Top videos

Traditionally, the appendix is removed through an incision in the right lower abdominal wall. In most laparoscopic appendectomies, surgeons operate through 3 small incisions (each ¼ to ½ inch) while watching an enlarged image of the patient's internal organs on a television monitor.

Spinal anesthesia is done in a similar way. But the anesthetic medicine is injected using a much smaller needle, directly into the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the spinal cord. The area where the needle will be inserted is first numbed with a local anesthetic. Then the needle is guided into the spinal canal, and the anesthetic is injected. This is usually done without the use of a catheter. Spinal anesthesia numbs the body below and sometimes above the site of the injection. The person may not be able to move his or her legs until the anesthetic wears off.

A lot of women want to know what type of vaginal discharge is normal during pregnancy, and when you're not pregnant. So let's start out by talking about what's normal when you're not pregnant. It's normal to have about 1/2 teaspoon to 1 teaspoon of whitish, creamy, tannish discharge on most days of your cycle in between periods, with the exception of the time of ovulation. Actually, around the time of ovulation, it's normal to notice the discharge becoming more slippery and clear, almost like egg whites. And this is actually a sign that you can watch for to know when you're ovulating. And if you're seeing this type of discharge and you're trying to have a baby, then you should start to time intercourse with ovulation to increase your chances of conceiving.

Things nurses should know about their patients. As a new nurse, it can be hard trying to determine what information you need to know during your shift. In addition, nurses can get extremely busy and strapped for time, so how do you keep up with all of the things you need to know?
🟣Nursing Resume Templates and Job Guide🟣
eBook: https://registerednursern.creator-spring.com/
Paperback: https://amzn.to/3QvzH3W (affiliate ad)
Free Report Sheet Templates: https://www.registerednursern.....com/nursing-report-s
In this video, Nurse Sarah explains some of the most important things nurses need to know about their patients. However, these things can vary depending on your specialty and patient population. These tips are designed to help new nurses begin to think like a nurse.
Some examples of thing nurses should know about their patients include their allergies, code status, diagnosis, medications, vital signs, and much more.
Website: https://www.registerednursern.com/
More Videos: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R2XMro13dD0&list=UUPyMN8DzkFl2__xnTEiGZ1w
Nursing Gear: https://teespring.com/stores/registerednursern
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/registerednursern_com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RegisteredNurseRNs
Twitter: https://twitter.com/NursesRN
Popular Playlists:
NCLEX Reviews: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf
Fluid & Electrolytes: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf
Nursing Skills: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLQrdx7rRsKf

First aid steps to help stop or shorten a seizure or prevent an emergency situation. This may involve giving a rescue treatment (often called "as needed" medicine or treatment) that has been recommended by your health care team. The rescue treatments described here can be given by non-medical people who are not in a hospital setting. They are intended for use by anyone (the person with seizures, family member or other observer) who has been trained in their use. These therapies can be given anywhere in the community
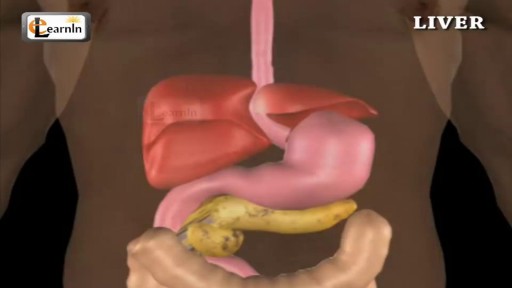
The liver regulates most chemical levels in the blood and excretes a product called bile. ... Production of bile, which helps carry away waste and break down fats in the small intestine during digestion. Production of certain proteins for blood plasma.
There many concerns and questions about how a breast augmentation procedure works. Dr. Linder a highly qualified plastic surgeon based in Beverly Hills, demystifies those worries. Dr. Stuart Linder is a Beverly Hills board certified plastic surgeon, specializing in body sculpting and reconstructive procedures including breast augmentation, reduction, lift, liposuction and tummy tuck. He is board-certified by the American Board of Plastic Surgery and is affiliated with the American College of Surgeons, the American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons and the American Medical Association. Website: www.drlinder.com