Top videos

New Minimally Invasive Procedure with No Pain or Downtime… From Dr. Michael Goodman, Caring For Women Wellness Center Laser Vaginal Tightening for Improved Sexual Pleasure and Relief from Minimal Urinary Incontinence Laser Vaginal Therapy for reversing Vaginal Atrophy (Good also for Breast Cancer Survivors with Vaginal Atrophy)

Hodgkin lymphoma has characteristics that distinguish it from other diseases classified as lymphoma, including the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells. These are large, cancerous cells found in Hodgkin lymphoma tissues, named for the scientists who first identified them. Hodgkin lymphoma is one of the most curable forms of cancer. NHL represents a diverse group of diseases distinguished by the characteristics of the cancer cells associated with each disease type. Most people with NHL have a B-cell type of NHL (about 85 percent). The others have a T-cell type or an NK-cell type of lymphoma. Some patients with fast-growing NHL can be cured. For patients with slow-growing NHL, treatment may keep the disease in check for many years.

To get started, you need to find your pelvic floor muscles by stopping urination in midstream. If you succeed, you have located the right muscles. Once you have located your pelvic floor muscles, tighten the contraction for about 5 seconds, before relaxing for another 5 seconds.
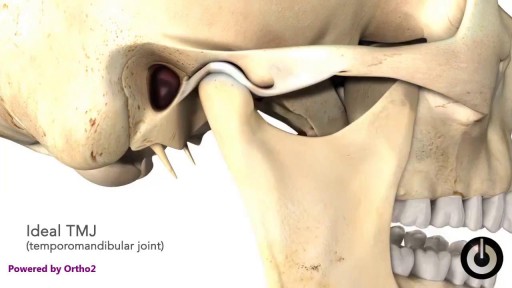
What Causes TMD? We don’t know what causes TMD. Dentists believe symptoms arise from problems with the muscles of your jaw or with the parts of the joint itself. Injury to your jaw, the joint, or the muscles of your head and neck -- like from a heavy blow or whiplash -- can lead to TMD. Other causes include: Grinding or clenching your teeth, which puts a lot of pressure on the joint Movement of the soft cushion or disc between the ball and socket of the joint Arthritis in the joint Stress, which can cause you to tighten facial and jaw muscles or clench the teeth

The surgical procedure uses your own fat, so it is the most natural way to augment your buttocks. Over the last few years, the buttocks have received more press coverage than ever before. People of all ages and body types are having the Brazilian Butt Lift procedure.
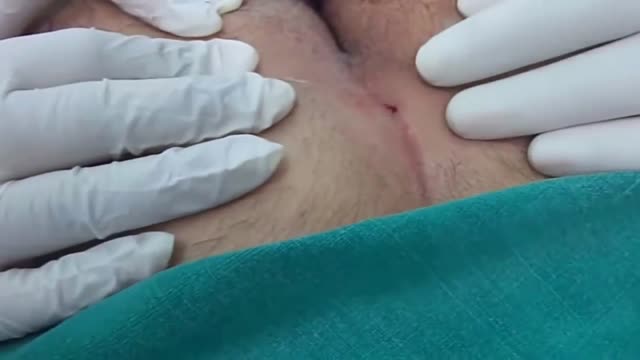
A pilonidal sinus (PNS) is a small cyst or abscess that occurs in the cleft at the top of the buttocks. A PNS usually contains hair, dirt, and debris. It can cause severe pain and can often become infected. If it becomes infected, it may ooze pus and blood and have a foul odor. A PNS is a condition that mostly affects men and is also common in young adults. It’s also more common in people who sit a lot, like cab drivers.

If you’re like me, you probably hook your chest tube up to a Pleur-Evac, put it on the ground, then back away slowly. Who knows what goes on in that mysterious bubbling white box? Hopefully this will post shed some light. Isn’t this just a container for stuff that comes out of the chest? Why does it look so complicated? It’s complicated because the detection/collection of air and fluid require different setups. Most commercial models also allow you to hook the drainage system to wall suction, so you can quickly evacuate the pleural space. This requires its own setup. Because of the need to juggle air, fluid and suction, the most common commercial system includes 3 distinct chambers. If you were to simplify the device, or build one out of spare bottles and tubes, it might look like this: