Top videos

Hirschsprung's (HIRSH-sproongz) disease is a condition that affects the large intestine (colon) and causes problems with passing stool. The condition is present at birth (congenital) as a result of missing nerve cells in the muscles of the baby's colon. A newborn who has Hirschsprung's disease usually can't have a bowel movement in the days after birth. In mild cases, the condition might not be detected until later in childhood. Uncommonly, Hirschsprung's disease is first diagnosed in adults.
For Employees of Hospitals, Schools, Universities and Libraries: Download 8 FREE medical animations from Nucleus by signing up for a free trial: http://nmal.nucleusmedicalmedi....a.com/free-trial-mem
Biology students: Subscribe to the Nucleus Biology channel to see new animations on biology and other science topics, plus short quizzes to ace your next exam: https://bit.ly/3lH1CzV
This medical animation depicts Laser Eye Surgery, a procedure that permanently changes the shape of the cornea, the clear covering over the front of the eye.
#lasik #eye #cornea
ANCE00185

A 76 year-old, female, presented with a three day history of melena without any abdominal pain. She had one episode of hematemesis (about 100 ml blood) in the emergency room, patient has a strong alcoholic drink abuse.
An upper endoscopy with magnification was performed.
multiple ulcers were detected across of the gastric camera,
esophageal varices was also detected
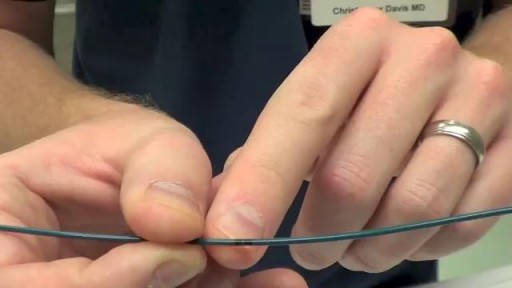
Transvenous cardiac pacing, also called endocardial pacing, is a potentially life saving intervention used primarily to correct profound bradycardia. It can be used to treat symptomatic bradycardias that do not respond to transcutaneous pacing or to drug therapy.
This anatomical implant was originally placed in 1997. Due to the dark yellow color inside the implant it is clear the implant has been ruptured for quite some time. When implants rupture, it is important to have them replaced as soon as possible to avoid excessive scarring in the breasts. If too much scar tissue has accumulated around the deflated implant, it becomes difficult to create a normal breast shape in the future. Therefor its important to know the signs of a ruptured implant such as, painful to touch, visible asymmetry or loss of integrity to the bag. Dr. Stuart Linder 9675 Brighton Way Suite 420 Beverly Hills, CA 90210
Recommended range without diabetes is 70 to 130mg/dL. (The standard for measuring blood glucose is "mg/dL" which means milligrams per deciliter.) If your blood glucose level is above 130mg/dL, that's fasting hyperglycemia. Fasting hyperglycemia is a common diabetes complication.

This video shows you how to examine the hand and wrist and how to identify common causes of pain.
This video clip is part of the FIFA Diploma in Football Medicine and the FIFA Medical Network. To enrol or to find our more click on the following link http://www.fifamedicalnetwork.com
The Diploma is a free online course designed to help clinicians learn how to diagnose and manage common football-related injuries and illnesses. There are a total of 42 modules created by football medicine experts. Visit a single page, complete individual modules or finish the entire course.
The network provides the opportunity for clinicians around the world to meet and share ideas relating to football medicine. Ask about an interesting case, debate current practice and discuss treatment strategies. Create a profile and log on to interact with other health professionals from around the globe.
This is not medical advice. The content is intended as educational content for health care professionals and students. If you are a patient, seek care of a health care professional.

Epilepsy surgery is reserved for people whose seizures are not well controlled by seizure medicines. This situation is sometimes called being "medically refractory" or "drug resistant." In children, the definition of medically refractory is even more individualized to the specific child's situation. Surgery may be considered for some children after weeks to months of treatment with seizure medicines.
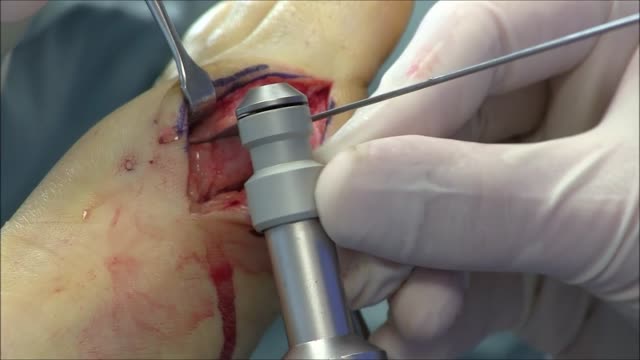
Bunions can be very painful. ... Bunion removal is a surgical procedure that corrects a deformed area of the foot near the big toe. Bunion removal is sometimes called a bunionectomy, bunion surgery, or hallux valgus correction. Hallux valgus is a Latin phrase that means “foot deformity
The venipuncture procedure is complex, requiring both knowledge and skill to perform. Each phlebotomist generally establishes a routine that is comfortable for her or him. Several essential steps are required for every successful collection procedure: Identify the patient. Assess the patient's physical disposition (i.e. diet, exercise, stress, basal state). Check the requisition form for requested tests, patient information, and any special requirements. Select a suitable site for venipuncture. Prepare the equipment, the patient and the puncture site. Perform the venipuncture. Collect the sample in the appropriate container. Recognize complications associated with the phlebotomy procedure. Assess the need for sample recollection and/or rejection. Label the collection tubes at the bedside or drawing area. Promptly send the specimens with the requisition to the laboratory.

http://smoking-videos.plus101.com
Quit Smoking Forever Formula Videos - How To Quit Smoking In As Fast As 1 Week Without Agitation, Cravings Or Withdrawal Symptoms.You're about to uncover the 3 elements that will rapidly boost your chances of success to quit smoking and not only that, you'll learn ways to escape cravings and how to avoid a relapse that can happen in the future even to people with the most willpower.

Bone tumors include abnormal healing of an injury, inherited conditions, radiation therapy. It can also be caused by bone cancer or another cancer that has spread to the bone from other parts of the body. A bone tumor may cause a painless mass. Some people have dull, aching pain. And in some cases, minor injury causes a fracture near the tumor. Treatments include surgery and radiation. Some noncancerous tumors go away without treatment
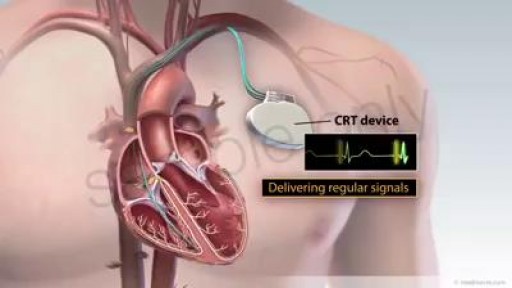
CRT is a clinically proven treatment option for some individuals with heart failure. A CRT device sends small electrical impulses to both lower chambers of the heart to help them beat together in a more synchronized pattern. This may improve the heart’s ability to pump blood and oxygen to your body. A CRT system is made up of two parts. The heart device, which is actually a tiny computer, plus a battery, contained in a small titanium metal case that is about the size of a pocket watch. Insulated wires, called leads, that are implanted to carry information signals from your heart to the heart device and to carry electrical impulses to your heart After the device system is implanted, an external computer, called a programmer, located at your doctor's office or clinic can be used to program the heart device and retrieve information from your heart device that will assist your doctor in your heart failure treatment. Your doctor will schedule periodic monitoring which may be done remotely if physician deems appropriate