Top videos

MRCPCH Clinical Revision - more videos at http://mrcpch.paediatrics.co.uk
Revise for your MRCPCH Clinical exam, with videos and high quality content created by the London Paediatrics Trainees Committee.
Examiner: Jonathan Round
Candidate: Amitav Parida
Filming: Mary Chesshyre, Huey Miin Lee, Chris Kelly
Thank you to the Evelina Children's Hospital for allowing us to film during their MRCPCH Revision Course (https://www.guysandstthomaseve....nts.co.uk/mrcpch-cli

-A finding of ASC on cytology requires further investigation to exclude precancerous lesions. Recommendations differ for women age 21 -24 and those age ;::25. For women age 21 -24 with ASCUS or low-grade squamous intraepitheliallesion (LSIL), current guidelines recommend repeating Pap smear in one year. In this younger patient population, HPV infection is transient and malignant transformation is rare. Therefore, colposcopy is not performed unless the patient demonstrates ASC-US or LSIL on 3

Tummy Tuck ( Classic Method ) : Surgery | 3D Animation
How long does tummy tuck last?
Tummy tuck results are considered permanent, insofar that the fat cells and skin removed during an abdominoplasty cannot grow back. Likewise, the internal sutures placed to repair abdominal muscles are designed to remain in place indefinitely.
What is tummy tuck surgery?
A tummy tuck — also known as abdominoplasty — is a cosmetic surgical procedure to improve the shape and appearance of the abdomen. During a tummy tuck, excess skin and fat are removed from the abdomen. Connective tissue in the abdomen (fascia) usually is tightened with sutures as well.
How much does tummy tuck cost?
How much does it cost? It can cost from about £5,000 to £10,000 to have an abdominoplasty in the UK, plus the cost of any consultations or follow-up care.
How painful is a tummy tuck?
A tummy tuck requires significant downtime
At the beginning, you will be fatigued, swollen and sore. It is normal to have moderate pain during these first several days, although this will steadily improve. It is vital to allow yourself time to focus on rest and healing.
What is the disadvantage of tummy tuck?
The cons of a tummy tuck include: A full abdominoplasty is a major operation with a considerable recovery. Expect to postpone strenuous activities for at least 6 weeks. Results take time.
Is tummy tuck more painful than C section?
That's something many women want to know. While patients have different experiences, most plastic surgeons would agree that a cesarean section is more painful than most tummy tucks.
- Tummy tuck
- Abdominoplasty
- Abdominal tuck
- Tummy tuck procedure
- Tummy tuck process
- Tummy tuck surgery
- Tummy tuck operation
- Tummy tuck video
- Tummy tuck recovery
- Tummy tuck before and after
- Abdominoplasty surgery
- Abdominal contouring surgery
- Postpartum tummy tuck
- Post pregnancy tummy tuck
- Mini tummy tuck
- Tummy tuck cost
- Tummy tuck risks
- Tummy tuck complications
- How long does a tummy tuck take
- Tummy tuck scarring
- Tummy tuck skin removal
- Tummy tuck muscle tightening
#tummytuck
#abdominoplasty
#plastic_surgery
#cosmetic_surgery
#body_contouring
#tummy_tuck_surgery
#surgery
#cosmetic_procedure
#beauty
#health
#fitness
#medical_animation
#3d_animation
#medical_video
#explainer_video
#education
Subscribe and 🔔 to the BBC 👉 https://bit.ly/BBCYouTubeSub
Watch the BBC first on iPlayer 👉 https://bbc.in/iPlayer-Home http://www.bbc.co.uk/human Richard Edwards undergoes a double hand transplant in which his hands are amputated and replaced with hands from a donor. This is the first time this has been done. Three months later the new hands are already changing his life.
#bbc
All our TV channels and S4C are available to watch live through BBC iPlayer, although some programmes may not be available to stream online due to rights. If you would like to read more on what types of programmes are available to watch live, check the 'Are all programmes that are broadcast available on BBC iPlayer?' FAQ 👉 https://bbc.in/2m8ks6v.
