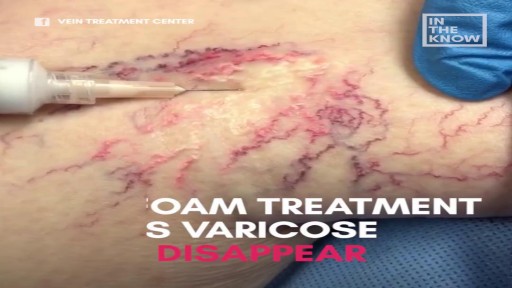
Top videos
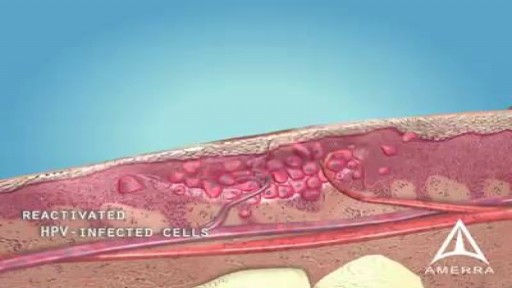
A wart is a skin growth caused by some types of the virus called the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV infects the top layer of skin, usually entering the body in an area of broken skin. The virus causes the top layer of skin to grow rapidly, forming a wart. Most warts go away on their own within months or years.
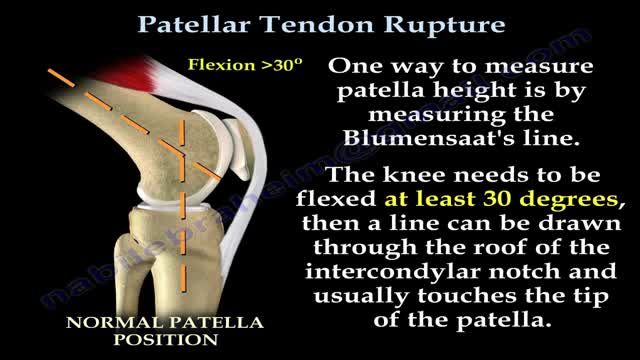
Patellar tendon rupture is a rupture of the tendon that connects the patella to the tibia. The superior portion of the patellar tendon attaches on the posterior portion of the patella, and the posterior portion of the patella tendon attaches to the tibial tubercle on the front of the tibia.

Renal artery stenosis is the narrowing of one or more arteries that carry blood to your kidneys (renal arteries). Narrowing of the arteries prevents normal amounts of oxygen-rich blood from reaching your kidneys. Your kidneys need adequate blood flow to help filter waste products and remove excess fluids. Reduced blood flow may increase blood pressure in your whole body (systemic blood pressure) and injure kidney tissue.
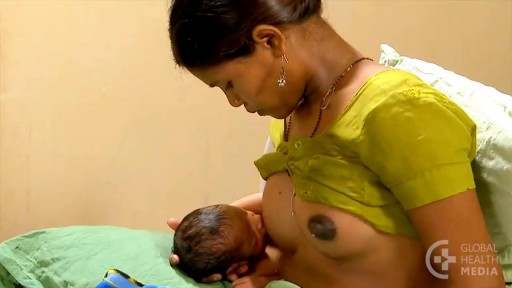
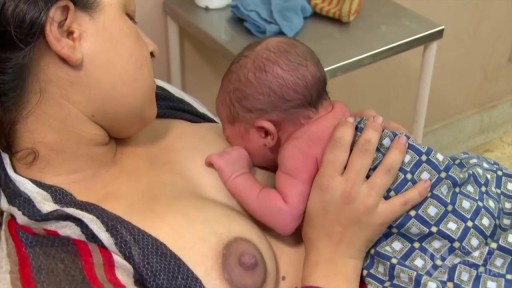
For the first few days after giving birth, a new mother’s breasts remain soft. They will produce colostrum. Colostrum, the first milk, is available in just the right amount, and is rich in immune factors that protect newborns. Sometime during the next few days, the breasts will become full, firm, warm, and perhaps tender. When this occurs, people say: “the milk is coming in!” The scientific term for this event is: engorgement. Engorgement is normal, and lasts for various periods of time depending on the individual woman. Some women experience only a day or so of mild, easy-to-manage engorgement. For other women, engorgement may be more intense, and can last from several days to two weeks.

