Top videos
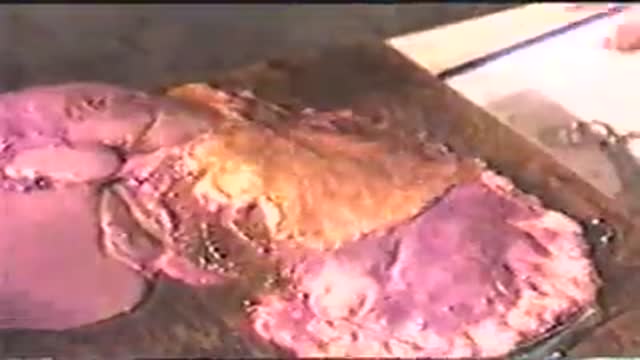
Microsurgical bipolar cautery tonsillectomy compares favorably with traditional techniques in terms of intraoperative bleeding, postoperative pain, otalgia, and hemorrhage. This technique combines the hemostatic advantage of cautery dissection, the excellent visualization achieved by a microscope, and, with the use of a video, greatly improves the physician's ability to teach how to perform a tonsillectomy.
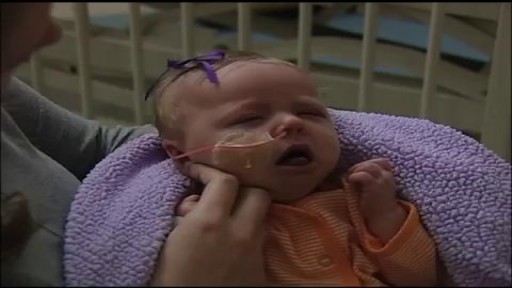
Whooping cough (pertussis) is a highly contagious respiratory tract infection. In many people, it's marked by a severe hacking cough followed by a high-pitched intake of breath that sounds like "whoop." Before the vaccine was developed, whooping cough was considered a childhood disease. Now whooping cough primarily affects children too young to have completed the full course of vaccinations and teenagers and adults whose immunity has faded. Deaths associated with whooping cough are rare but most commonly occur in infants. That's why it's so important for pregnant women — and other people who will have close contact with an infant — to be vaccinated against whooping cough.
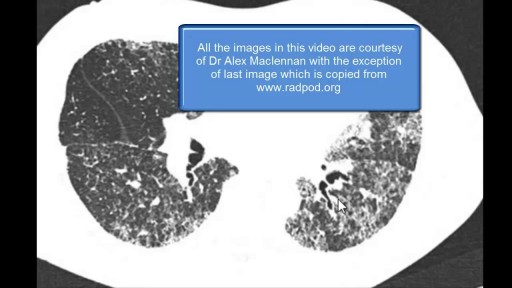
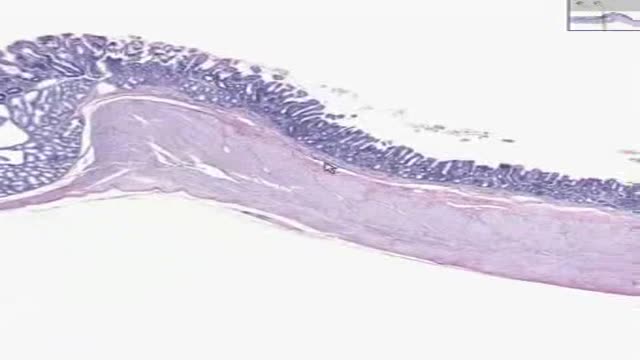
The diffuse lung diseases tend to cause infiltrative opacification in the periphery of the lung. As the name of the group of diseases suggests, they are diffuse. While the consolidation or ground-glass change is usually bilateral, it may be localised, e.g. radiation pneumonitis.

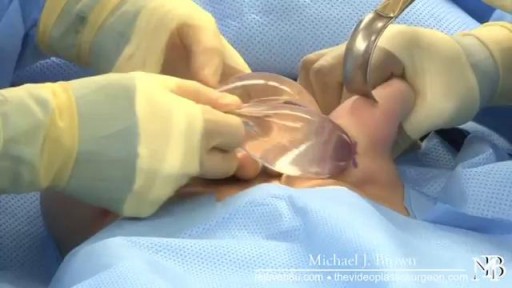
Dr. David Sneed of Aesthetica Med Spa in Austin discusses the latest liposuction technique known as Body Jet Water Liposuction - which is quickly gaining popularity due to the procedure being less invasive than traditional liposuction techniques, therefore minimizing recovery time and pain.
