cyanoacrylate), surgical staples, and tapes to substitute for sutures has supplemented the armamentarium of wound closure techniques. Aesthetic closure of a wound, whether traumatic or surgically induced, is based on knowledge of healing mechanisms and skin anatomy (see the image below), as well as an appreciation of suture material and closure technique. Choosing the proper materials and wound closure technique ensures optimal healing.[1]