Top videos

Peripheral artery disease (P.A.D.) is a disease in which plaque builds up in the arteries that carry blood to your head, organs, and limbs. Plaque is made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium, fibrous tissue, and other substances in the blood. When plaque builds up in the body's arteries, the condition is called atherosclerosis. Over time, plaque can harden and narrow the arteries. This limits the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your organs and other parts of your body. P.A.D. usually affects the arteries in the legs, but it also can affect the arteries that carry blood from your heart to your head, arms, kidneys, and stomach. This article focuses on P.A.D. that affects blood flow to the legs.
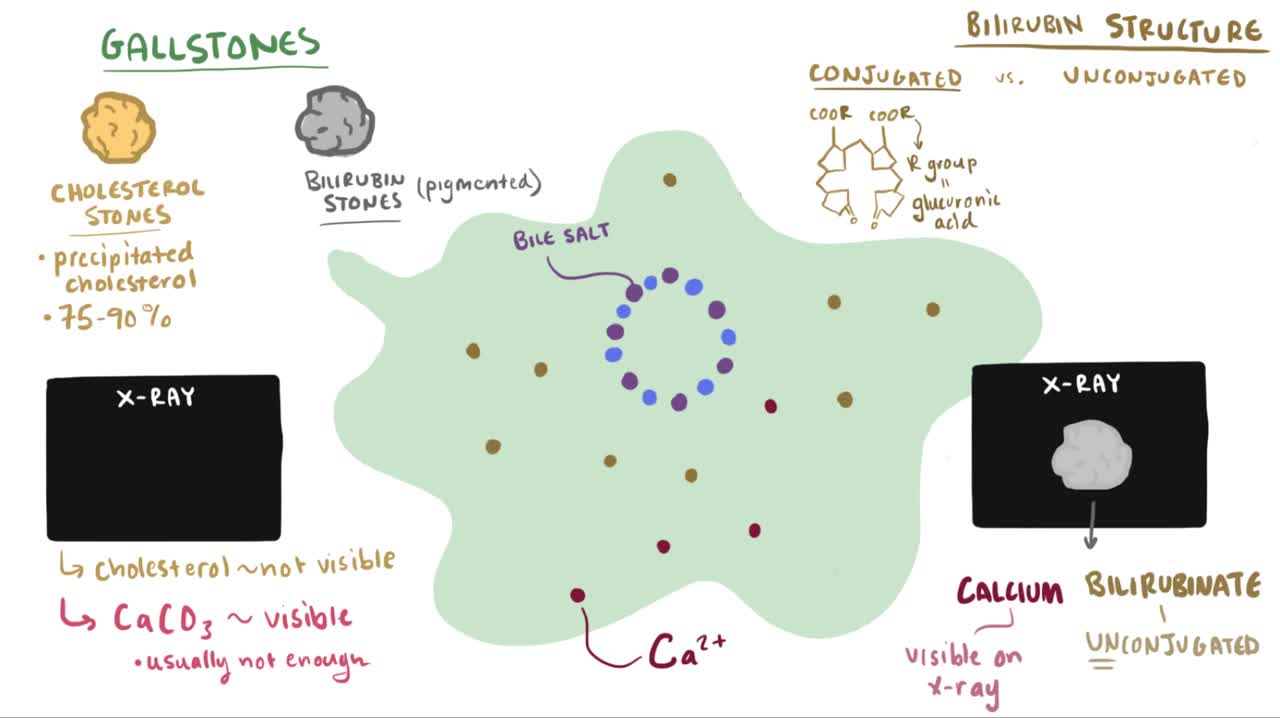
Cholelithiasis involves the presence of gallstones (see the image below), which are concretions that form in the biliary tract, usually in the gallbladder. Choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of 1 or more gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD).

Orthopedic spine surgeons and vascular surgeons at UW Health in Madison, WI work together to perform minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion (Mini-ALIF). With this type of spinal fusion surgery, patients have smaller incisions, usually spend less time in the hospital and typically return to daily activities more quickly. Learn more https://www.uwhealth.org/ALIF

Strep throat is a bacterial infection that can make your throat feel sore and scratchy. Strep throat accounts for only a small portion of sore throats. If untreated, strep throat can cause complications, such as kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever can lead to painful and inflamed joints, a specific type of rash or heart valve damage. Strep throat is most common in children, but it affects people of all ages. If you or your child has signs or symptoms of strep throat, see your doctor for prompt testing and treatment.

Elizabeth Stephens, MD joined the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery at Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota in 2019. To learn more about Dr. Stephens’ practice: https://www.mayoclinic.org/bio....graphies/stephens-el
Elizabeth H. Stephens, M.D., Ph.D., is an Assistant Professor of Surgery in Cardiovascular Surgery specializing in congenital cardiac surgery. She received her medical degree from Baylor College of Medicine and Ph.D in Bioengineering from Rice University focusing on tissue engineering heart valves. Her adult cardiothoracic training was completed at Columbia University and congenital training at Lurie Children's Hospital in Chicago. Her clinical areas of expertise include the treatment of:
• Neonates, infants, and children with complex congenital heart disease
• Adult patients with congenital heart disease, including patients previously repaired
• Valve disease, including Ebstein's anomaly
• Pediatric patients with heart failure, including mechanical circulatory support and heart transplantation
• Patients with vascular rings and tracheal stenosis
In addition to her clinical areas of expertise, Dr. Stephens is active in outcomes research relative to congenital heart disease and is extensively published on various cardiac surgery conditions. She has a particular interest in education, including serving on national committees and mentoring trainees of all levels.

