Top videos
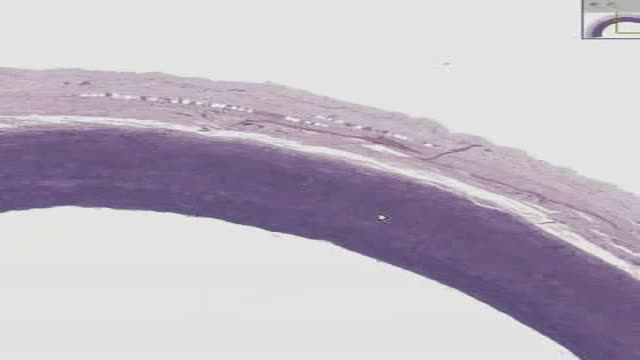
Sclerotherapy is a medical procedure used to eliminate varicose veins and veins. Sclerotherapy involves an injection of a solution (generally a salt solution) directly into the vein. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel, causing it to collapse and stick together and the blood to clot.

The surgical procedure uses your own fat, so it is the most natural way to augment your buttocks. Over the last few years, the buttocks have received more press coverage than ever before. People of all ages and body types are having the Brazilian Butt Lift procedure.
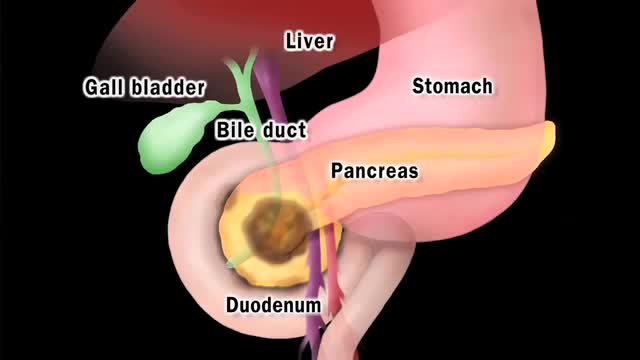
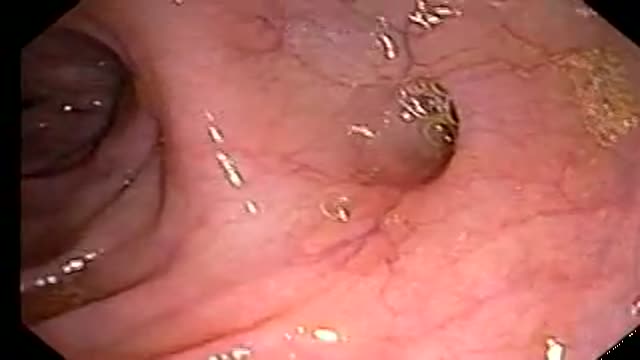
Pancreatic cancer begins in the tissues of your pancreas — an organ in your abdomen that lies horizontally behind the lower part of your stomach. Your pancreas secretes enzymes that aid digestion and hormones that help regulate the metabolism of sugars. Pancreatic cancer often has a poor prognosis, even when diagnosed early. Pancreatic cancer typically spreads rapidly and is seldom detected in its early stages, which is a major reason why it's a leading cause of cancer death. Signs and symptoms may not appear until pancreatic cancer is quite advanced and complete surgical removal isn't possible.

Start in RLQ (so you don’t miss a giant spleen). Get your fingers set then ask patient to take a deep breath. Don’t dip your fingers or do anything but wait. When patient expires, take up new position. Note lowest point of spleen below costal margin, texture of splenic contour, and tenderness If spleen is not felt, repeat with pt lying on right side. Gravity may bring spleen within reach. “LET THE SPLEEN PALPATE YOUR FINGERS AND NOT THE OTHER WAY AROUND. THERE IS NO GOLD, SO DON’T DIG!”
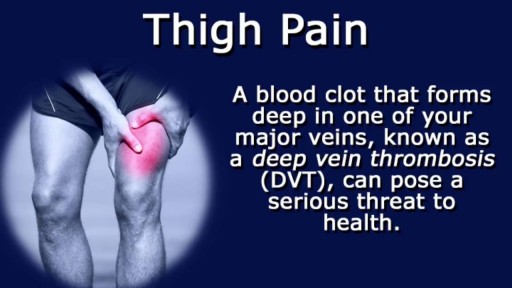
Thigh pain is most often caused by injuries to bones, joints, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other soft tissues or blood vessels. These injuries are often caused during sports competition, or strain from overuse, obesity, or pregnancy.
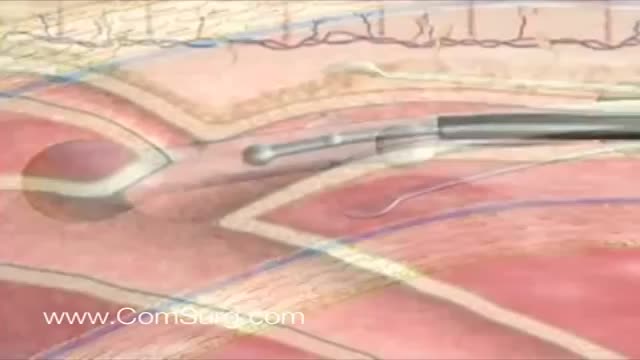
Like the VenaCure EVLT® procedure, which uses a laser to ablate the varicose vein, VNUS RF treatment is an alternative to more invasive leg stripping surgery. It is used primarily to treat the great saphenous veins (GSV), small saphenous vein (SSV), and other superficial veins in the legs.
Most babies will move into delivery position a few weeks prior to birth, with the head moving closer to the birth canal. When this fails to happen, the baby’s buttocks and/or feet will be positioned to be delivered first. This is referred to as “breech presentation.” Breech births occur in approximately 1 out of 25 full-term births.
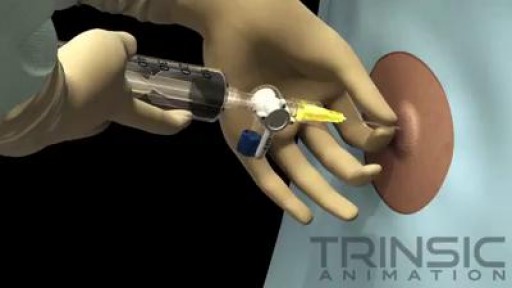
Thoracentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the pleural space between the lungs and the chest wall. This procedure is done to remove excess fluid, known as a pleural effusion, from the pleural space to help you breathe easier. It may be done to determine the cause of your pleural effusion. Some conditions such as heart failure, lung infections, and tumors can cause pleural effusions.

Cluster headaches, which occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, are one of the most painful types of headache. A cluster headache commonly awakens you in the middle of the night with intense pain in or around one eye on one side of your head. Bouts of frequent attacks, known as cluster periods, can last from weeks to months, usually followed by remission periods when the headaches stop. During remission, no headaches occur for months and sometimes even years. Fortunately, cluster headache is rare and not life-threatening. Treatments can make cluster headache attacks shorter and less severe. In addition, medications can reduce the number of cluster headaches.