Top videos
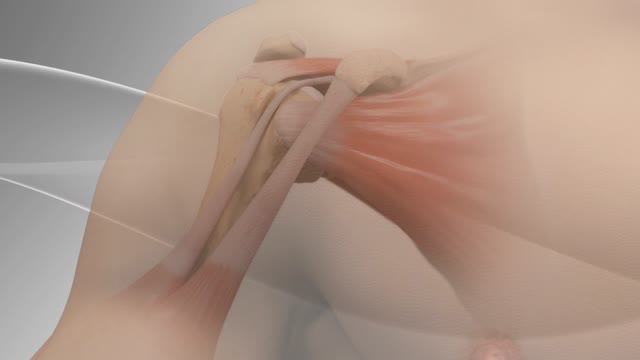
Biceps tenodesis surgery is performed when the biceps tendon is damaged, or the rotator cuff tendon or cartilage ring in the shoulder is torn. The biceps tendon is a strong rope‐like structure connecting the upper end of the biceps muscle to the bones in the shoulder. In biceps tenodesis surgery, the biceps tendon is separated from the shoulder and reattached to the humerus, or the upper arm bone.

Brain tumor survivor Robert Alvarez and neurosurgeon Sujit Prabhu, M.D., explain why and how Robert played the guitar during his surgery for a grade II astrocytoma. It was the first time a brain tumor patient played a musical instrument during an awake craniotomy at MD Anderson.
Read Robert Alvarez's story: https://www.mdanderson.org/pub....lications/cancerwise
Learn about awake craniotomy for brain tumors: https://www.mdanderson.org/pub....lications/cancerwise
Request an appointment at MD Anderson by calling 1-877-632-6789 or online at: https://my.mdanderson.org/Requ....estAppointment?cmpid

If you have an upcoming procedure at UC Davis Children’s Surgery Center, this video provides information and details of what you and your family can expect from arrival to check-in through to surgery and after care.
This video is also available in these languages:
Arabic: https://youtu.be/ERPikb0prlI
Dari: https://youtu.be/UW5fT433IGQ
Punjabi: https://youtu.be/Xq6PV2qtOMo
Russian: https://youtu.be/v223nDdN1b4
Spanish: https://youtu.be/4Jr4dkzAaWA
——
At UC Davis Children’s Hospital, we put your child at the center of everything that we do. It’s personalized care, uniquely sized for your child. You’ll see it in our child-friendly designs throughout the hospital, our farm-to-fork approach to dining, our playrooms and teen rooms and our team that feels like family. UC Davis Children’s Hospital is Sacramento’s only nationally ranked, comprehensive hospital for children, serving infants, children, adolescents and young adults with primary, subspecialty and critical care.
UC Davis Children’s Hospital: https://children.ucdavis.edu
Children’s Surgery Center: https://health.ucdavis.edu/chi....ldren/services/child
Child Life and Creative Arts Therapy: https://health.ucdavis.edu/chi....ldren/services/child
Fetal Care and Treatment Center: https://health.ucdavis.edu/chi....ldren/services/fetal
See the latest news from UC Davis Health: https://health.ucdavis.edu/newsroom
Kids Considered podcast: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLM7qvIv8N9R
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/UCDavisChildrensHospital
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/ucdavischildren
Twitter/X: https://twitter.com/UCDavisChildren
——
#surgery #childrenshospital #surgeryrecovery #ucdavis

What are the disadvantages of male condoms? a moderately high failure rate when used improperly or inconsistently. the potential for diminished sensation. skin irritation, such as contact dermatitis, due to latex sensitivity or allergy. allergic reactions to spermicides, lubes, scents, and other chemicals in the condoms.
If it is not removed, tooth decay will begin. The acids in plaque damage the enamel covering your teeth. It also creates holes in the tooth called cavities. Cavities usually do not hurt, unless they grow very large and affect nerves or cause a tooth fracture.

Bone tumors include abnormal healing of an injury, inherited conditions, radiation therapy. It can also be caused by bone cancer or another cancer that has spread to the bone from other parts of the body. A bone tumor may cause a painless mass. Some people have dull, aching pain. And in some cases, minor injury causes a fracture near the tumor. Treatments include surgery and radiation. Some noncancerous tumors go away without treatment

A spermatocelectomy is surgery to remove a spermatocele. A spermatocele is a cyst (sac of fluid) that contains sperm. It forms inside your scrotum on the outside of your testicle. The cyst is most often attached to your epididymis. The epididymis is a tube that stores sperm.
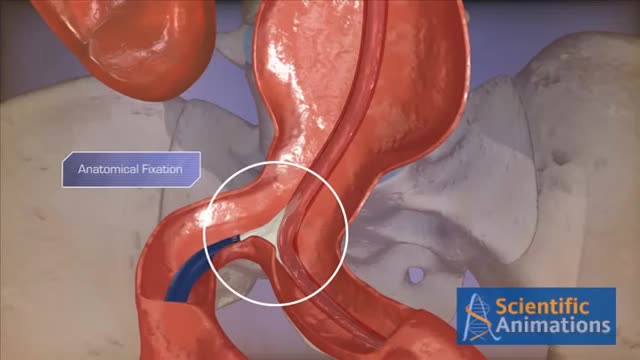
Abdominal aortic aneurysms can weaken the aorta, your body’s largest blood vessel. This can develop into a potentially serious heath problem that can be fatal if the aneurysm bursts, causing massive internal bleeding. Endovascular stent grafting, or endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR), is a newer form of treatment for abdominal aortic aneurysm that is less invasive than open surgery. Endovascular stent grafting uses an endovascular stent graft to reinforce the wall of the aorta and to help keep the damaged area from rupturing.

A 76 year-old, female, presented with a three day history of melena without any abdominal pain. She had one episode of hematemesis (about 100 ml blood) in the emergency room, patient has a strong alcoholic drink abuse.
An upper endoscopy with magnification was performed.
multiple ulcers were detected across of the gastric camera,
esophageal varices was also detected

Image result for Stop Arterial Bleeding The Femoral Artery is located in the crease of the groin area. Pressure placed here will stop bleeding in leg wounds. Direct Pressure and Elevation should be continued while applying pressure to pressure points. Finally, A pressure bandage should be placed over the dressing and wound