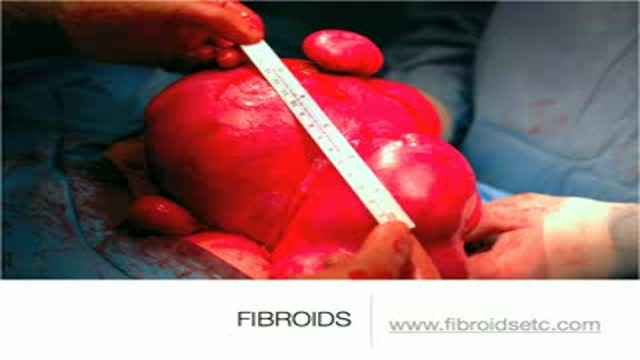
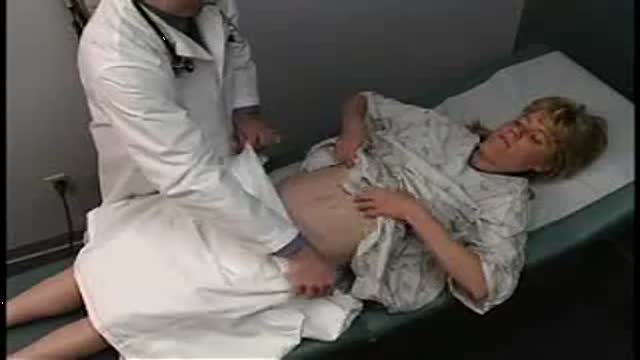
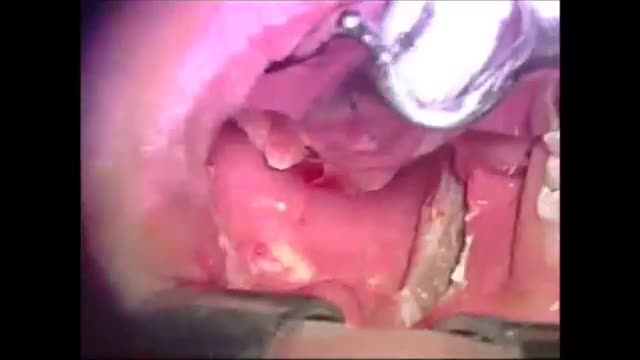
A uterine fibroid (also uterine leiomyoma, myoma, fibromyoma, leiofibromyoma, fibroleiomyoma, and fibroma) (plural of ... myoma is ...myomas or ...myomata) is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor that originates from the smooth muscle layer (myometrium) and the accompanying connective tissue of the uterus. Fibroids are the most common benign tumors in females and typically found during the middle and later reproductive years. While most fibroids are asymptomatic, they can grow and cause heavy and painful menstruation, painful sexual intercourse, and urinary frequency and urgency. Uterine fibroids is the major indication for hysterectomy in the US.[2] Fibroids are often multiple and if the uterus contains too many leiomyomatas to count, it is referred to as uterine leiomyomatosis. The malignant version of a fibroid is uncommon and termed a leiomyosarcoma.

St. Luke's originally broadcast this live in a webcast and later re-purposed it for air on KCRG-TV9 as an educational video. It is hosted by Ashley Hinson, KCRG-TV9 anchor and Dr. Sandeep Munjal. Dr. Jeff Nassif performs the knee replacement surgery on an eastern Iowa woman. St. Luke's has a rapid recovery joint replacement program, which gets people back to life quickly after surgery.

To save humanity, a dietitian travels to the past. A lot.
Subscribe now: https://www.youtube.com/c/funn....yordie?sub_confirmat
CREDITS:
Director: Elliot Dickerhoof
Producers: Chuck Armstrong, Charlie Stockman, Elliot Dickerhoof
Writers: Chuck Armstrong & Charlie Stockman
Actors: Chuck Armstrong, Charlie Stockman, Kelly Vrooman
Executive Producer: Darren Miller
DP: Cody Jacobs
Gaffer: Jordan Holtane
AC: Giselle Gonzalez
Sound Mixer: Marcos Castro
Costume Designer: Kate Bergh
Hair and Makeup Artist: Jessica Leigh Schwartz
PA: Elyssa Phillips
Get more Funny Or Die
-------------------------------
Like FOD on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/funnyordie
Follow FOD on Twitter: https://twitter.com/funnyordie
Follow FOD on Tumblr: http://funnyordie.tumblr.com/
Follow FOD on Instagram: http://instagram.com/funnyordie
Follow FOD on Vine: https://vine.co/funnyordie
Follow FOD on Pinterest: http://www.pinterest.com/funnyordie
Follow FOD on Google+: https://plus.google.com/+funnyordie
See the original at: http://www.funnyordie.com/videos/74dd9afee2
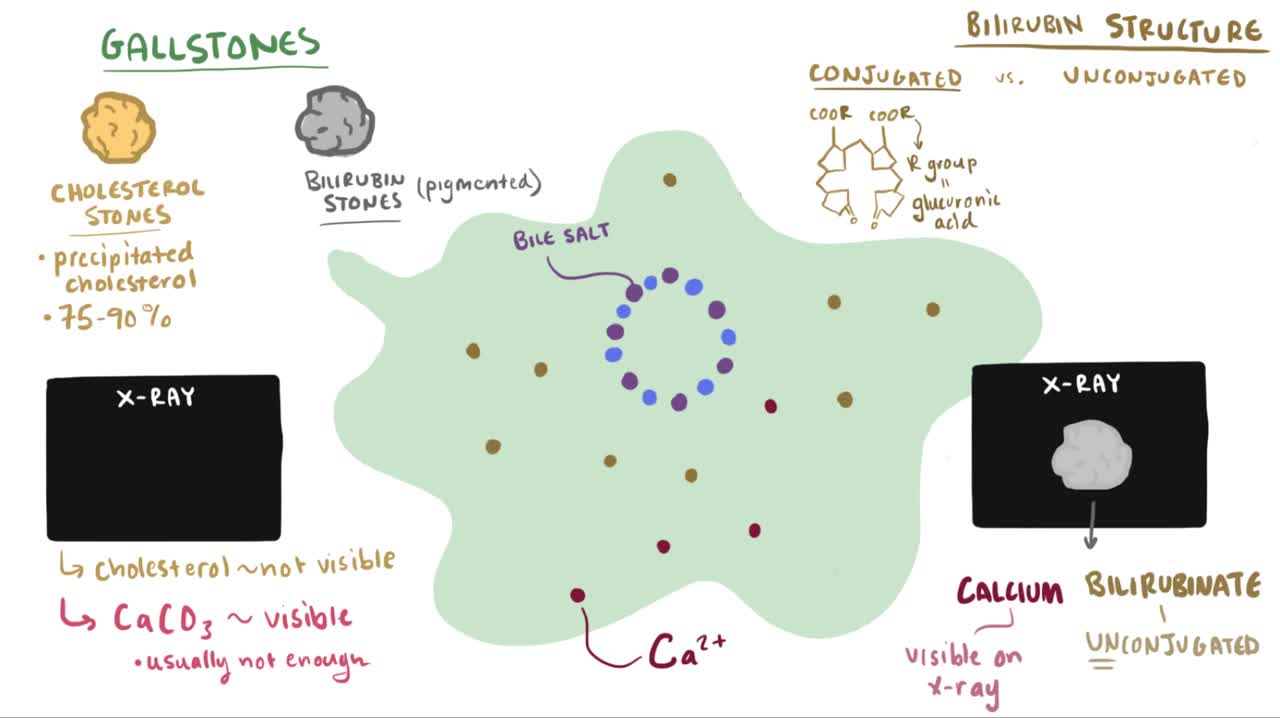
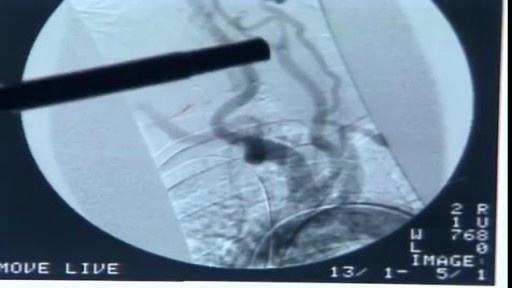
Cholelithiasis involves the presence of gallstones (see the image below), which are concretions that form in the biliary tract, usually in the gallbladder. Choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of 1 or more gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD).

Abortion pills can help one to terminate pregnancy at home without letting others know- which is very true. But if you are not cautions enough, it wouldn’t be secured, doing in private. This might be due to the nosy neighbor or friends who peep up any time in the day. Arrange things for and take precautions, to avoid getting your private affair publicly few seconds.