Top videos

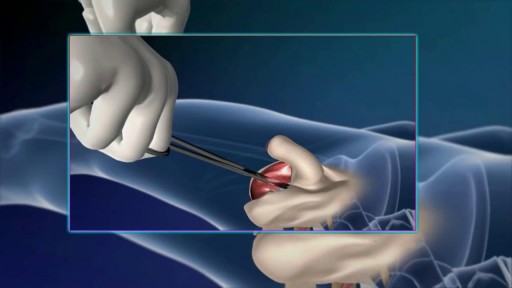
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure to remove tissue from inside your uterus. Doctors perform dilation and curettage to diagnose and treat certain uterine conditions — such as heavy bleeding — or to clear the uterine lining after a miscarriage or abortion. In a dilation and curettage — sometimes spelled "dilatation" and curettage — your doctor uses small instruments or a medication to open (dilate) your cervix — the lower, narrow part of your uterus. Your doctor then uses a surgical instrument called a curette to remove uterine tissue. Curettes used in a D&C can be sharp or use suction
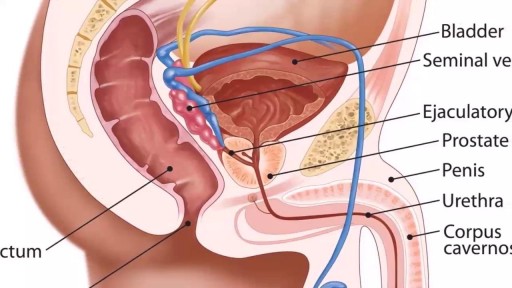
Central venous catheter. Diagram showing a tunneled central line inserted into the right subclavian vein. A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line, central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein.

Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer. There are three major types of skin cancer — Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma and melanoma. Out of these, Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. Melanoma appears on the skin as a new spot or growth or a change in an already existing mole. It is often fast growing and can spread to other parts of your body, including your bones, liver, and lungs to form a new cancer.
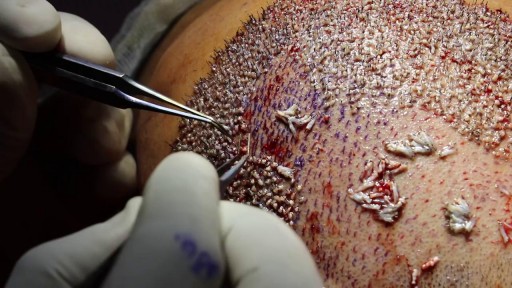
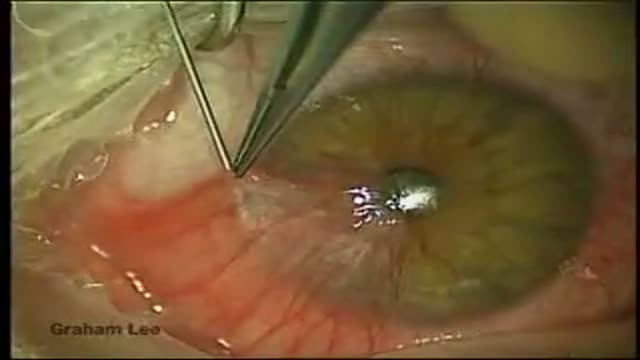
This implantation method is very common and used in both FUE hair transplant surgery and strip surgery (FUSS). During this implantation method, site creation and graft implantation are performed simultaneously as part of a one or two step process.