Los mejores videos
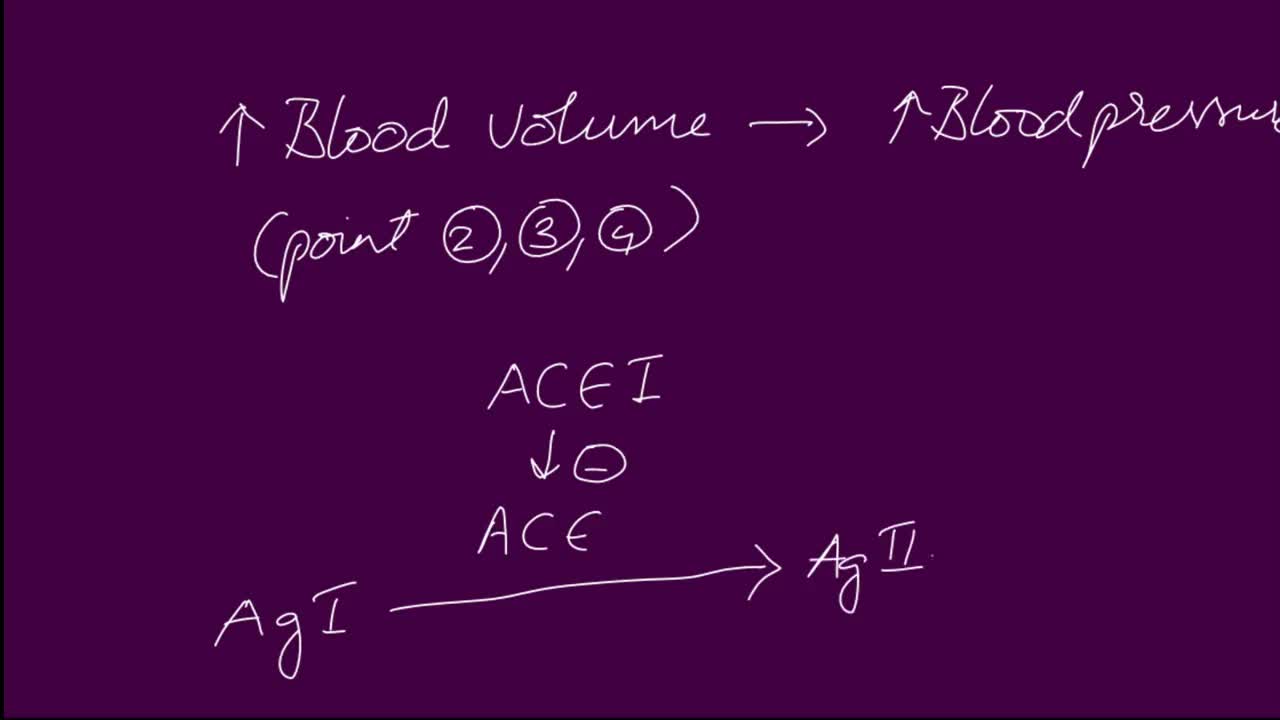
ACE Inhibitor Mechanisms. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are agents used to relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure. They prevent an enzyme from producing angiotensin II, which narrows blood vessels and raises blood pressure, meaning the heart has to work harder to pump blood around the body.
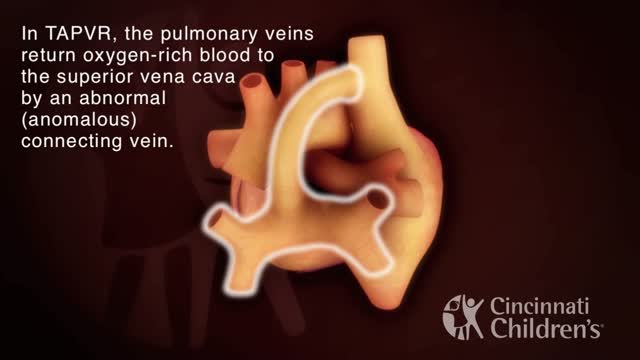
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR) is a rare congenital malformation in which pulmonary veins that return oxygen-rich blood from the lungs do not connect normally to the left atrium. Instead all four pulmonary veins drain abnormally to the right atrium. Heart models and animation were developed by the Cincinnati Children's Heart Institute in conjunction with Cincinnati Children's Critical Care Media Lab.

