Top videos
Occiput or cephalic — the baby's head is down, and the baby is facing the mother's abdomen. This position results in back pain and a prolonged labor. Transverse — the baby is lying crosswise in the uterus, side-to-side over the mother's pelvis, in a horizontal position rather than vertical.

What goes into providing anesthesia for cardiac surgery where a patient's heart is completely arrested? In this video, I take you into the operating room during a surgery and talk with Dr. Benji Salter, program director for Mt. Sinai Hospital's cardiothoracic anesthesiology fellowship program.
While no patient information is shown in this video, the patient did provide written consent for filming to occur during surgery. Permission was also obtained from Mount Sinai Hospital's Department of Anesthesiology as well as the hospital's Press Office.
Chapters
0:00 Start
0:44 Surgery background
1:40 Case preparation
2:45 Anesthesia equipment
6:21 Echocardiography
7:16 Preparing for bypass
8:34 Stopping the heart
9:06 Fellowship
10:46 Why cardiac anesthesia?
11:52 Coming off of bypass
13:06 Post-op recovery
The information in this video is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. All content, including text, graphics, images, and information, contained in this video is for general information purposes only and does not replace a consultation with your own doctor/health professional.
#Anesthesiology #Residency #MedicalSchool
soaking the wound in cool water for five minutes or longer. taking acetaminophen or ibuprofen for pain relief. applying lidocaine (an anesthetic) with aloe vera gel or cream to soothe the skin. using an antibiotic ointment and loose gauze to protect the affected area.

Mommy Makeover plastic surgery in NYC and is a fairly new phenomena. This video, from 5thavenue surgery; http://www.5thavesurgery.com, goes through a case study of a patient getting plastic surgery in NYC. Check out what a Mommy Makeover can do for your body and what Plastic Surgery can do for you.

If you’re wondering ‘what’s the cause of my knee pain?’ or ‘what kind of knee pain do I have?’ the position of your knee pain can often tell you what type of knee pain you have.
You confirm this if you know the common symptoms an aggravations for each type of knee problem. So if you want to know ‘why my knee hurts’... here’s a quick look at the most common type of knee problems...
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (Or Runner’s Knee) (Old Name: Chondromalacia Patellae)
Infrapatellar Fat Pad Syndrome (Hoffa's Syndrome)
Patella Tendonitis (Jumper’s Knee)
Prepatellar Bursitis
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Meniscus Tear
Medial Collateral Ligament Tear
Osteoarthritic Knee Pain
Pes Anserine Bursitis.
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
Quadriceps Tendinopathy
Popliteus Strain
Baker’s Cyst
ACL Or PCL Tear/Rupture
---------------------------------------
Check out my channel...
https://youtube.com/@BodyFixExercises
OTHER VIDEOS:
How To Fix Pain In The Front Of The Knee… (Runner's Knee) https://youtu.be/g0qmx_0enAA
Knee Strengthening Exercises To Prevent Knee Pain
https://youtu.be/Pk-ae_lyx7M
How To Treat Patellar Tendinopathy (Jumper’s Knee) & Quadriceps Tendinopathy
https://youtu.be/MkPwsb-rQwU
---------------------------------------
#bodyfixexercises #kneepainrelief #kneepain

Warning: This video contains actual surgical footage, which may not be suitable for all viewers.
To learn more about coronary artery bypass surgery, please visit http://cle.clinic/3b7dqpE
Cardiothoracic surgeon Faisal Bakaeen, MD, discusses how he does single and bilateral internal mammary arteries, and the benefits of doing this type of coronary artery bypass.
If you liked the video hit like and subscribe for more!

