Top videos
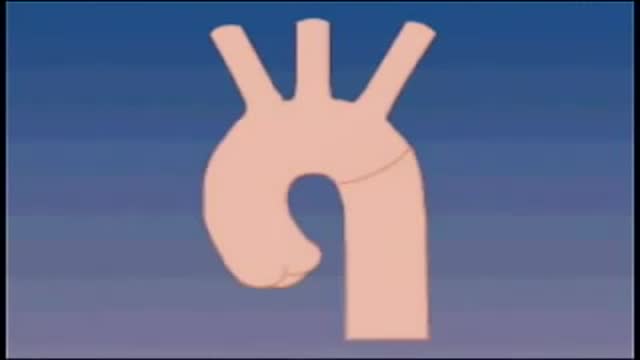
Although the exact cause of abdominal aortic aneurysms is unknown, a number of factors may play a role, including: Tobacco use. ... Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis). ... High blood pressure. ... Blood vessel diseases in the aorta. ... Infection in the aorta. ... Trauma. ... Heredity.
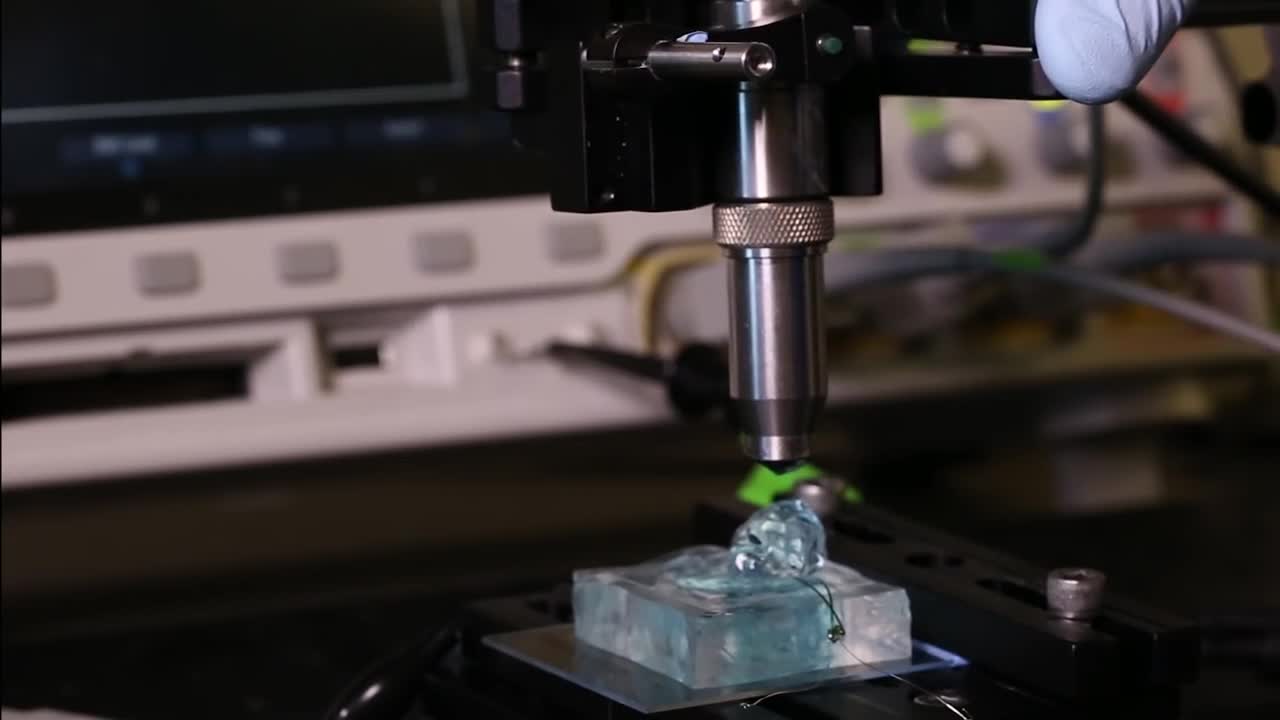

University of California, Berkeley engineers have built the first dust-sized, wireless sensors that can be implanted in the body, bringing closer the day when a Fitbit-like device could monitor internal nerves, muscles or organs in real time.

How To Stop Hair Loss Naturally, Hair Regrowth Shampoo, Tips For Hair Regrowth, Hair Loss Stop--- http://how-to-regrow-your-hair.info-pro.co/ --- Natural Hair Regrowth Treatment, Looking for ideas on natural hair regrowth treatment? There are actually a lot of safe and effective natural methods that you can try in order to reverse hair loss. So what are those natural methods? Here are some of them: Eat your way to better hair: Hard to believe isn’t it? To think that what you’re actually eating can affect your hair in so many ways, positively and negatively. Want to slow down the process of hair loss and get your hair back to the healthy original state you always remembered it in? Then you might want to start transitioning over to a low fat high fiber diet. Aside from this, you’ll also want to concentrate on foods that contain biotins, which play an essential role in maintaining healthy hair. Fish, cooked eggs, whole milk, and various nuts and fruits – all of these are good sources of biotins so it’s best that you take note of them. Drink plenty of water: It’s not only that gets thirsty, as even your hair requires the moisture that water provides. Dehydration can lead to symptoms like constipation, eczema, thick dandruff, wrinkly skin, foul breath and hair loss. Remember that your body is made up of 98% water and you need to maintain it at optimum levels if you want to keep your hair in place. An easy way to quickly replenish and establish enough water in your body is to routinely drink at least 8 ounces of water immediately after you urinate. You’ll know you’re getting enough water when you observe that you are urinating more frequently. Supplements: The fact that you are experiencing hair loss is a surefire indication that something is amiss in the nutrition department. If you are however looking for a definitive guide on the products that will be available, one useful source you can use will be found at http://how-to-regrow-your-hair.info-pro.co/

Hirschsprung's (HIRSH-sproongz) disease is a condition that affects the large intestine (colon) and causes problems with passing stool. The condition is present at birth (congenital) as a result of missing nerve cells in the muscles of the baby's colon. A newborn who has Hirschsprung's disease usually can't have a bowel movement in the days after birth. In mild cases, the condition might not be detected until later in childhood. Uncommonly, Hirschsprung's disease is first diagnosed in adults.
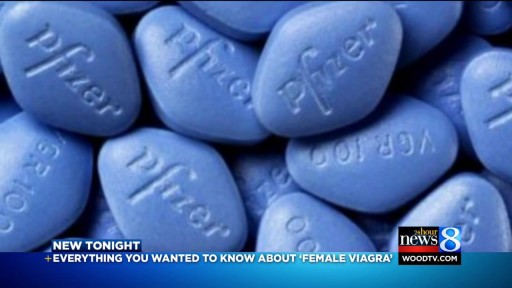
Given the success of drugs to treat erectile dysfunction, such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis) and vardenafil (Levitra), drug companies have sought a comparable drug for women. Viagra has even been tried as a treatment for sexual dysfunction in women. However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) hasn't approved this use of Viagra. Indeed, until recently there were no FDA-approved drugs for treating sexual arousal or sexual desire problems in women. Yet 4 in 10 women report having sexual concerns. A prescription medication known as flibanserin (Addyi) — originally developed as an antidepressant — has been approved by the FDA as a treatment for low sexual desire in premenopausal women. A daily pill, Addyi may boost sex drive in women with low sexual desire and who find the experience distressing. Potentially serious side effects include low blood pressure, dizziness and fainting, particularly if the drug is mixed with alcohol. Experts recommend that you stop taking the drug if you don't notice an improvement in your sex drive after eight weeks.

A young patient undergoes state of the art robotic surgery for Ovarian Cancer and Endometrial Cancer in Chicago, IL. The surgery is performed by noted gynecologic oncologist and expert robotic surgeon M. Patrick Lowe MD. Dr Lowe has been performing robotic surgery since 2006 and is one of a few gynecologic oncologist in the United States who utilizes robotics for ovarian cancer.