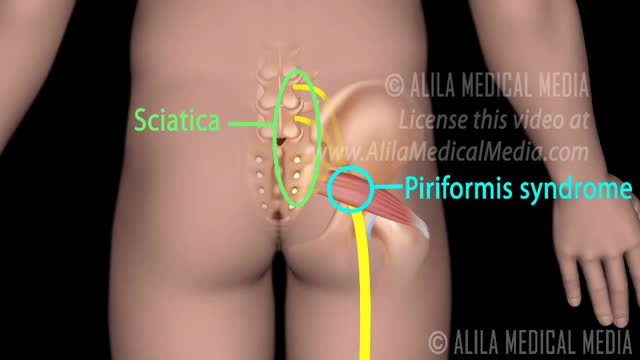
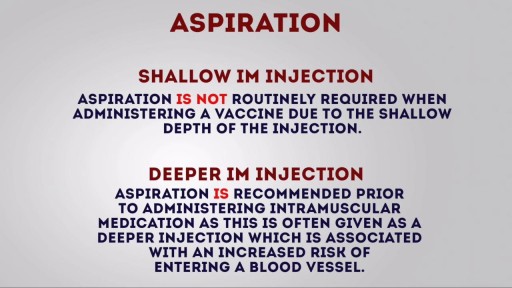
Top videos