Although it demands an advanced set of skills that remain substantially hard to do, many of the salient steps of “open” surgery, including suturing, are credibly “replicated” in its laparoscopic counterpart with the intention of achieving similar optimal results. This video demonstrates how to tie Laparoscopic Roeder's Knot. Laparoscopic Roeder's Knot is one of the oldest knots used in laparoscopic surgery. It is used most commonly during laparoscopic appendectomy surgery. Recent literature, though abundant with numerous reports pertaining to a variety of endoscopic knotting techniques and technologies, appears to lack scientific data but Roeder's knot is a time tasted extracorporeal slip knot that is secure for 6-8 mm diameter tubular structure.
For more information please contact:
World Laparoscopy Hospital
Cyber City, Gurugram, NCR DELHI
INDIA 122002
Phone & WhatsApp: +919811416838, + 91 9999677788
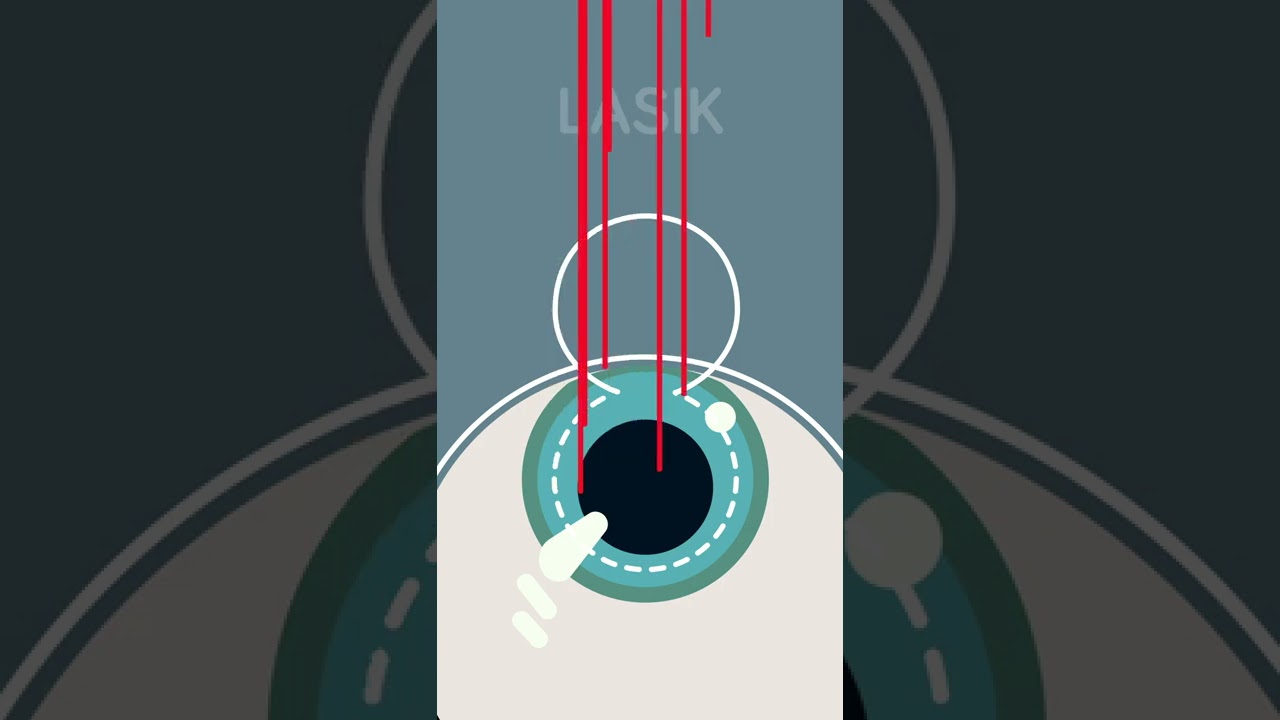
Ever considered getting laser eye surgery, but didn’t know how it worked? Allow us to help!
There are three different main types of laser eye surgery: LASIK, SMILE, and Surface Laser Treatments, and each can be explained pretty easily.
LASIK uses two lasers to open up a thin flap on the surface of the cornea, and then reshapes the cornea underneath. The flap is then placed back over the reshaped cornea, and heals independently with time.
SMILE uses one laser to reshape the cornea through a small, self-healing hole.
And Surface Eye Treatments remove the clear skin over the eye, to then reshape the cornea underneath with - you guessed it - a laser!

