Top videos
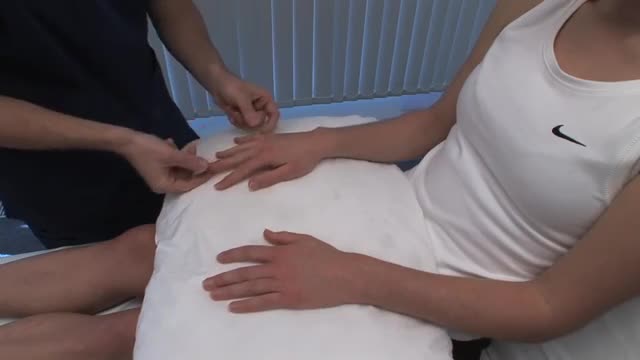
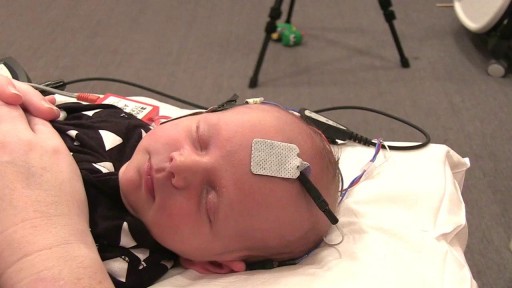
Bone marrow biopsy and bone marrow aspiration are procedures to collect and examine bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside some of your larger bones. Bone marrow biopsy and aspiration can show whether your bone marrow is healthy and making normal amounts of blood cells. Doctors use these procedures to diagnose and monitor blood and marrow diseases, including some cancers, as well as fevers of unknown origin. Bone marrow has a fluid portion and a more solid portion. In bone marrow biopsy, your doctor uses a needle to withdraw a sample of the solid portion. In bone marrow aspiration, a needle is used to withdraw a sample of the fluid portion.

Hodgkin lymphoma has characteristics that distinguish it from other diseases classified as lymphoma, including the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells. These are large, cancerous cells found in Hodgkin lymphoma tissues, named for the scientists who first identified them. Hodgkin lymphoma is one of the most curable forms of cancer. NHL represents a diverse group of diseases distinguished by the characteristics of the cancer cells associated with each disease type. Most people with NHL have a B-cell type of NHL (about 85 percent). The others have a T-cell type or an NK-cell type of lymphoma. Some patients with fast-growing NHL can be cured. For patients with slow-growing NHL, treatment may keep the disease in check for many years.

Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the tissue deep in your lungs becomes scarred over time. This tissue gets thick and stiff. That makes it hard for you to catch your breath, and your blood may not get enough oxygen. Causes of pulmonary fibrosis include environmental pollutants, some medicines, some connective tissue diseases, and interstitial lung disease. Interstitial lung disease is the name for a large group of diseases that inflame or scar the lungs. In most cases, the cause cannot be found. This is called idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
James Burke Fine DMD by James Burke Fine DMD Periodontal disease is a gum condition caused by the buildup of bacteria along and below the teeth's gumline. Acute forms are usually associated with pain from oral tissue gone bad – also known as necrotizing gingivitis or trench mouth – whereas chronic forms are painless but have a more long-term impact on your overall, systemic health. The most common chronic form is gingivitis, whose bleeding, puffiness and redness comes from an organized mass of bacteria called plaque. You may know it can advance into a form called periodontitis. If these conditions are left untreated, however, it can also lead to infections within other parts of the body, such as the lungs.

New Minimally Invasive Procedure with No Pain or Downtime… From Dr. Michael Goodman, Caring For Women Wellness Center Laser Vaginal Tightening for Improved Sexual Pleasure and Relief from Minimal Urinary Incontinence Laser Vaginal Therapy for reversing Vaginal Atrophy (Good also for Breast Cancer Survivors with Vaginal Atrophy)