***SUBSCRIBE WITHIN THE NEXT 28 DAYS FOR A CHANCE TO WIN $1,000!***
Did you know only 20% of our video content is on YouTube? Try out our membership for FREE today! → https://bit.ly/3mWibYe
Try our NCLEX Prep FREE → https://bit.ly/3xYAOkT
Head to https://bit.ly/3mWibYe to get access to the other 80%, along with 800+ study guides, customizable quiz banks with 3,000+ test-prep questions, and answer rationales!
Popular Playlists:
NCLEX Fluid & Electrolytes: https://bit.ly/39BSHXs
Heart Failure (CHF): https://bit.ly/2u5zfDm
Myocardial Infarction (MI): https://bit.ly/3bN9AAk
Addison’s vs. Cushing: https://bit.ly/2STvute
Diabetes Mellitus & DKA vs HHNS: https://bit.ly/37D8nbs
Cardiomyopathy: https://bit.ly/38CwcSg
IV Fluids: Hypertonic, Hypotonic & Isotonic: https://bit.ly/2P45BWx
SIADH vs Diabetes Insipidus: https://bit.ly/2wq6Bhb
Follow us on social media for more EXCLUSIVE content 👋
More Videos: https://bit.ly/37CRttH
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/simplenursing.com_
TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/simplenursing
Thank you for the support & for tuning in!
Remember… don’t be scared, BE PREPARED!
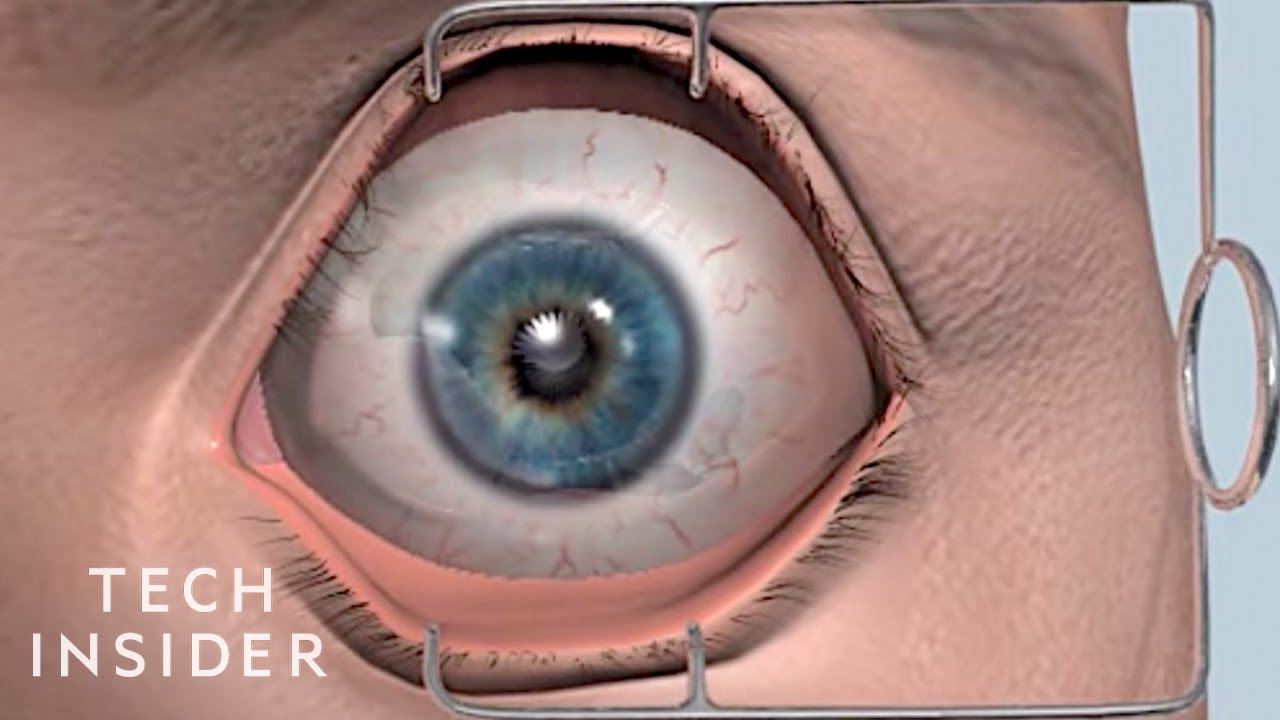
Medical technology continues to advance and help doctors continue to treat patients. From face transplants to LASIK eye surgery watch the video below for 8 medical procedures that are improving lives.
MORE MEDICAL CONTENT:
Meet The 24-Year-Old Whose Prosthetic Limbs Are Changing Lives
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E0dbagxeMT0
Lifelike Medical Robot Actually Bleeds
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IjnhmcCQLsc
Medical Tourniquet Works Like A Zip Tie
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k9q27yVxPL8
------------------------------------------------------
#Medicine #Surgery #TechInsider
Tech Insider tells you all you need to know about tech: gadgets, how-to's, gaming, science, digital culture, and more.
Visit us at: https://www.businessinsider.com
TI on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/techinsider
TI on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/tech_insider/
TI on Twitter: https://twitter.com/techinsider
TI on Amazon Prime: http://read.bi/PrimeVideo
INSIDER on Snapchat: https://insder.co/2KJLtVo
------------------------------------------------------
8 Medical Procedures That Are Improving Lives

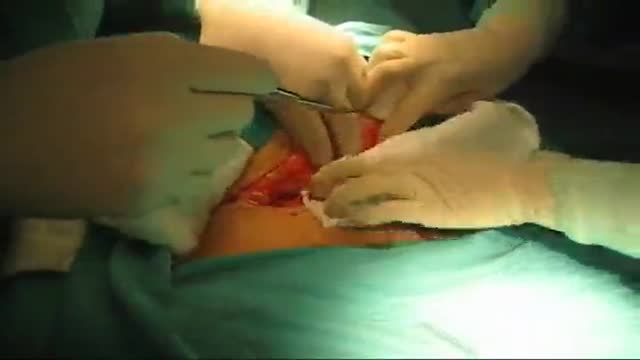
"Axillary Artery to Vein AV Graft for Dialysis Access"
Houston Methodist DeBakey Heart & Vascular Center, presents a cardiovascular procedure featuring Maham Rahimi, MD, M. Mujeeb Zubair, MD, and Louis Gomez, MD, as they demonstrate “Axillary Artery to Vein AV Graft for Dialysis Access".
Surgery: Maham Rahimi, MD, M. Mujeeb Zubair, MD, and Louis Gomez, MD
Narration: M. Mujeeb Zubair, MD
__________________________
FOR MORE INFORMATION
DeBakey CV Education: https://www.houstonmethodist.o....rg/education/medical
Follow Us:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/debakeycvedu
Twitter: https://twitter.com/DeBakeyCVedu
Livestream: https://livestream.com/debakey
Want concise, relevant reviews of the hottest topics in CV medicine? Subscribe for FREE to the Methodist DeBakey Cardiovascular Journal for quarterly, peer-reviewed issues delivered to your door.
https://journal.houstonmethodist.org/