There many concerns and questions about how a breast augmentation procedure works. Dr. Linder a highly qualified plastic surgeon based in Beverly Hills, demystifies those worries. Dr. Stuart Linder is a Beverly Hills board certified plastic surgeon, specializing in body sculpting and reconstructive procedures including breast augmentation, reduction, lift, liposuction and tummy tuck. He is board-certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery and is affiliated with the American College of Surgeons, the American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons and the American Medical Association. Website: www.drlinder.com

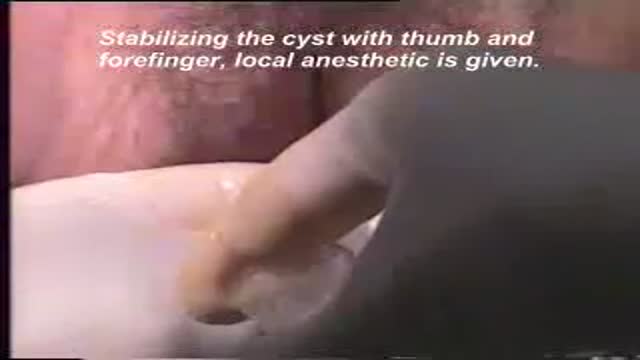
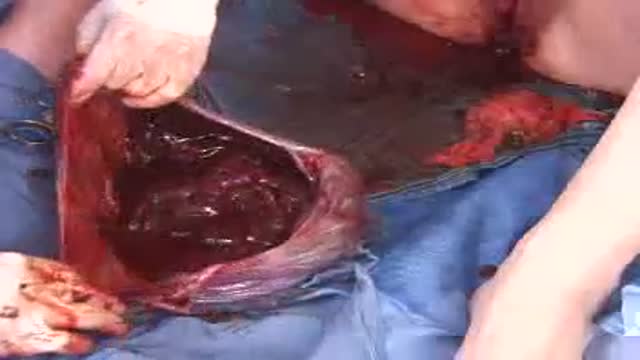
This is how Paraumbilical hernia looks like and how it is examined although it looks very simple but in exam it can be very difficult to perform all steps in small amount of time. This can be short case or even long of #cpsp #fcps #mbbs #medicalstudent #mbbsexams #plab2 #plab #plab1 and MS #genernalknowledge #surgery exams
#para-umbilical hernia
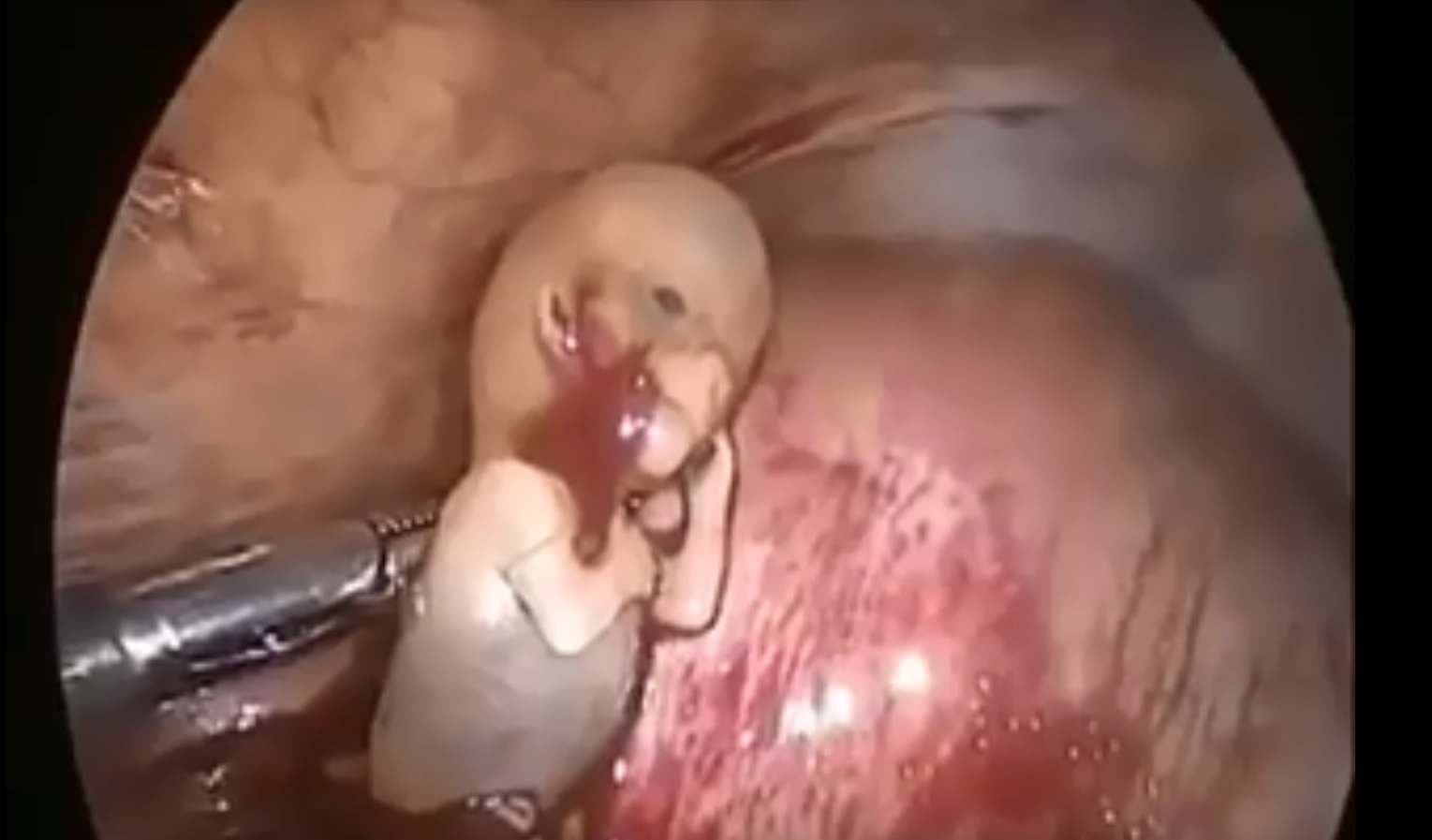
