Top videos
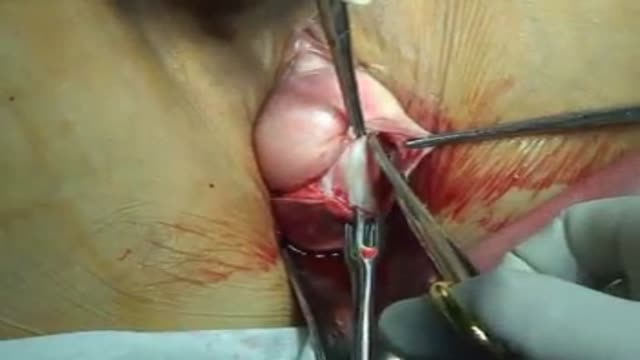
Repair performed with the PROLIFT Pelvic Floor Repair System - the total implant. The objective of the PROLIFT procedure is to achieve a a complete anatomic repair of pelvic floor defects in a standardized way. The repair is achieved by the placement of the synthetic non-absorbable polyprolylen mesh... implant via a vaginal approach.
At one time, women who had delivered by cesarean section in the past would usually have another cesarean section for any future pregnancies. The rationale was that if allowed to labor, many of these women with a scar in their uterus would rupture the uterus along the weakness of the old scar. Over time, a number of observations have become apparent: Most women with a previous cesarean section can labor and deliver vaginally without rupturing their uterus. Some women who try this will, in fact, rupture their uterus. When the uterus ruptures, the rupture may have consequences ranging from near trivial to disastrous. It can be very difficult to diagnose a uterine rupture prior to observing fetal effects (eg, bradycardia). Once fetal effects are demonstrated, even a very fast reaction and nearly immediate delivery may not lead to a good outcome. The more cesarean sections the patient has, the greater the risk of subsequent rupture during labor. The greatest risk occurs following a “classical” cesarean section (in which the uterine incision extends up into the fundus.) The least risk of rupture is among women who had a low cervical transverse incision. Low vertical incisions probably increase the risk of rupture some, but usually not as much as a classical incision. Many studies have found the use of oxytocin to be associated with an increased risk of rupture, either because of the oxytocin itself, or perhaps because of the clinical circumstances under which it would be contemplated. Pain medication, including epidural anesthetic, has not resulted greater adverse outcome because of the theoretical risk of decreasing the attendant’s ability to detect rupture early. The greatest risk of rupture occurs during labor, but some of the ruptures occur prior to the onset of labor. This is particularly true of the classical incisions. Overall successful vaginal delivery rates following previous cesarean section are in the neighborhood of 70 This means that about 30of women undergoing a vaginal trial of labor will end up requiring a cesarean section. Those who undergo cesarean section (failed VBAC) after a lengthy labor will frequently have a longer recovery and greater risk of infection than had they undergone a scheduled cesarean section without labor. Women whose first cesarean was for failure to progress in labor are only somewhat less likely to be succesful in their quest for a VBAC than those with presumably non-recurring reasons for cesarean section. For these reasons, women with a prior cesarean section are counseled about their options for delivery with a subsequent pregnancy: Repeat Cesarean Section, or Vaginal Trial of Labor. They are usually advised of the approximate 70successful VBAC rate (modified for individual risk factors). They are counseled about the risk of uterine rupture (approximately 1in most series), and that while the majority of those ruptures do not lead to bad outcome, some of them do, including fetal brain damage and death, and maternal loss of future childbearing. They are advised of the usual surgical risks of infection, bleeding, anesthesia complications and surgical injury to adjacent structures. After counseling, many obstetricians leave the decision for a repeat cesarean or VBAC to the patient. Both approaches have risks and benefits, but they are different risks and different benefits. Fortunately, most repeat cesarean sections and most vaginal trials of labor go well, without any serious complications. For those choosing a trial of labor, close monitoring of mother and baby, with early detection of labor abnormalities and preparation for

An antisperm antibody test looks for special proteins (antibodies) that fight against a man's sperm in blood, vaginal fluids, or semen. The test uses a sample of sperm and adds a substance that binds only to affected sperm. Semen can cause an immune system response in either the man's or woman's body. The antibodies can damage or kill sperm. If a high number of sperm antibodies come into contact with a man's sperm, it may be hard for the sperm to fertilize an egg. The couple has a hard time becoming pregnant. This is called immunologic infertility.

This procedure describes one of the most versatile approaches to the anterior skull base for large tumors of the sinonasal cavity. It may be used with or without a craniofacial resection. The benefits of this approach are: wide access around the tumor; good postoperative cosmesis; & decreased operative & postoperative morbidity. We have used this approach for many bilateral tumors of the nasal & sinus cavities that approach &/or invade the skull base & brain. This video show the resection of a large esthesioneuroblastoma.