Top videos

Abortion pills can help one to terminate pregnancy at home without letting others know- which is very true. But if you are not cautions enough, it wouldn’t be secured, doing in private. This might be due to the nosy neighbor or friends who peep up any time in the day. Arrange things for and take precautions, to avoid getting your private affair publicly few seconds.
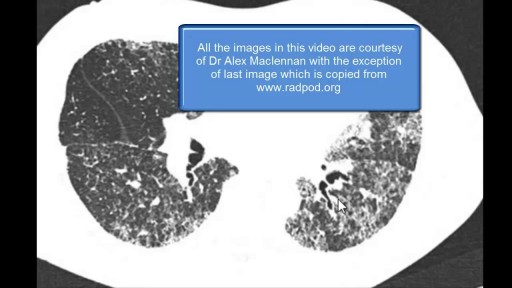
The diffuse lung diseases tend to cause infiltrative opacification in the periphery of the lung. As the name of the group of diseases suggests, they are diffuse. While the consolidation or ground-glass change is usually bilateral, it may be localised, e.g. radiation pneumonitis.
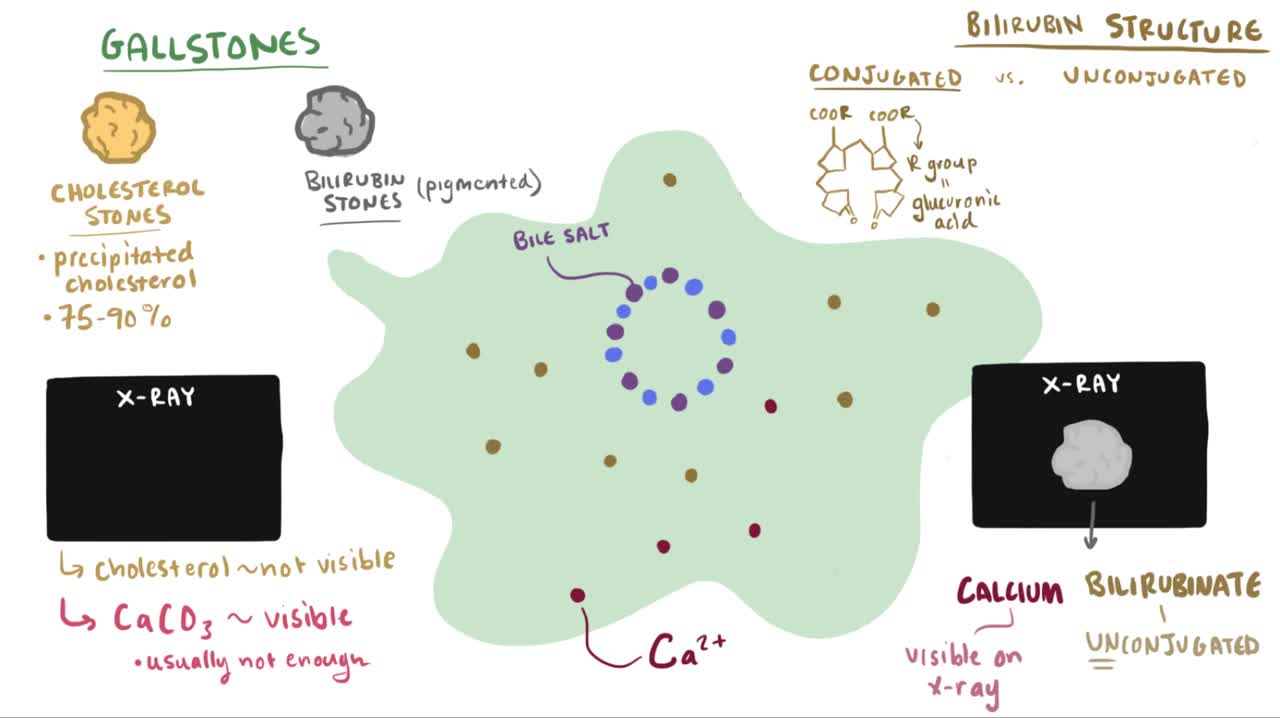
Cholelithiasis involves the presence of gallstones (see the image below), which are concretions that form in the biliary tract, usually in the gallbladder. Choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of 1 or more gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD).

nkylosing spondylitis (pronounced ank-kih-low-sing spon-dill-eye-tiss), or AS, is a form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, although other joints can become involved. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort
Prinzmetal's or Prinzmetal angina (/ˈprɪntsmɛtəl/, sounds like "prints metal") (also known as variant angina, vasospastic angina (VSA), angina inversa, or coronary vessel spasm) is a syndrome typically consisting of angina (cardiac chest pain) at rest that occurs in cycles.

systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). This is most likely secondary to sepsis from an infection of the patient's Hickman catheter given the associated skin findings, although culture results are needed to confirm this diagnosis. The patient's low blood pressure is likely secondary to developing septic shock, and he has already appropriately been treated with intravenous fluids. Catheter removal is indicated given his hemodynamic instability. Catheter removal is also indicated in patients with severe sepsis with organ hypoperfusion, endocarditis, suppurative thrombophlebitis, or persistent bacteremia after 72 hours of appropriate antibiotic therapy. Long term catheters should also be removed if culture results are positive for S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, fungi, or mycobacteria.

Inflammation of the uvula is known as uvulitis. Your uvula will appear red, puffy, and larger than normal. Other symptoms of uvulitis may include: itching burning a sore throat spots on your throat snoring difficulty swallowing trouble breathing If you have a swollen uvula along with a fever or abdominal pain, consult with your doctor right away. In rare cases, the uvula can swell enough to block your airway. Swelling of the throat is a life-threatening event. If this happens, seek immediate medical attention. What causes a swollen uvula? Causes Inflammation is your body’s response when it’s under attack. Triggers for inflammation include: environmental and lifestyle factors an infection trauma genetics Environmental and Lifestyle Factors The most common food allergies are peanuts tree nuts milk eggs wheat soy fish, including shellfish You could be having an allergic reaction to something you touched, swallowed, or breathed in. Some common allergens include: food irritants , such as dust, animal dander, or pollen medication exposure to chemicals or other toxic substances, including tobacco Infection You can get viral infections or bacterial infections. Examples of viral infections include: the common cold the flu mononucleosis chickenpox measles croup The most common bacterial infection is strep throat, which occurs due to Streptococcus pyogenes, which is a type of group A Streptococcus. If you have infected tonsils, or tonsillitis, severe inflammation can cause them to push against and irritate your uvula. Trauma Trauma to the uvula can happen if you need an intubation, such as during surgery. Your uvula can also be injured during a tonsillectomy. This is a procedure to remove your tonsils, which are located on both sides of your uvula. Your throat and uvula can also become irritated if you have acid reflux disease or if you vomit frequently. Genetics A condition called hereditary angioedema (HAE) can cause swelling of the uvula and throat, as well as swelling of the face, hands, and feet. Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. It’s an uncommon genetic mutation that occurs in 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 50,000 people. It’s rare, but there are case reports of individuals who have an elongated uvula, which can also interfere with breathing. What are the risk factors for a swollen uvula? Risk Factors Anyone can get uvulitis, but adults get it less often than children do. You’re at increased risk if you: have allergies use tobacco products are exposed to chemicals and other irritants in the environment have a weakened immune system, making you more susceptible to infections How is a swollen uvula diagnosed? Diagnosis If you have fever or swelling of your throat, see your doctor. Be prepared to give a complete medical history. Tell your doctor: about all the over-the-counter and prescription medications you take if you’re a smoker or you chew tobacco if you’ve recently tried new foods if you’ve been exposed to chemicals or unusual substances about your other symptoms, such as abdominal pain, fever, or dehydration Your doctor may be able to make a diagnosis through a physical exam. It’s likely you’ll also need a throat swab to evaluate for strep or to obtain secretions for culture to determine if you have another bacterial or fungal infection. This test is known as the rapid strep test. You may also need a nasal swab to test for influenza. Blood testing can help identify or rule out some other infectious agents. If those tests are inconclusive, you may need to see an allergist. Blood and skin tests can help identify foods or other substances that cause a reaction. Learn more: Allergy testing » If necessary, imaging tests can provide a more detailed view of your throat and the surrounding area. What’s the treatment for a swollen uvula? Treatment When you have something like the common cold, swelling usually clears up on its own without treatment. Otherwise, treatment will depend on how severe your symptoms are, as well as what’s causing the inflammation. Infection Viral infections tend to clear up without treatment. The only upper respiratory infection for which an antiviral medication is available is influenza. Antibiotics can treat bacterial infections. Even after symptoms clear up, take all the medication as prescribed. If your condition may be contagious, stay home until your doctor tells you that you’re no longer at risk of spreading it to others. Allergy If you test positive for an allergy, try to avoid the allergen in the future. Doctors usually treat allergies with antihistamines or steroids. Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic reaction. Doctors use epinephrine to treat this reaction. Hereditary angioedema Your doctor may treat HAE with any of the following: anabolic steroids, or androgens antifibrinolytics C1 inhibitors, such as C1 esterase inhibitor (Berinert) or C1 esterase inhibitor (recombinant) (Ruconest) a plasma kallikrein inhibitor, such as ecallantide (Kalbitor) bradykinin receptor antagonist, such as icatibant injection (Firazyr) Tell your doctor if you have new or worsening symptoms, and follow up as necessary. Tips for relief home treatment If you have a swollen uvula or sore throat, it’s your body’s way of telling you that something is wrong. A few home remedies can help keep you strong and soothe your irritated throat. Make sure you’re getting enough fluids. If your throat hurts when you drink, try drinking small amounts throughout the day. Your urine should be light in color. If it’s dark yellow or brown, you’re not drinking enough and may be dehydrated. Additional tips include the following: Cool your throat by sucking on ice chips. Frozen juice bars or ice cream may also do the trick. Gargle with warm salt water to ease your dry, scratchy throat. Aim for a full night’s sleep, and nap during the day if you can. What’s the outlook? Outlook A swollen uvula isn’t a common occurrence. Most of the time it clears up without treatment. If you have an infection, prompt treatment should take care of the problem within a week or two. If you have allergies that lead to swelling of the uvula or throat, do your best to avoid that allergen. You should also be prepared to deal with an attack if you come into contact with the substance again. If you’ve ever had anaphylaxis, ask your doctor if you should carry injectable epinephrine (EpiPen) in case of emergency. People with HAE must learn to recognize triggers and early warning signs of an attack. Talk to your doctor about how to manage HAE. Article Resources Was this article helpful?Yes No Share Tweet Email Print Read This Next 9-Month-Old Baby: Developmental Milestones and Guidelines 9-Month-Old Baby: Developmental Milestones and Guidelines Read More » All of the ‘Firsts’ That Come with Breast-Feeding All of the ‘Firsts’ That Come with Breast-Feeding Read More » 5 Types of Health Professionals You Should Know About 5 Types of Health Professionals You Should Know About Read More » What’s the Difference Between a Fracture and a Break? What’s the Difference Between a Fracture and a Break? Read More » Is Corn a Vegetable? Is Corn a Vegetable? Read More » Advertisement Advertisement Advertisement