Labia minoraplasty is an elective procedure that can reduce the size and reshape the inner vaginal lips. Large or asymmetrical labia minora can leave you feeling self-conscience in tight clothing or during intimacy. Long labia may result in rubbing, irritation or discomfort during intercourse and exercise. Certain skin conditions can cause increased sensitivity or tearing of the labia minora. In some cases, the labia minora may be fused with tissue in the labia majora and require medical correction.
Caesarean section is the most common way to deliver a breech baby in the USA, Australia, and Great Britain. Like any major surgery, it involves risks. Maternal mortality is increased by a Caesarean section, but still remains a rare complication in the First World. Third World statistics are dramatically different, and mortality is increased significantly. There is remote risk of injury to the mother’s internal organs, injury to the baby, and severe hemorrhage requiring hysterectomy with resultant infertility. More commonly seen are problems with noncatastrophic bleeding, postoperative infection and wound healing problems. It should be added that the increase in maternal mortality rates could be slightly skewed due to the fact that Caesarean sections are often used during high-risk pregnancies and/or when mortality is already a strong possibility.
One large study has confirmed that elective cesarean section has lower risk to the fetus and a slightly increased risk to the mother, than planned vaginal delivery of the breech however elements of the methodology used have undergone some criticism.
The same birth injuries that can occur in vaginal breech birth may rarely occur in Caesarean breech delivery. A Caesarean breech delivery is still a breech delivery. However the soft tissues of the uterus and abdominal wall are more forgiving of breech delivery than the hard bony ring of the pelvis. If a Caesarean is scheduled in advance (rather than waiting for the onset of labor) there is a risk of accidentally delivering the baby too early, so that the baby might have complications of prematurity. The mother’s subsequent pregnancies will be riskier than they would be after a vaginal birth (uterine rupture). The presence of a uterine scar will be a risk factor for any subsequent pregnancies.

A water birth means at least part of your labor, delivery, or both happen while you’re in a birth pool filled with warm water. It can take place in a hospital, a birthing center, or at home. A doctor, nurse-midwife, or midwife helps you through it. In the U.S., some birthing centers and hospitals offer water births. Birthing centers are medical facilities that offer a more homelike setting than a hospital and more natural options for women having babies. The use of a birthing pool during the first stage of labor might: Help ease pain Keep you from needing anesthesia Speed up your labor The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), which sets guidelines for pregnancy and childbirth care in the U.S., says a water birth during the first stage of labor may have some benefits but delivering your baby underwater should be considered an experimental procedure with risks. The first stage is from when contractions start until your cervix is fully dilated.
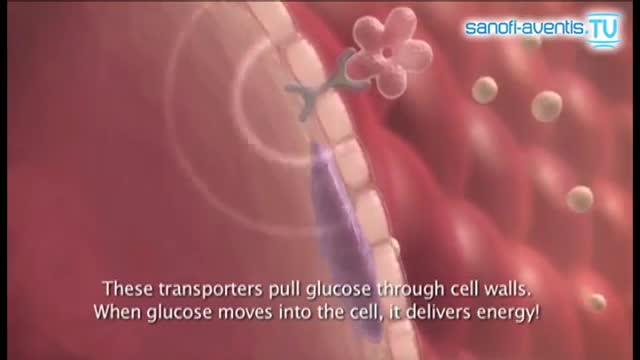
This hormone, insulin, causes the liver to convert more glucose into glycogen (this process is called glycogenesis), and to force about 2/3 of body cells (primarily muscle and fat tissue cells) to take up glucose from the blood through the GLUT4 transporter, thus decreasing blood sugar.

Ear irrigation is a routine procedure used to remove excess earwax, called cerumen, or foreign materials from the ear. The ear naturally secretes earwax to protect, lubricate, keep debris out, and regulate bacterial growth. Under normal conditions, the body keeps the amount of earwax in the ears .

nkylosing spondylitis (pronounced ank-kih-low-sing spon-dill-eye-tiss), or AS, is a form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, although other joints can become involved. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort