Top videos

The cause for TS is unknown. Early research suggested that TS is an inherited condition (often, the person's near or distant relatives have had some form of transient or chronic tic disorder or associated symptoms). Recent studies point to a combination of environmental and genetic factors as a cause of the disorder. The specific genes involved in the development of TS are still being investigated. Studies suggest that TS has a neurological basis and results from an abnormality which affects the brain's metabolism of certain neurotransmitters (chemicals in the brain that regulate behavior.) Current research being funded by the Tourette Syndrome Association (TSA) will help provide more information about the causes and genetic factors of TS.
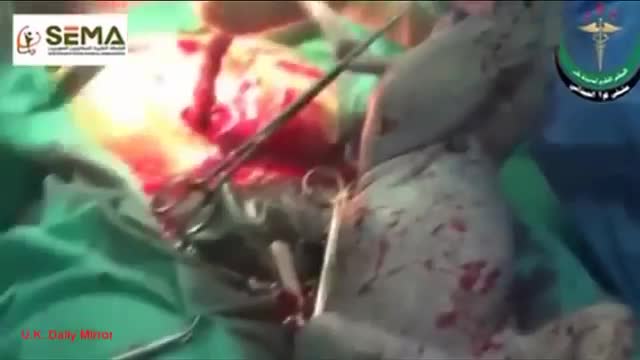
Doctors save the life of an unborn baby who was injured along with her mother in a missile attack in the Syrian city of Aleppo. The video shows a team of emergency medical workers delivering the baby by Cesarean section and then treating the newborn for the shrapnel wounds covering her body and one very large gash in her head. “Medics can be seen frantically reviving the baby, after delivering her by emergency cesarean, as she lies motionless,” the article states. “Eventually the tiny newborn begins to cry and seemingly comes to life as she is given an oxygen mask and rubbed vigorously.” “According to Reuters, the woman also has three other children, all of whom were injured in the attack, but are reported by doctors in the hospital to be in a good condition,” the Daily Mirror article states. The article does not provide the gestational age of the baby before it was delivered. The article said the pregnant woman was hit by a barrel bomb – “crude explosives and shrapnel and dropped from helicopters used by [Syrian] President Bashir al-Assad’s regime." The article notes an estimated 7.6 million Syrians have been displaced by the ongoing civil war and that 320,000, including 11,000 children, have been killed in the conflict. The Daily Mirror also reports that the doctors suggested that the tiny girl be named Amal, which means hope in Arabic. UK Daily Mirror: Incredible footage shows Syrian doctors perform lifesaving caesarean after missile strike leaves shrapnel embedded in unborn baby's face

When placement of a urethral catheter is contraindicated or unsuccessful, percutaneous suprapubic urinary bladder catheterization is a commonly performed procedure to relieve urinary retention. [1, 2] This topic describes the Catheter over needle technique. The Seldinger technique is described in the Clinical Procedures topic Suprapubic Aspiration.

https://bit.ly/3HIStRc #shorts
Tracheotomy and tracheostomy are surgical procedures that create an opening in the trachea (windpipe) to help patients breathe when they have difficulty doing so through the nose or mouth. Though they are similar in purpose, there are some key differences between them.
Tracheotomy is a temporary procedure that involves creating a small incision in the trachea to insert a breathing tube. The tube is typically removed once the patient no longer requires it, and the incision heals on its own. Tracheostomy, on the other hand, is a more permanent solution that involves creating a hole in the trachea and inserting a tracheostomy tube, which remains in place for an extended period.
Indications for these procedures include:
Airway obstruction due to trauma, tumors, or infection
Severe respiratory distress or failure
Prolonged mechanical ventilation
Inability to protect the airway due to neurological disorders or impaired consciousness
Steps for performing a tracheotomy and tracheostomy:
Preparation: The patient is positioned, and the neck area is cleaned and draped. Local anesthesia is often administered, although general anesthesia may be used in some cases.
Incision: A small incision is made in the neck, and the muscles and tissues are carefully separated to expose the trachea.
Tracheal opening: A small opening is made in the trachea, typically between the second and third tracheal rings.
Tube insertion: A tracheotomy tube is inserted through the incision and into the trachea for a tracheotomy, while a tracheostomy tube is inserted for a tracheostomy. Both tubes are secured in place.
Confirmation: Proper placement of the tube is confirmed by listening for breath sounds and checking for adequate ventilation.
Pre-operative care typically involves a thorough assessment of the patient's medical history, as well as any necessary imaging studies or lab tests to ensure the procedure is appropriate and safe. Informed consent should be obtained from the patient or their legal representative.
Post-operative care includes monitoring the patient's vital signs, ensuring the tube remains secure and patent, and managing any pain or discomfort. For tracheostomy patients, regular cleaning and maintenance of the stoma (the opening in the trachea) and the tracheostomy tube are essential to prevent infection and other complications. Long-term care may involve speech therapy, respiratory therapy, and support from a multidisciplinary team to address any ongoing needs.
It's crucial to remember that these procedures should only be performed by trained medical professionals in a clinical setting.
for additional information about this procedure check our article @ www.medicalartsshop.com
For more free resources, find us on Pinterest & Facebook pages:
https://www.pinterest.ca/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.facebook.com/Medicalartsofficial
https://www.youtube.com/@medic....alarts?sub_confirmat
https://www.instagram.com/medicalartsofficial/
https://www.tiktok.com/@medicalarts
This video and associated content are for entertainment and educational purposes only!!

