Top videos

There are four major blood groups determined by the presence or absence of two antigens – A and B – on the surface of red blood cells: Group A – has only the A antigen on red cells (and B antibody in the plasma) Group B – has only the B antigen on red cells (and A antibody in the plasma) Group AB – has both A and B antigens on red cells (but neither A nor B antibody in the plasma) Group O – has neither A nor B antigens on red cells (but both A and B antibody are in the plasma)
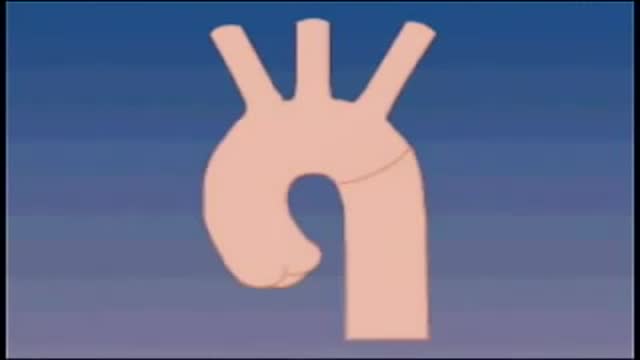
Although the exact cause of abdominal aortic aneurysms is unknown, a number of factors may play a role, including: Tobacco use. ... Hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis). ... High blood pressure. ... Blood vessel diseases in the aorta. ... Infection in the aorta. ... Trauma. ... Heredity.

This video demonstrates how to perform an abdominal examination in an OSCE station.
You can access our step-by-step OSCE guide to accompany this video here: https://geekymedics.com/abdominal-examination/
Check out our other awesome clinical skills resources including:
• 🔥 Geeky Medics Bundles (discounted products): https://app.geekymedics.com/purchase/bundles/
• ✨ 1000+ OSCE Stations: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/osce-stations
• 🏥 Geeky Medics OSCE Revision Book: https://app.geekymedics.com/purchase/book/
• 📝 150+ PDF OSCE Checklists: https://geekymedics.com/pdf-osce-checklists/
• 🗂️ 3000+ OSCE Flashcards: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/flashcard-col
• 📱 Geeky Medics OSCE App: https://geekymedics.com/geeky-medics-app/
• 🩺 Medical Finals SBA Question Pack: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/medical-stude
• 💊 PSA Question Pack: https://app.geekymedics.com/pu....rchase/prescribing-s
Chapters:
- Introduction 00:00
- General inspection 00:35
- Hands 00:47
- Asterixis 01:20
- Arms and axilla 01:32
- Face, eyes & mouth 01:45
- Lymph node palpation 02:19
- Chest inspection 02:50
- Inspection of abdomen 03:02
- Palpation of abdomen 03:34
- Percussion of abdomen 05:36
- Shifting dullness 06:30
- Auscultation of abdomen 06:55
- Summary 07:29
Subscribe to our newsletter to be the first to know about our latest content: https://geekymedics.com/newsletter/ ✉️
Join the Geeky Medics community: 👩👩👧👧
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/geekymedics
Instagram: https://instagram.com/geekymedics
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/geekymedics
Always adhere to your medical school/local hospital guidelines when performing examinations or clinical procedures. DO NOT perform any examination or procedure on patients based purely upon the content of these videos. Geeky Medics accepts no liability for loss of any kind incurred as a result of reliance upon the information provided in this video.
Some people have found this video useful for ASMR purposes.
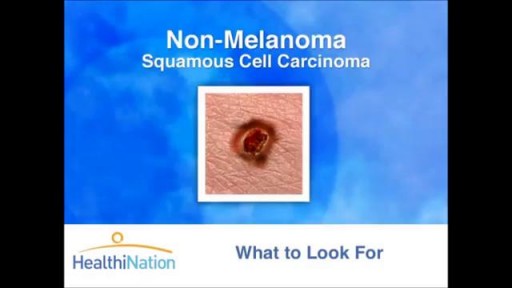
The Skin Cancer Foundation, founded in 1979 by dermatologist and Mohs surgeon Perry Robins, MD, is a global organization solely devoted to educating the public and medical community about skin cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment
Bone marrow biopsy and bone marrow aspiration are procedures to collect and examine bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside some of your larger bones. Bone marrow biopsy and aspiration can show whether your bone marrow is healthy and making normal amounts of blood cells. Doctors use these procedures to diagnose and monitor blood and marrow diseases, including some cancers, as well as fevers of unknown origin. Bone marrow has a fluid portion and a more solid portion. In bone marrow biopsy, your doctor uses a needle to withdraw a sample of the solid portion. In bone marrow aspiration, a needle is used to withdraw a sample of the fluid portion.

A young patient undergoes state of the art robotic surgery for Ovarian Cancer and Endometrial Cancer in Chicago, IL. The surgery is performed by noted gynecologic oncologist and expert robotic surgeon M. Patrick Lowe MD. Dr Lowe has been performing robotic surgery since 2006 and is one of a few gynecologic oncologist in the United States who utilizes robotics for ovarian cancer.

Most healthy children are inattentive, hyperactive or impulsive at one time or another. It’s normal for preschoolers to have short attention spans and be unable to stick with one activity for long. Even in older children and teenagers, attention span often depends on the level of interest. The same is true of hyperactivity. Young children are naturally energetic — they often are still full of energy long after they’ve worn their parents out. In addition, some children just naturally have a higher activity level than others do. Children should never be classified as having ADHD just because they’re different from their friends or siblings. Children who have problems in school but get along well at home or with friends are likely struggling with something other than ADHD. The same is true of children who are hyperactive or inattentive at home, but whose schoolwork and friendships remain unaffected.

Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer. There are three major types of skin cancer — Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma and melanoma. Out of these, Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. Melanoma appears on the skin as a new spot or growth or a change in an already existing mole. It is often fast growing and can spread to other parts of your body, including your bones, liver, and lungs to form a new cancer.