How to improve your eyesight at home? Exercising your eyes is one of those simple things that very few people do. However, it can help you maintain excellent vision. Here are 10 exercises that will take you no more than ten minutes to do. You can give them a try right now while watching this video – we are going to do all of them with you! Exercise #1. Blink for a minute. Exercise #2. Rotate your head while staring ahead. Exercise #3. Look to your right and left. Exercise #4. Close your eyes and relax. Exercise #5. Move your gaze in different directions. Exercise #6. Close and open your eyes. Exercise #7. Push against your temples with your fingers. Exercise #8. Draw geometric figures with your gaze. Exercise #9. Move your eyeballs up and down. Exercise #10. Strengthen your eyes’ near and far focusing.
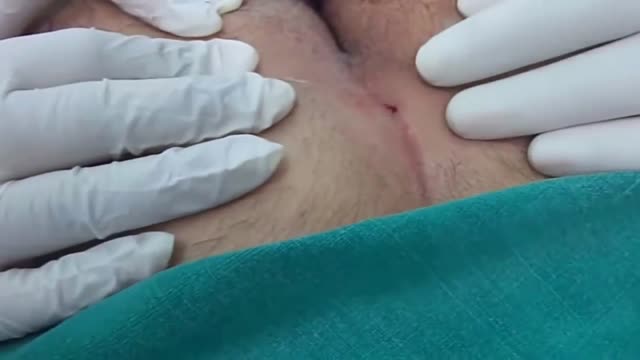
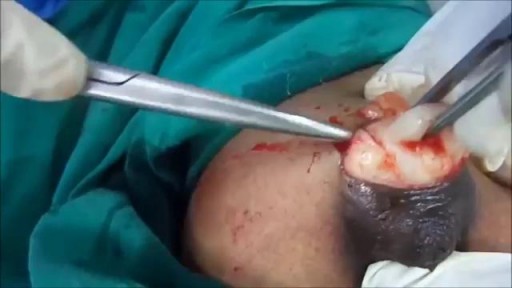
A pilonidal sinus (PNS) is a small cyst or abscess that occurs in the cleft at the top of the buttocks. A PNS usually contains hair, dirt, and debris. It can cause severe pain and can often become infected. If it becomes infected, it may ooze pus and blood and have a foul odor. A PNS is a condition that mostly affects men and is also common in young adults. It’s also more common in people who sit a lot, like cab drivers.
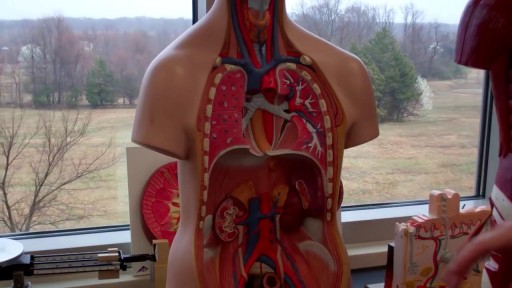
The digestive system is a group of organs working together to convert food into energy and basic nutrients to feed the entire body. Food passes through a long tube inside the body known as the alimentary canal or the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract).
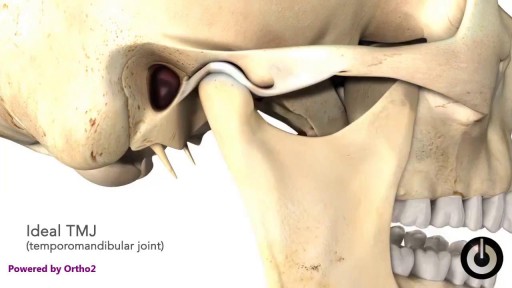
What Causes TMD? We don’t know what causes TMD. Dentists believe symptoms arise from problems with the muscles of your jaw or with the parts of the joint itself. Injury to your jaw, the joint, or the muscles of your head and neck -- like from a heavy blow or whiplash -- can lead to TMD. Other causes include: Grinding or clenching your teeth, which puts a lot of pressure on the joint Movement of the soft cushion or disc between the ball and socket of the joint Arthritis in the joint Stress, which can cause you to tighten facial and jaw muscles or clench the teeth
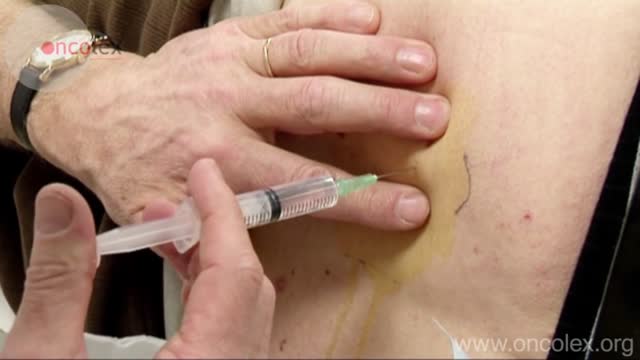
Sclerotherapy is a medical procedure used to eliminate varicose veins and veins. Sclerotherapy involves an injection of a solution (generally a salt solution) directly into the vein. The solution irritates the lining of the blood vessel, causing it to collapse and stick together and the blood to clot.

The surgical procedure uses your own fat, so it is the most natural way to augment your buttocks. Over the last few years, the buttocks have received more press coverage than ever before. People of all ages and body types are having the Brazilian Butt Lift procedure.