Top videos

Cluster headaches, which occur in cyclical patterns or clusters, are one of the most painful types of headache. A cluster headache commonly awakens you in the middle of the night with intense pain in or around one eye on one side of your head. Bouts of frequent attacks, known as cluster periods, can last from weeks to months, usually followed by remission periods when the headaches stop. During remission, no headaches occur for months and sometimes even years. Fortunately, cluster headache is rare and not life-threatening. Treatments can make cluster headache attacks shorter and less severe. In addition, medications can reduce the number of cluster headaches.

In this compilation, Barnsley Hospital is facing a very busy day with a high number of patients being treated, the doctors and nurses face some of their toughest shifts when they treat critical patients and rare illnesses as well as making tough decisions.
⌚️Timecodes:
00:00 Season 2 Episode 1
08:56 Season 4 Episode 1
16:53 Season 3 Episode 10
30:36 Season 3 Episode 13
37:45 Season 2 Episode 9
46:51 Season 1 Episode 2
52:52 Season 1 Episode 3
58:02 Season 2 Episode 2
01:09:39 Season 2 Episode 11
01:18:37 Season 2 episode 12
🟦 Click Link below to subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCHPgATT2HtFrxmueq
About Casualty 24/7:
Casualty 24/7 shows how the doors of Barnsley A&E department are open every hour, of every day. They allow a peek inside their medical emergency teams, and how they deal with critical situations revolving around people's lives and illnesses. The team are close-knit and exchange typical Yorkshire humour to get them through their often long and tough days.
Watch our playlists:
🔵 Season 1 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Season 2 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Season 3 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Season 4 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Compilation Videos of Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
#SeriousIllness #Casualty247 #EmergencyServices #AandE #BHNFT #OurFutureSouthYorkshire

Histology of all the different types of cartilage. This video is a part of our Histology Video Course (https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDynxT
All Histology Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDynxT
Thank you to our sponsor Doc2Doc Lending, the Personal Lending platform designed for Doctors, by Doctors. Check out https://doc2doclending.com/davinci to learn more today.
Additional YouTube Content
Biochemistry videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDzCUC
Anatomy Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDz2dK
DaVinci Cases Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDyJUl
The DaVinci Hour Podcast: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDwSm9
DaVinci Academy Website: https://www.dviacademy.com/

https://bit.ly/3HIStRc #shorts
Tracheotomy and tracheostomy are surgical procedures that create an opening in the trachea (windpipe) to help patients breathe when they have difficulty doing so through the nose or mouth. Though they are similar in purpose, there are some key differences between them.
Tracheotomy is a temporary procedure that involves creating a small incision in the trachea to insert a breathing tube. The tube is typically removed once the patient no longer requires it, and the incision heals on its own. Tracheostomy, on the other hand, is a more permanent solution that involves creating a hole in the trachea and inserting a tracheostomy tube, which remains in place for an extended period.
Indications for these procedures include:
Airway obstruction due to trauma, tumors, or infection
Severe respiratory distress or failure
Prolonged mechanical ventilation
Inability to protect the airway due to neurological disorders or impaired consciousness
Steps for performing a tracheotomy and tracheostomy:
Preparation: The patient is positioned, and the neck area is cleaned and draped. Local anesthesia is often administered, although general anesthesia may be used in some cases.
Incision: A small incision is made in the neck, and the muscles and tissues are carefully separated to expose the trachea.
Tracheal opening: A small opening is made in the trachea, typically between the second and third tracheal rings.
Tube insertion: A tracheotomy tube is inserted through the incision and into the trachea for a tracheotomy, while a tracheostomy tube is inserted for a tracheostomy. Both tubes are secured in place.
Confirmation: Proper placement of the tube is confirmed by listening for breath sounds and checking for adequate ventilation.
Pre-operative care typically involves a thorough assessment of the patient's medical history, as well as any necessary imaging studies or lab tests to ensure the procedure is appropriate and safe. Informed consent should be obtained from the patient or their legal representative.
Post-operative care includes monitoring the patient's vital signs, ensuring the tube remains secure and patent, and managing any pain or discomfort. For tracheostomy patients, regular cleaning and maintenance of the stoma (the opening in the trachea) and the tracheostomy tube are essential to prevent infection and other complications. Long-term care may involve speech therapy, respiratory therapy, and support from a multidisciplinary team to address any ongoing needs.
It's crucial to remember that these procedures should only be performed by trained medical professionals in a clinical setting.
for additional information about this procedure check our article @ www.medicalartsshop.com
For more free resources, find us on Pinterest & Facebook pages:
https://www.pinterest.ca/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.facebook.com/Medicalartsofficial
https://www.youtube.com/@medic....alarts?sub_confirmat
https://www.instagram.com/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.tiktok.com/@medicalarts
This video and associated content are for entertainment and educational purposes only!!
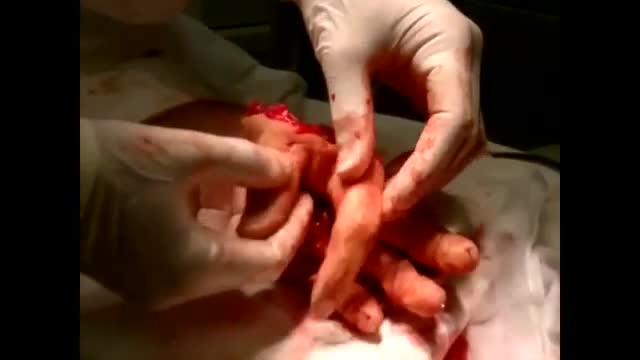
Since the first replant more than 50 years ago, thousands of severed body parts have been reattached, preserving the quality of life for thousands of patients through improved function and appearance that the void remaining after amputation cannot provide. Ronald Malt performed the first replantation on May 23, 1962 at Massachusetts General Hospital on a 12-year-old boy who had his right arm amputated in a train accident. [1, 2] This amputation occurred at the level of the humeral neck.