Ellis demonstrates how to administer an intradermal, subcutaneous, and intramuscular injection.
Our Critical Nursing Skills video tutorial series is taught by Ellis Parker MSN, RN-BC, CNE, CHS and intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for your nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI and NCLEX.
#NCLEX #ClinicalSkills #injections #HESI #Kaplan #ATI #NursingSchool #NursingStudent #Nurse #RN #PN #Education #LVN #LPN #nurseeducator
00:00 What to expect
00:20 Intradermal injections
00:35 Cleaning site
00:54 Explaining bevel up
1:40 Inserting needle
2:00 Injecting medication
2:16 Withdrawing needle
2:29 Subcutaneous Injections
2:39 Selecting site for subcutaneous injections
3:08 Cleaning subcutaneous injections site
3:18 Pinching subcutaneous injections site
3:30 Inserting needle subcutaneous injections
4:13 Injecting medication subcutaneous injections
4:23 Post injection
4:36 Intramuscular injection
4:54 Locating intramuscular injection site
5:18 Cleaning intramuscular injection site
5:38 Inserting needle intramuscular injection
6:28 Anchoring needle intramuscular injection
6:44 Injecting medication intramuscular injection
6:55 Withdrawing needle intramuscular injection
7:05 Disposing of needle
7:43 Cleaning site
8:00 Displacing with Z-track
8:10 Inserting needle
8:23 Releasing tissue
🚨 Reminder: shipping deadlines are looming 👀
🎁 Regular Shipping: Order by Friday, December 15
🚀 Expedited Shipping: Order by Monday, December 18
🔍 Still searching for last-minute gifts? Consider a Level Up RN Gift Card! 💌 It’s not only a thoughtful present but also the perfect way to share treasures like Pharmacology Flashcards OR digital treasures like Flashables Digital Nursing Flashcards & the Level Up RN membership. Give the gift of knowledge this holiday season! 🧠⚡️💖 bit.ly/LevelUpRNGC
🚪 Access our Cram Courses, Quizzes and Videos all in one ad free space with Level Up RN Membership https://bit.ly/LevelUpRNMembership
Want more ways to MASTER Clinical Skills? Check out our flashcards & videos!
👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇👇
👉 https://bit.ly/clinicalnursingskills 👈
☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆☝️👆
This is your one-stop-shop for materials to help you LEARN & REVIEW so you can PASS Nursing School.
🤔🤔🤔 DO YOU WANT TO PASS your classes, proctored exams and the NCLEX? 🤔🤔🤔 Our resources are the best you can buy. They are built with a single goal: help you pass with no fluff. Everything you need, and nothing you don’t. Don’t take our word for it, though! Check out our hundreds of ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ reviews from nurses who passed their exams and the NCLEX with Level Up RN.
🗂️ Our Ultimate Nursing School Survival kit is your number 1 resource to get through nursing school and to pass the NCLEX. Whether you're just starting school or you’re already prepping for the NCLEX, this bundle of flashcards is the best you can buy. It covers all the information you need to know to pass all your exams and it has FREE shipping!
➡️ https://bit.ly/TUNSSK ⬅️
L👀king for EVEN MORE resources to survive Nursing School? Make your Nursing School experience your own! Life’s difficult enough—learning shouldn’t be.
🪅 Games https://nursesquad.com
💻 Digital resources https://bit.ly/NursingStudyCourses
📅 Organizational tools https://bit.ly/OrganizingSchool
✨Want perks? Join our channel!
https://youtube.com/leveluprn/join
🏷 Head to https://leveluprn.com/specials for all our latest deals!🥳️
📧 LOOKING FOR FREE RESOURCES TO HELP WITH YOUR EXAMS? Get exclusive tips, latest video releases and more delivered to your email!
➡️ https://leveluprn.com/signup ⬅️
⚕ 👩 LEVEL UP NURSE SQUAD 👩⚕️
All of the nurses at Level Up RN are here to help! Cathy Parkes started helping her fellow classmates back when she was in nursing school, tutoring so they could pass their exams and graduate. After she got her BSN and started working as an RN at Scripps Encinitas Hospital, she started this YouTube channel to help nursing students around the world. Since then she has built a team of top-notch dedicated nurses and nurse educators who are focused on improving nursing education and supporting career advancement for nurses everywhere. With flashcards, videos, courses, organizational tools and more, we are singularly focused on helping students and nurses Level Up on their exams and nursing careers.

Multiple sclerosis (MS) involves an immune-mediated process in which an abnormal response of the body’s immune system is directed against the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS is made up of the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves.

A lot of women want to know what type of vaginal discharge is normal during pregnancy, and when you're not pregnant. So let's start out by talking about what's normal when you're not pregnant. It's normal to have about 1/2 teaspoon to 1 teaspoon of whitish, creamy, tannish discharge on most days of your cycle in between periods, with the exception of the time of ovulation. Actually, around the time of ovulation, it's normal to notice the discharge becoming more slippery and clear, almost like egg whites. And this is actually a sign that you can watch for to know when you're ovulating. And if you're seeing this type of discharge and you're trying to have a baby, then you should start to time intercourse with ovulation to increase your chances of conceiving.

Spinal anesthesia is done in a similar way. But the anesthetic medicine is injected using a much smaller needle, directly into the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the spinal cord. The area where the needle will be inserted is first numbed with a local anesthetic. Then the needle is guided into the spinal canal, and the anesthetic is injected. This is usually done without the use of a catheter. Spinal anesthesia numbs the body below and sometimes above the site of the injection. The person may not be able to move his or her legs until the anesthetic wears off.

St. Luke's originally broadcast this live in a webcast and later re-purposed it for air on KCRG-TV9 as an educational video. It is hosted by Ashley Hinson, KCRG-TV9 anchor and Dr. Sandeep Munjal. Dr. Jeff Nassif performs the knee replacement surgery on an eastern Iowa woman. St. Luke's has a rapid recovery joint replacement program, which gets people back to life quickly after surgery.
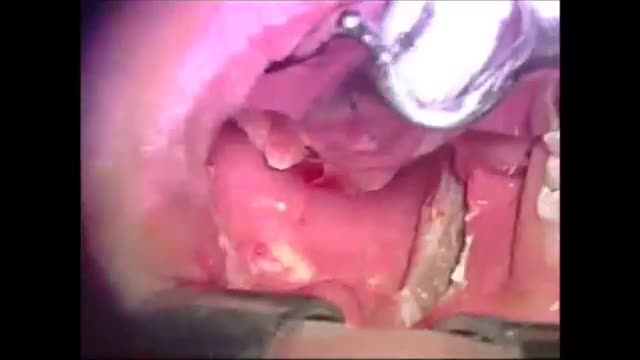
Microsurgical bipolar cautery tonsillectomy compares favorably with traditional techniques in terms of intraoperative bleeding, postoperative pain, otalgia, and hemorrhage. This technique combines the hemostatic advantage of cautery dissection, the excellent visualization achieved by a microscope, and, with the use of a video, greatly improves the physician's ability to teach how to perform a tonsillectomy.
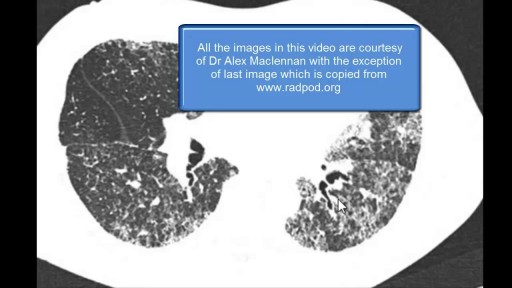
The diffuse lung diseases tend to cause infiltrative opacification in the periphery of the lung. As the name of the group of diseases suggests, they are diffuse. While the consolidation or ground-glass change is usually bilateral, it may be localised, e.g. radiation pneumonitis.