Top videos
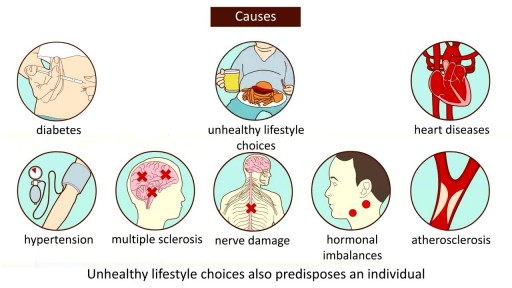
Here are seven ways to start reining in your risks today, before a stroke has the chance to strike. Lower blood pressure. ... Lose weight. ... Exercise more. ... Drink — in moderation. ... Treat atrial fibrillation. ... Treat diabetes. ... Quit smoking.
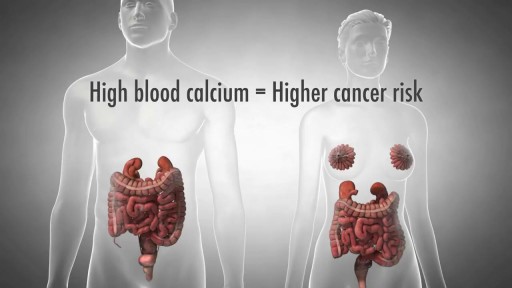
The digestive system is a group of organs working together to convert food into energy and basic nutrients to feed the entire body. Food passes through a long tube inside the body known as the alimentary canal or the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract).

In breastfeeding, the latch is the moment everything comes together: Your baby takes a big mouthful of your nipple and areola (or "latches on"), begins to suck, and draws out your milk. When your baby has established a good latch, your nipple soreness is minimized and your little one gets the nourishment he needs. How do you pull all that off? First and most important, have faith in yourself and your baby. "Babies are designed to breastfeed," says Emily Pease, R.N., international board certified lactation consultant (IBCLC), of Swedish Hospital's Breastfeeding Center in Seattle. "They are born with instincts that help them find Mom's breast and latch on often with very little assistance. And if problems do come up, there are lots of ways to troubleshoot." Here are more steps to get a good latch right from the start.

Otto Placik MD. a board certified Chicago Illinois based plastic surgeon presents instructional video on post genital surgery (labia minora reduction aka labiaplasty or labioplasty or clitoral hood reduction) massage exercises for treatment of labum minora psot surgical fibrosis or hypersensitivity. Photos pictures and video of anatomic models are reviewed . Great for patients thinking about or planning labiaplasty or vaginal cosmetic surgery
Sciatica is often characterized by one or more of the following symptoms: Constant pain in only one side of the buttock or leg (rarely in both legs) Pain that is worse when sitting Leg pain that is often described as burning, tingling, or searing (versus a dull ache) Weakness, numbness, or difficulty moving the leg, foot, and/or toes A sharp pain that may make it difficult to stand up or walk Pain that radiates down the leg and possibly into the foot and toes (it rarely occurs only in the foot) Sciatica Causes and Treatments Video Watch: Sciatica Causes and Treatments Video Sciatic pain can vary from infrequent and irritating to constant and incapacitating. Symptoms are usually based on the location of the pinched nerve. While symptoms can be painful and potentially debilitating, it is rare that permanent sciatic nerve damage (tissue damage) will result, and spinal cord involvement is possible but rare.
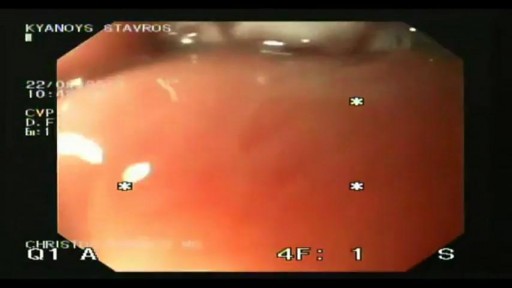
Barrett's esophagus is a complication of chronic (long lasting) and usually severe gastrointestinal reflux disease (GERD), but occurs in only a small percentage of patients with GERD. Criteria are needed for screening patients with GERD for Barrett's esophagus. Until validated criteria are available, it seems reasonable to do screening endoscopies in GERD patients who cannot be taken off acid suppression therapy after two to three years. The diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus rests upon seeing (at endoscopy) a pink esophageal lining that extends a short distance (usually less than 2.5 inches) up the esophagus from the gastroesophageal junction and finding intestinal type cells (goblet cells) on biopsy of the lining. There is a small but definite increased risk of cancer of the esophagus (adenocarcinoma) in patients with Barrett's esophagus.

Have you ever wondered if your toothbrush bristles are too hard or soft or whether or not it even mattered? Contrary to popular belief, the extra soft or soft bristle option is the best choice you can make when it comes to selecting your bristle. The soft bristles are gentler on the gums and because of their delicate nature, it’s easier for them to glide in between teeth. Using hard or medium bristles increases your risk of receding gums and also heightens tooth sensitivity, since you are wearing down the enamel on your teeth with the rough nature. Schedule a dental appointment now to learn more! visit : https://www.urbndental.com/

How to Improve Sexual Health or Stamina part 4 All Solution of Male Disorder Male Infertility Diagnostic and Treatment Re-Slim Care Latest Technology in Pakistan Dr. Aslam Naveed is a well known sexologist in Pakistan. He has treated more than 1 Lac patients since last 30 years of clinical Practice in sexology, he knows how to help the people facing sexual disorders. Contact: 02134965050, 03432821919 www.sexologistpakistan.com https://www.facebook.com/menssexcareclinic/ https://youtu.be/_fRbtwWtLoE Part 1 https://youtu.be/S17bCnwCLuI Part 2 https://youtu.be/CPAXxkdz7mM Part 3 https://youtu.be/YlsdBZJ4prg Part 4 https://youtu.be/fylxbK4azvs Part 5 https://youtu.be/Zb8TcdgJ7Io Part 6 https://youtu.be/0wbDDNAwsmo Part 7 https://youtu.be/gHDmwfsMgTw Part 8 https://youtu.be/IasXoRKUlV4 Part 9 ADDRESS: Men’s Care Modern Hospital, Opposite, Safari Park, University Road, Karachi, Pakistan.

A man's age matters. As men get older, the chances of conceiving and having a healthy child decline. Male fertility starts to decline after 40 when sperm quality decreases. This means it takes longer for their partners to conceive and when they do, there's an increased risk of miscarriage.