26 years old man lost his right hand thumb and index fingers with an industrial machine.the thumb amputated part was not found. the thumb is much more important of any other finger in the hand and should be reconstructed by any means. so the index amputated part was filleted and replanted over the thumb stump. the video is taken 1 year after replantation. You can see another videos in my site: https://drliaghatclinic.com, https://instagram.com/liaghatclinic, https://t.me/liaghatclinic
The E.coli bacteria has claimed 14 lives and infected more than 300 hundred in the country. It has now spread to other European states.
Facing an increasing number of cases, German health authorities warned people to avoid eating raw cucumber, tomatoes and lettuce.
Reinhard Burger, President of Robert Koch Institute, said, "As for the present situation there is no reason to give the all-clear yet and it is possible the original source of the infection is still active and could lead to further infections."
The first cases of the EHEC outbreak were noticed in Northern Germany, but infections are now spreading across the country.
Cases haves spiked compared to other years, and are still rising.
Daniel Bahr, German Health Minister, said, "The result is that we unfortunately still have to prepare for a rising number of cases. Exercising caution is still recommended and we ask our citizens to be particularly careful. "
But, the German government says it's working around the clock to stop the outbreak and clarify how it arose.
Ilse Aigner, German Agriculture Minister, said, "Together, we face a big challenge to piece together hundreds or thousands of mosaic pieces from Germany and abroad into an overall picture that gives us a clear answer on how this terrible infection arose. "
In the meantime, experts are advising not to eat pre-packaged or prepared salad, which may contain the bacteria.
Renal replacement therapies are a set of interventions and techniques aimed at replacement of the filtering function of the kidneys. These include both dialysis and renal transplant. In this presentation we will talk about the indication and modalities of dialysis. This includes hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis and continuous renal replacement therapies. The circuit diagram of each modalities along with its procedure and complications are also discussed.

New research from Mount Sinai Health System says these surgeries have limited effectiveness and can be economically unjustifiable when they're done on patients with less severe symptoms.
» Subscribe to NBC News: http://nbcnews.to/SubscribeToNBC
» Watch more NBC video: http://bit.ly/MoreNBCNews
NBC News is a leading source of global news and information. Here you will find clips from NBC Nightly News, Meet The Press, and original digital videos. Subscribe to our channel for news stories, technology, politics, health, entertainment, science, business, and exclusive NBC investigations.
Connect with NBC News Online!
Visit NBCNews.Com: http://nbcnews.to/ReadNBC
Find NBC News on Facebook: http://nbcnews.to/LikeNBC
Follow NBC News on Twitter: http://nbcnews.to/FollowNBC
Follow NBC News on Google+: http://nbcnews.to/PlusNBC
Follow NBC News on Instagram: http://nbcnews.to/InstaNBC
Follow NBC News on Pinterest: http://nbcnews.to/PinNBC
New Study Questions Effectiveness Of Knee Replacement Surgery | NBC Nightly News

Dr. Shaun Kunisaki is an Associate Professor of Surgery at The Johns Hopkins University and Associate Chief of Strategy and Integration in the Division of General Pediatric Surgery at the Johns Hopkins Children's Center. His clinical practice spans the full breadth of pediatric general surgery, but he is recognized both regionally and nationally for this expertise in complex thoracic surgical problems in the fetus and young child. As Director of Pediatric Esophageal Surgery, he specializes in the management of long-gap esophageal atresia. In this role within the Johns Hopkins Children Center Fetal Program, he helps counsel parents with pregnancies complicated by fetal anomalies.
Learn more about Dr. Kunisaki at https://www.hopkinsmedicine.or....g/profiles/results/d

Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer. There are three major types of skin cancer — Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma and melanoma. Out of these, Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. Melanoma appears on the skin as a new spot or growth or a change in an already existing mole. It is often fast growing and can spread to other parts of your body, including your bones, liver, and lungs to form a new cancer.