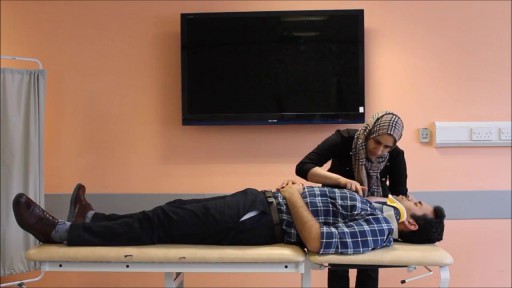
This particular video is intended as a demonstration of Neurologic Examination. This demonstration is intended as an example of a neurologic exam which may be used as part of the initial evaluation of patients with complaints that may have an underlying neurologic origin. This video is solely for educational purposes and intended for use to prepare for OSCEs incorporating standardized patient encounters. It is not intended as a demonstration of a comprehensive neurologic examination and is not intended as medical advice or medical guidelines.
It is not intended as a complete instructional video and should not be considered a source of complete physical examination instruction.
Instead, it should be treated as a supplement to independent learning using primary Osteopathic Clinical Skills instructional resources. Clinical skills are best learned and developed with support from faculty in the context of a complete Osteopathic Medical School Curriculum.
Osteopathic Clinical Skills is a channel dedicated to discussing and exploring Osteopathic Clinical Skills concepts for medical students, residents, and clinicians and presenting them in an easy to understand manner.
Attributions:
Many thanks to the University of North Texas Health Science Center Texas College of Osteopathic Medicine (UNTHSC - TCOM) for permitting use of the Simulation facilities and equipment during the production of this video.
Additional thanks to the UNTHSC-TCOM standardized patient and faculty volunteers who participated in this production and provided permission for the use of their image in this video.
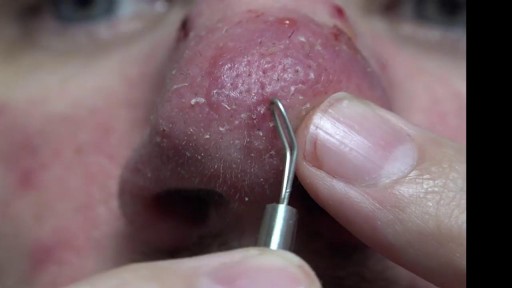
Cystic acne is a severe type of acne in which the pores in the skin become blocked, leading to infection and inflammation. The skin condition mainly affects the face, but also often affects the upper trunk and upper arms. Acne most often affects adolescents and young adults, with an estimated 80 percent of people between 11 and 30 years of age experiencing acne at some point. Cystic acne is the most severe form and affects far fewer people. In 2009, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that acne was the top reason people gave for visiting a dermatologist.

Ankle fusion (arthrodesis) This is a surgical procedure which joins together the main bones of the ankle joint (the tibia and the talus). However, depending on the technique your surgeon will use, occasionally the fibula will be included in this procedure. The two joint surfaces which generate the pain are removed.

The infection is generally transmitted by direct contact with the mucus or sores of someone else with strep. Common symptoms include sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck. Rarely, complications can involve the heart or kidneys. Treatment is important to reduce complications. Oral antibiotics like penicillin, amoxicillin, cephalexin, or azithromycin are commonly used. Other medicines such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help with pain and fever.