Top videos

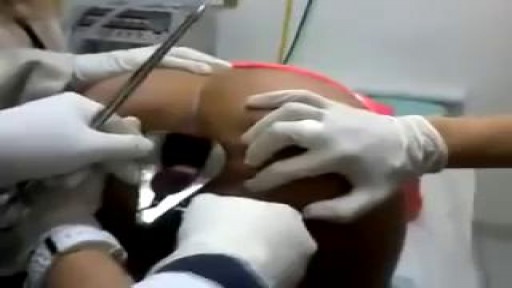
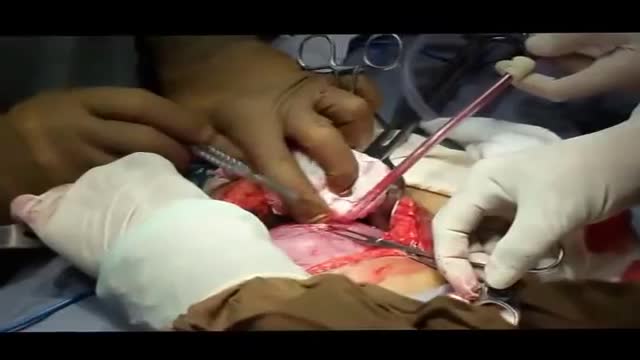
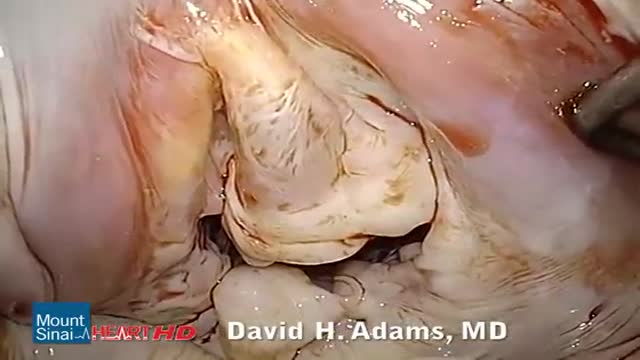
"Laparoscopic Placement of a
Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter"
Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart & Vascular Center, presents a cardiovascular procedure featuring Eric K. Peden, MD, Shri Timbalia, MD, and Kenneth Livingston as they demonstrate “Laparoscopic Placement of a
Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter".
Surgery: Eric K. Peden, MD, Shri Timbalia, MD, and Kenneth Livingston
Narration: Kenneth Livingston
** This medical education program may contain graphic content. **
_________________________________
A DeBakey CV Education event
Presented by Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart & Vascular Center.
Building on Dr. Michael E. DeBakey’s commitment to excellence in education, Houston Methodist DeBakey CV Education is an epicenter for cardiovascular academic and clinical educational programs that support the provision of optimal care to patients suffering from cardiovascular conditions and diseases.
FOR MORE INFORMATION
DeBakey CV Education:
https://www.houstonmethodist.o....rg/education/medical
For the latest education and training opportunities from DeBakey CV Education: http://bit.ly/HMdebakeyemail
Follow Us:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/debakeycvedu
Twitter: https://twitter.com/DeBakeyCVedu
Livestream: https://livestream.com/debakey
SmugMug: https://debakey.smugmug.com/
Want concise, relevant reviews of the hottest topics in CV medicine? Subscribe for FREE to the Methodist DeBakey Cardiovascular Journal for quarterly, peer-reviewed issues delivered to your door.
https://journal.houstonmethodist.org/