Brachytherapy or localized radiation treatment can be used in certain patients with breast cancer. Depending on tumor size and other factor, physicians may use APBI or accelerated partial breast irradiation. Dr. Elizabeth Tapen, a radiation oncologist, reviews brachytherapy for breast cancer.

Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment that involves placing sperm inside a woman's uterus to facilitate fertilization. The goal of IUI is to increase the number of sperm that reach the fallopian tubes and subsequently increase the chance of fertilization
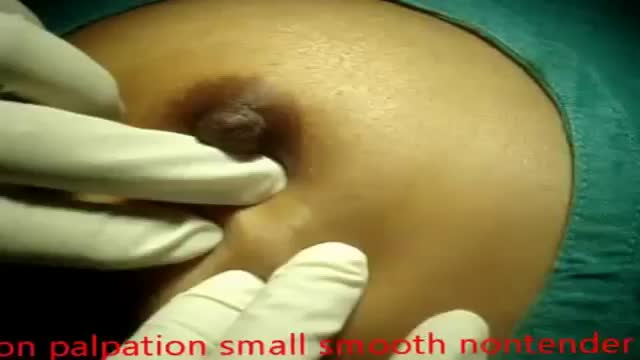
Fibroadenomas (fy-broe-ad-uh-NO-muhz) are solid, noncancerous breast tumors that occur most often in adolescent girls and women under the age of 30. You might describe a fibroadenoma as firm, smooth, rubbery or hard with a well-defined shape. Usually painless, a fibroadenoma might feel like a marble in your breast, moving easily under your skin when touched. Fibroadenomas vary in size, and they can get bigger or even shrink on their own. Fibroadenomas are among the most common breast lumps in young women. Treatment may include monitoring to detect changes in the size or feel of the fibroadenoma, a biopsy to evaluate the lump, or surgery to remove it.

An animation of blood flow inside the hollow fiber of a hemofilter, or a dialyzer, and the flow of the dialysate in an opposite direction with increased extraction of waste and small molecules from the blood as the concentration of these molecules is reduced downstream and exposed to new dialysate.
To learn about Hemodialysis..
https://www.thevirtualnephrolo....gist.com/specialties
The Virtual Nephrologist is your gateway to optimal health.
To learn more about Hypertension, Kidney Disease and Dialysis:
https://thevirtualnephrologist.com/
About Dr. Rifai:
Dr. Ahmad Oussama Rifai is certified by the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) in the specialty of Internal Medicine and the sub-specialty of Nephrology.
MEET DR. RIFAI
https://www.thevirtualnephrologist.com/rifai/
Follow The Virtual Nephrologist on SOCIAL MEDIA:
-Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/thevirtualnephrologist
-Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/thevirtualnephrologist/
-Twitter: https://twitter.com/VNephrologist
-TikTok: https://www.tiktok.com/@thevirtualnephrologist
Schedule a virtual consult:
https://www.thevirtualnephrolo....gist.com/schedule-a-
Best wishes for great health | The Virtual Nephrologist
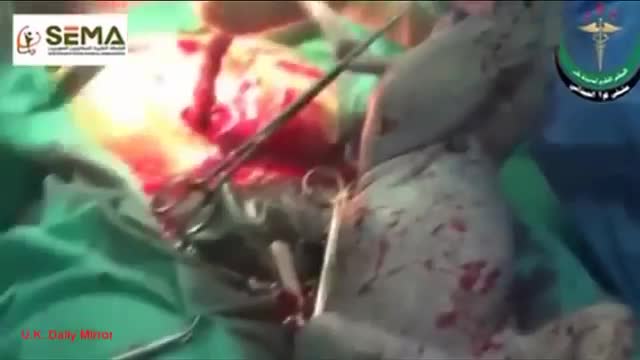
Doctors save the life of an unborn baby who was injured along with her mother in a missile attack in the Syrian city of Aleppo. The video shows a team of emergency medical workers delivering the baby by Cesarean section and then treating the newborn for the shrapnel wounds covering her body and one very large gash in her head. “Medics can be seen frantically reviving the baby, after delivering her by emergency cesarean, as she lies motionless,” the article states. “Eventually the tiny newborn begins to cry and seemingly comes to life as she is given an oxygen mask and rubbed vigorously.” “According to Reuters, the woman also has three other children, all of whom were injured in the attack, but are reported by doctors in the hospital to be in a good condition,” the Daily Mirror article states. The article does not provide the gestational age of the baby before it was delivered. The article said the pregnant woman was hit by a barrel bomb – “crude explosives and shrapnel and dropped from helicopters used by [Syrian] President Bashir al-Assad’s regime." The article notes an estimated 7.6 million Syrians have been displaced by the ongoing civil war and that 320,000, including 11,000 children, have been killed in the conflict. The Daily Mirror also reports that the doctors suggested that the tiny girl be named Amal, which means hope in Arabic. UK Daily Mirror: Incredible footage shows Syrian doctors perform lifesaving caesarean after missile strike leaves shrapnel embedded in unborn baby's face