Top videos
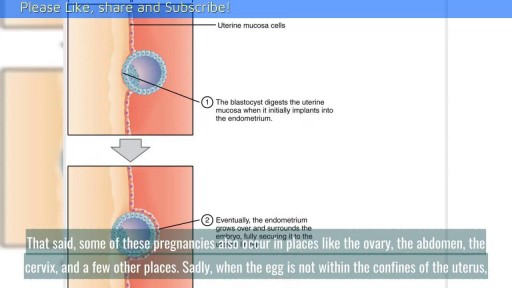
When Does Implantation Occur in Pregnancy? || Common gynaecological problems in women There are a lot of things going on in early pregnancy. The first thing that you need to understand is the menstrual cycle. A good understanding of this can help you understand how the other parts play into the process. A huge part of the menstrual cycle that is the basis of pregnancy is ovulation. Ovulation typically occurs fourteen days prior to the beginning of menstruation, the point when the uterine lining is sloughed off if no pregnancy has occurred.

-Failure to thrive (FTT) is not a diagnosis in itself; rather, it is a term used to describe failure to gain weight in children younger than two years old. Children categorized as FTT weigh less than the 5th percentile for their age; more severe cases involve a slowing of linear growth and head circumference as well. The three causes of FTT are inadequate calorie intake, inadequate calorie absorption, and increased calorie requirements. Newborn infants need 110 kcal/kg/day, while children up to twelve months need 100

The ACL is one of the four main ligaments within the knee that connect the femur to the tibia. The knee is essentially a hinged joint that is held together by the medial collateral (MCL), lateral collateral (LCL), anterior cruciate (ACL) and posterior cruciate (PCL) ligaments.

Vaginal discharge serves an important housekeeping function in the female reproductive system. Fluid made by glands inside the vagina and cervix carries away dead cells and bacteria. This keeps the vagina clean and helps prevent infection. Most of the time, vaginal discharge is perfectly normal. The amount can vary, as can odor and hue (its color can range from clear to a milky white-ish), depending on the time in your menstrual cycle. For example, there will be more discharge if you are ovulating, breastfeeding, or are sexually aroused. The smell may be different if you are pregnant or you haven't been diligent about your personal hygiene. None of those changes is cause for alarm. However, if the color, smell, or consistency seems significantly unusual, especially if it accompanied by vaginal itching or burning, you could be noticing an infection or other condition. What causes abnormal discharge? Any change in the vagina's balance of normal bacteria can affect the smell, color, or discharge texture. These are a few of the things that can upset that balance:
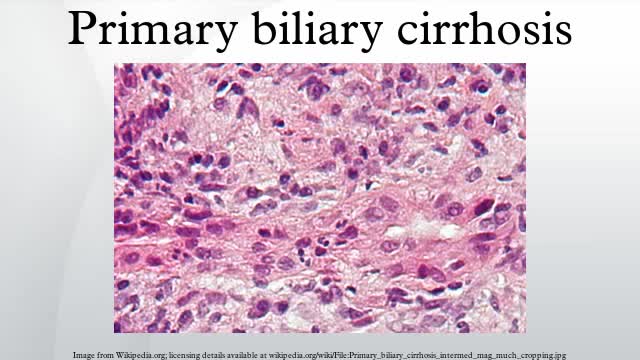
Primary biliary cirrhosis, sometimes called PBC, is a disease in which the bile ducts in your liver are slowly destroyed. Bile, a fluid produced in your liver, plays a role in digesting food and helps rid your body of worn-out red blood cells, cholesterol and toxins. When bile ducts are damaged, as in primary biliary cirrhosis, harmful substances can build up in your liver and sometimes lead to irreversible scarring of liver tissue (cirrhosis). Primary biliary cirrhosis is considered an autoimmune disease, in which the body turns against its own cells. Researchers think it is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Primary biliary cirrhosis usually develops slowly and medication can slow its progression, especially if treatment begins early.
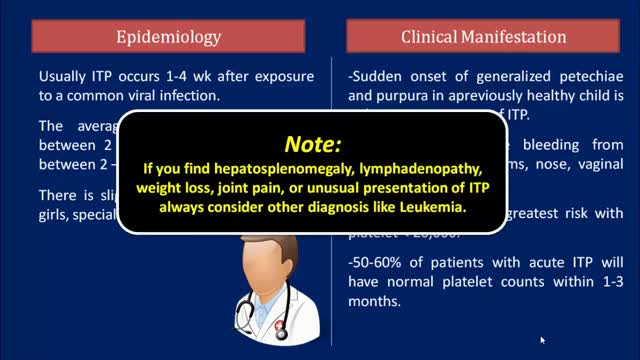
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is a disorder that can lead to easy or excessive bruising and bleeding. The bleeding results from unusually low levels of platelets — the cells that help blood clot. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, which is also called immune thrombocytopenia, affects children and adults. Children often develop ITP after a viral infection and usually recover fully without treatment. In adults, the disorder is often long term. If you don't have signs of bleeding and your platelet count isn't too low, you may not need any treatment. In rare cases, the number of platelets may be so low that dangerous internal bleeding occurs. Treatment options are available.
A surgeon begins the PPH stapled hemorrhoidectomy by inserting a circular anal dilator and obturator into the anal canal and then securing the dilator in place with four sutures. The surgeon then inserts a PPH anoscope into the obturator. Next, he places a circumferential purse-string suture of 2-0 Monocryl on a UR-6 needle 4 cm proximal to the dentate line. The surgeon opens a PPH stapler and places its anvil across the purse string. The stapler is then closed and fired; it is held closed for two minutes to improve hemostasis. Prior to firing the stapler in a female patient, the surgeon places a gloved finger in the vagina to ensure the vaginal mucosa and rectal-vaginal septum are not trapped within the jaws of the closed stapler. The surgeon then opens and removes the stapler.

Cannula are often introduced into blood vessels in 80% of patients in the hospital for treatment. This can be a daunting experience to patients and stressful to doctors as multiple attempts are used. This may result in introducing spreading MRSA, E Coli & Chlostredium living on your skin into blood and results in Invasive MRSA infection.
Skin is often not adequatly cleaned during subsequent atempts as doctors/nurses do not wait for 1 min after applying cleaning solution on the skin before they puncture your skin.
Multiple punctured sites allow CA-MRSA to enter blood stream resulting in bacteremia and death.
Our mission is to reduce spreading invasive CA-MRSA in the hospitals by developing alternative technique to introduce cannulae.
Medifix was created by doctors with a mission to reduce the threat of spreading antibiotic resustant bacteria to mankind.

White stretch marks are unsightly marks that are found along the thighs, abdomen and upper arms. These are marks that could be due to a recent weight loss, trauma or pregnancy. Stretch marks can affect your confidence if you wear revealing outfits and so you should do all you can to remove them.
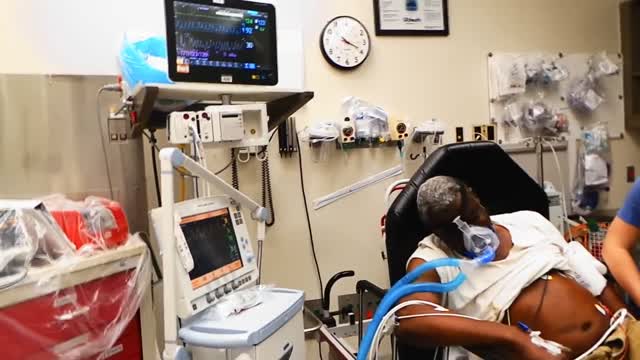
Pulmonary edema is almost always treated in the emergency room or hospital. You may need to be in an intensive care unit (ICU). Oxygen is given through a face mask or tiny plastic tubes are placed in the nose. A breathing tube may be placed into the windpipe (trachea) so you can be connected to a breathing machine (ventilator) if you cannot breathe well on your own. The cause of edema should be identified and treated quickly. For example, if a heart attack has caused the condition, it must be treated right away. Medicines that may be used include: Diuretics that remove excess fluid from the body Medicines that strengthen the heart muscle, control the heartbeat, or relieve pressure on the heart

If levels of both vitamins are extremely high, there is more than a 17-fold greater risk that a child will develop autism, the researchers said. Most of the women in the study said they took multivitamins — which would include folic acid and vitamin B12 — throughout their pregnancy.

The Epley Maneuver for Vertigo can be very effective at relieving vertigo symptoms, but it’s a procedure that should be performed by a physical therapist or other health care professional. This video is for demonstration purposes only. See Doctor Jo’s blog post about the Epley

It is a specialized bodily fluid that supplies essential substances and nutrients, such as sugar, oxygen, and hormones to our cells, and carries waste away from those cells, this waste is eventually flushed out of the body in urine, feces, sweat, and lungs (carbon dioxide). Blood also contains clotting agents.

To treat your tinnitus, your doctor will first try to identify any underlying, treatable condition that may be associated with your symptoms. If tinnitus is due to a health condition, your doctor may be able to take steps that could reduce the noise. Examples include: Earwax removal.

Morning erections have colloquially been termed as “morning wood” while scientifically it is called nocturnal penile tumescence. It is a normal and healthy physiological reaction and response that most men experience in their lives. Morning erections are really the ending of a series of erections that happen to men during the night. Healthy men can, on average, have anywhere between three to five erections in a full night of sleep, each of which lasts from 25-35 minutes.