Histology of all the different types of cartilage. This video is a part of our Histology Video Course (https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDynxT
All Histology Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDynxT
Thank you to our sponsor Doc2Doc Lending, the Personal Lending platform designed for Doctors, by Doctors. Check out https://doc2doclending.com/davinci to learn more today.
Additional YouTube Content
Biochemistry videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDzCUC
Anatomy Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDz2dK
DaVinci Cases Videos: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDyJUl
The DaVinci Hour Podcast: https://youtube.com/playlist?l....ist=PLnr1l7WuQdDwSm9
DaVinci Academy Website: https://www.dviacademy.com/
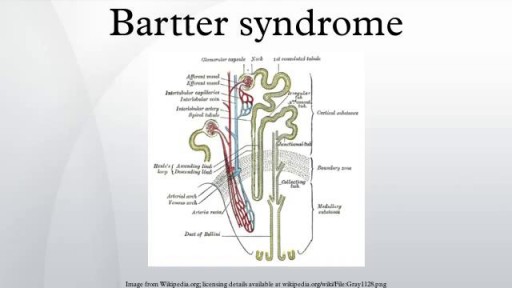
Bartter syndrome is a rare inherited defect in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. It is characterized by low potassium levels (hypokalemia), increased blood pH (alkalosis), and normal to low blood pressure. There are two types of Bartter syndrome: neonatal and classic

This 35 years old man lost his right wrist in metal lathe cut machine. the video is taken about 2 years after replantation. You can see another videos in my site: https://drliaghatclinic.com, https://instagram.com/liaghatclinic, https://t.me/liaghatclinic

In this compilation, Barnsley Hospital is facing a very busy day with a high number of patients being treated, the doctors and nurses face some of their toughest shifts when they treat critical patients and rare illnesses as well as making tough decisions.
⌚️Timecodes:
00:00 Season 2 Episode 1
08:56 Season 4 Episode 1
16:53 Season 3 Episode 10
30:36 Season 3 Episode 13
37:45 Season 2 Episode 9
46:51 Season 1 Episode 2
52:52 Season 1 Episode 3
58:02 Season 2 Episode 2
01:09:39 Season 2 Episode 11
01:18:37 Season 2 episode 12
🟦 Click Link below to subscribe: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UCHPgATT2HtFrxmueq
About Casualty 24/7:
Casualty 24/7 shows how the doors of Barnsley A&E department are open every hour, of every day. They allow a peek inside their medical emergency teams, and how they deal with critical situations revolving around people's lives and illnesses. The team are close-knit and exchange typical Yorkshire humour to get them through their often long and tough days.
Watch our playlists:
🔵 Season 1 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Season 2 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Season 3 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Season 4 Full Episodes | Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
🔵 Compilation Videos of Casualty 24/7:
https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLWrY8x74oDM
#SeriousIllness #Casualty247 #EmergencyServices #AandE #BHNFT #OurFutureSouthYorkshire

Detroit TV meteorologist Jessica Starr posted a heart-wrenching video on social media a month before dying by suicide this week. She had told viewers she was struggling in the aftermath of undergoing Lasik surgery. After learning of her death, her heartbroken colleagues on WJBK fought back tears live on TV. Twelve people have died by suicide after suffering pain and even blindness after the operation. Inside Edition also spoke to a doctor who wants the surgery banned. #InsideEdition

The discussion begins with a basic explanation of Bone biology taking into consideration the osteoblast and osteoclast balance. Concepts of RANK, RANK ligand and Osteoprotegerin are included. Risk factors for Osteoporosis such as Age, alcohol, smoking, sedentary lifestyle are also discussed.