Top videos

In as many as 80% of cases, doctors don’t find the exact reason for a curved spine. Scoliosis without a known cause is what doctors call “idiopathic.” Some kinds of scoliosis do have clear causes. Doctors divide those curves into two types -- structural and nonstructural. In nonstructural scoliosis, the spine works normally, but looks curved. Why does this happen? There are a number of reasons, such as one leg’s being longer than the other, muscle spasms, and inflammations like appendicitis. When these problems are treated, this type of scoliosis often goes away.
A stye (also called a hordeolum) is a small, red, painful lump that grows from the base of your eyelash or under the eyelid. Most styes are caused by a bacterial infection. There are two kinds of styes: External hordeolum: A stye that begins at the base of your eyelash. Most are caused by an infection in the hair follicle. It might look like a pimple. Internal hordeolum: A stye inside your eyelid. Most are caused by an infection in an oil-producing gland in your eyelid.

Peripheral artery disease (P.A.D.) is a disease in which plaque builds up in the arteries that carry blood to your head, organs, and limbs. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue, and other substances in the blood. When plaque builds up in the body's arteries, the condition is called atherosclerosis. Over time, plaque can harden and narrow the arteries. This limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your organs and other parts of your body. P.A.D. usually affects the arteries in the legs, but it also can affect the arteries that carry blood from your heart to your head, arms, kidneys, and stomach. This article focuses on P.A.D. that affects blood flow to the legs.

Orthopedic spine surgeons and vascular surgeons at UW Health in Madison, WI work together to perform minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion (Mini-ALIF). With this type of spinal fusion surgery, patients have smaller incisions, usually spend less time in the hospital and typically return to daily activities more quickly. Learn more https://www.uwhealth.org/ALIF
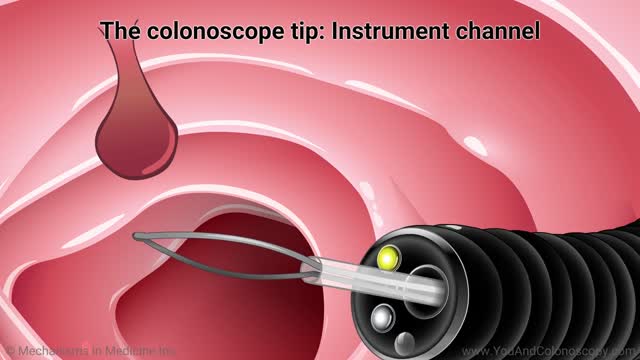
A colonoscope is the special tool used to perform a colonoscopy. It is a thin, flexible, tubular ‘telescope’ with a light and video camera that your doctor carefully guides through your colon in order to see and determine the health of your colon. Watch this animation to learn about the features of the colonoscope, how the colonoscopy procedure is performed and how polyps are removed, and the follow-up care you and your doctor should talk about after your procedure.
The major elements of the cardiac exam include observation, palpation and, most importantly, auscultation (percussion is omitted). As with all other areas of the physical exam, establishing adequate exposure and a quiet environment are critical. Initially, the patient should rest supine with the upper body elevated 30 to 45 degrees. Most exam tables have an adjustable top. If not, use 2 or 3 pillows. Remember that although assessment of pulse and blood pressure are discussed in the vital signs section they are actually important elements of the cardiac exam.
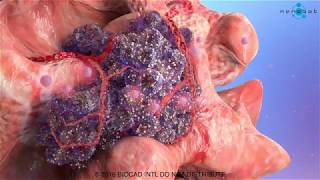
This cancer development medical video is devoted to elaborating the basics of cancer growth. We used advanced medical animation techniques to display such a complicated process.
What is happening in cancer development medical video
The fundamental abnormality described in the cancer development medical video is the nonstop unregulated multiplication of cancer cells. Being uncontrollable by body’s signals that regulate normal cell behavior; cancerous cells divide and grow populating neighboring normal tissues or even spread throughout the body. The overall lack of growth control acquired by cancer cells is due to the accumulated abnormalities in numerous cell regulatory mechanisms and is considered in some aspects of cell behavior that differs them from their healthy counterparts. The interaction of these cells is shown in our previous medical animation video.
Read full article on our webpage http://bit.ly/2LQj9ln
Follow us on Facebook https://www.facebook.com/Nanob....ot.Medical.Animation
Follow us on LinkedIn https://www.linkedin.com/compa....ny/nanobotmodels-med
Follow us on Twitter https://twitter.com/Nanobot_Studio
Follow us on Instagram https://www.instagram.com/nano....bot_medical_animatio
Follow us on Clutch https://clutch.co/profile/nano....bot-medical-animatio
Follow us on Behance https://www.behance.net/NanobotStudio
#cancer #tumor #oncology #metatastic #nanobot #visualscience #scientificcommunication #medicalanimation #animationvideo #animationdesign #animationstudio #animationmovie #nanotechnology #medicine #health #science #education #medschool #medicaleducation #animation_studio #animationstudio