#umbilical hernia #paraumbilical #hernia repair#laparoscopic paraumbilical hernia repair. #umbilical defect, #vetral hernia surgery. #herniatreatment #herniatreatment #ventral hernia hernia,#laparoscopic ventral hernia repair,umbilicus,carl lowe jr,hernia repair,training,north carolina,hernia repair surgery,charlotte,operation,laparoscopic,bulge,surgery,surgeon,dr. lowe,ipom repair,live surgery,mesh,
#mesh #ipom repair
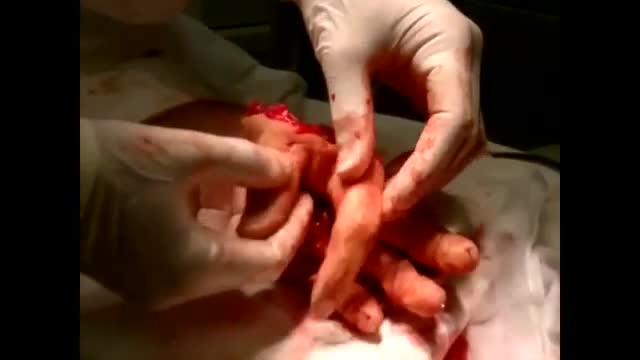
Since the first replant more than 50 years ago, thousands of severed body parts have been reattached, preserving the quality of life for thousands of patients through improved function and appearance that the void remaining after amputation cannot provide. Ronald Malt performed the first replantation on May 23, 1962 at Massachusetts General Hospital on a 12-year-old boy who had his right arm amputated in a train accident. [1, 2] This amputation occurred at the level of the humeral neck.
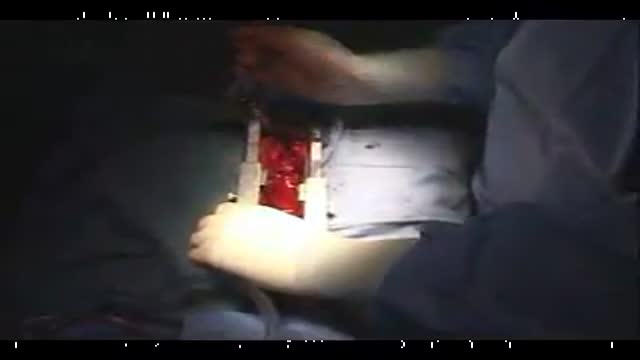
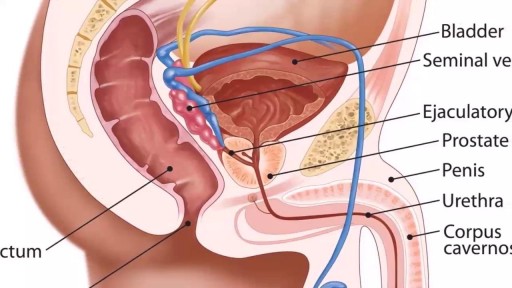
Open heart (coronary artery bypass, or CABG) surgery is performed in order to reroute, or "bypass," blood around blocked arteries, thereby improving the supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart. Surgeons usually use an artery from the chest wall to construct the "detour" around the blocked part of the artery. Veins from the legs are also used.