Epilepsy surgery is reserved for people whose seizures are not well controlled by seizure medicines. This situation is sometimes called being "medically refractory" or "drug resistant." In children, the definition of medically refractory is even more individualized to the specific child's situation. Surgery may be considered for some children after weeks to months of treatment with seizure medicines.
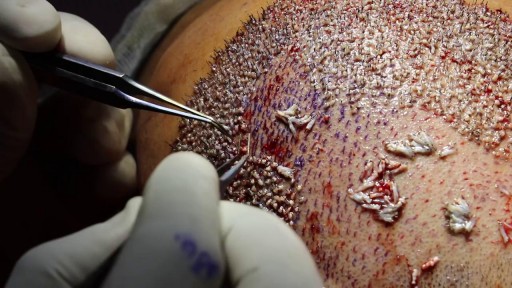
This implantation method is very common and used in both FUE hair transplant surgery and strip surgery (FUSS). During this implantation method, site creation and graft implantation are performed simultaneously as part of a one or two step process.

Must Watch Very Special New Funny Video 2023 Doctor Funny Video Injection Wala Funny Video | Comedy Video Episode 124 By Fun Comedy Ltd
@funcomedyltd
#funcomedyltd
#doctor
#comedy
#wala
Hello Dear Viewers,
If We have any mistake. please comment and tell us, what is our mistake? We will try to solve this mistake next. please watch our videos and give us confidence to trying best. Thank you for watching this video.
IMPORTANT NOTE:-
This video are no any kind of risk. This video are totally acting no risk no Dangerous act no Physical Harm or Death its ok for viewers.
injection wala comedy video injection wala video injection funny video injection injection wala injection injection doctor doctor doctor sui wala wala suji wala suji wala cartoon doctor cartoon funny video tui tui injection cartoon 22 cartoon video injection video cartoon cartoon comedy video doctor video wala cartoon busy fun ltd my family our fun tv fun tv 24 fun tv 420 funny day funny family ding dong bidik fun tv roma fun tv
#cartoon
#comedyvideo
#doctor_doctor
#busyfunltd
#newfunnyvideo2022
#newfunniestcomedy
#injectionfunnyvideo
#sui_wala
#myfamily
#busyfunltd
#funnyday
#bidikfuntv
#mohafuntv
#dingdong

For more than 25 years, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia — the first Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center in Pennsylvania — has provided unparalleled medical and surgical care for all injured children, including those with the most severe injuries.
Learn what makes the Trauma Center at CHOP a Level 1 Pediatric Trauma Center, and how our work toward trauma prevention, research advances and overall trauma awareness provides hope for reduced injuries in the future.
Learn more about the Trauma Center at CHOP: http://www.chop.edu/trauma.

The Ortolani method is an examination method that identifies a dislocated hip that can be reduced into the socket (acetabulum). Ortolani described the feeling of reduction as a “Hip Click” but the translation from Italian was interpreted a sound instead of a sensation of the hip moving over the edge of the socket when it re-located. After the age of six weeks, this sensation is rarely detectable and should not be confused with snapping that is common and can occur in stable hips when ligaments in and around the hip create clicking noises. When the Ortolani test is positive because the hip is dislocated, treatment is recommended to keep the hip in the socket until stability has been established

Nasal polyps are soft, painless, noncancerous growths on the lining of your nasal passages or sinuses. They hang down like teardrops or grapes. They result from chronic inflammation due to asthma, recurring infection, allergies, drug sensitivity or certain immune disorders. Small nasal polyps may not cause symptoms. Larger growths or groups of nasal polyps can block your nasal passages or lead to breathing problems, a lost sense of smell and frequent infections. Nasal polyps can affect anyone, but they're more common in adults. Medications can often shrink or eliminate nasal polyps, but surgery is sometimes needed to remove them. Even after successful treatment, nasal polyps often return.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) affects the brain and spinal cord. Early MS symptoms include weakness, tingling, numbness, and blurred vision. Other signs are muscle stiffness, thinking problems, and urinary problems. Treatment can relieve MS symptoms and delay disease progression.
The principal signs of cerebellar dysfunction are the following: Ataxia: unsteadiness or incoordination of limbs, posture, and gait. A disorder of the control of force and timing of movements leading to abnormalities of speed, range, rhythm, starting, and stopping.