Pain in joints or any part of body is very unpleasant and annoying experience. It is very common in people those suffering from arthritis. To get an end to all such pains, one can start using Generic Celebrex ( https://www.medexpressrx.com/celebrex-generic.aspx ). Here is a brief detail about this wonderful painkiller.

A Hundred Orgasms A Day follow the story of 3 women who were tormented every hour of everyday with the need to have orgasm. This documentary explain how Persistent Sexual Arousal Syndrome or PSAS causes this unusual condition. PSAS is a little know neurological disorder where women have symptoms of continuous uncontrollable genital arousal. This condition is unrelated to any kind of sensations of sexual desire. PSAS was initially documented by Doctor Sandra Leiblum in mid 2001, just recently recognized as a unique syndrome in medical science which has a comparable equivalent progressively more claimed by men. A few physicians makes use of the name Persistent Sexual Arousal Syndrome to reference the disorder in women; some others look at the syndrome of priapism in adult males to be a similar disorder. Most importantly, it is really not connected with hyper-sexuality, also known as nymphomania. Both hyper-sexuality, and nymphomania are not known diagnosable health conditions. Not only is it very rare, the disorder is also seldom reported by affected individual who may think it is embarrassing.
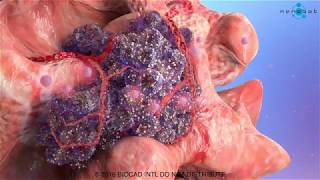
This cancer development medical video is devoted to elaborating the basics of cancer growth. We used advanced medical animation techniques to display such a complicated process.
What is happening in cancer development medical video
The fundamental abnormality described in the cancer development medical video is the nonstop unregulated multiplication of cancer cells. Being uncontrollable by body’s signals that regulate normal cell behavior; cancerous cells divide and grow populating neighboring normal tissues or even spread throughout the body. The overall lack of growth control acquired by cancer cells is due to the accumulated abnormalities in numerous cell regulatory mechanisms and is considered in some aspects of cell behavior that differs them from their healthy counterparts. The interaction of these cells is shown in our previous medical animation video.
Read full article on our webpage http://bit.ly/2LQj9ln
Follow us on Facebook https://www.facebook.com/Nanob....ot.Medical.Animation
Follow us on LinkedIn https://www.linkedin.com/compa....ny/nanobotmodels-med
Follow us on Twitter https://twitter.com/Nanobot_Studio
Follow us on Instagram https://www.instagram.com/nano....bot_medical_animatio
Follow us on Clutch https://clutch.co/profile/nano....bot-medical-animatio
Follow us on Behance https://www.behance.net/NanobotStudio
#cancer #tumor #oncology #metatastic #nanobot #visualscience #scientificcommunication #medicalanimation #animationvideo #animationdesign #animationstudio #animationmovie #nanotechnology #medicine #health #science #education #medschool #medicaleducation #animation_studio #animationstudio
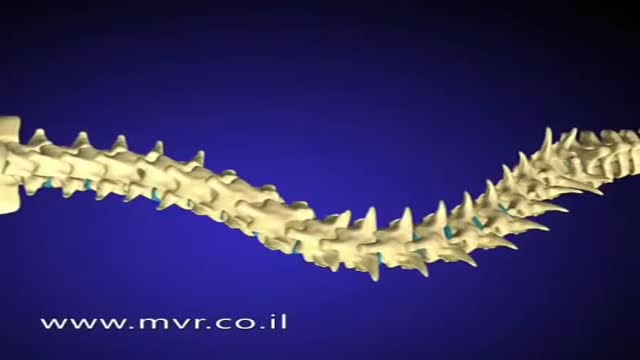
There are several approaches to scoliosis surgery, but all use modern instrumentation systems in which hooks and screws are applied to the spine to anchor long rods. The rods are then used to reduce and hold the spine while bone that is added fuses together with existing bone.
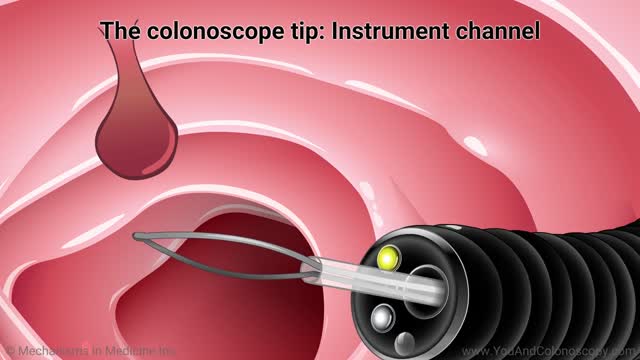
A colonoscope is the special tool used to perform a colonoscopy. It is a thin, flexible, tubular ‘telescope’ with a light and video camera that your doctor carefully guides through your colon in order to see and determine the health of your colon. Watch this animation to learn about the features of the colonoscope, how the colonoscopy procedure is performed and how polyps are removed, and the follow-up care you and your doctor should talk about after your procedure.

Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the inside lining of your stomach and the upper portion of your small intestine. The most common symptom of a peptic ulcer is stomach pain. Peptic ulcers include: Gastric ulcers that occur on the inside of the stomach Duodenal ulcers that occur on the inside of the upper portion of your small intestine (duodenum) The most common causes of peptic ulcers are infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) and long-term use of aspirin and certain other painkillers, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve, Anaprox, others). Stress and spicy foods do not cause peptic ulcers. However, they can make your symptoms worse.