Top videos

Mastitis is inflammation of tissue in one or both mammary glands inside the breast. Mastitis usually affects lactating women - women who are breastfeeding, producing milk. Hence, it is often referred to as lactation mastitis. The patient feels a hard, sore spot inside the breast.

Radiosurgery: Radiosurgery devices, such as the CyberKnife Robotic Radiosurgery System, offer patients a new option for the treatment of lung cancer. The CyberKnife® System is used to treat lung cancer patients who cannot tolerate surgery, have an inoperable tumor, or are seeking an alternative to surgery.

Here we’ll explain the symptoms of pancreatitis, how alcohol causes the condition and the other health problems it can lead to. You probably don’t pay much attention to your pancreas. But that small, tadpole-shaped organ behind your stomach and below your ribcage is pretty important. It produces two essential substances: digestive juices which your intestines use to break down food, and hormones that are involved in digestion, such as insulin, which regulates your blood sugar levels. Pancreatitis is when your pancreas becomes inflamed and its cells are damaged. Heavy drinking can cause pancreatitis. But if you drink within the government’s low risk unit guidelines, you should avoid upsetting this important organ.

An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles. The resulting bulge can be painful, especially when you cough, bend over or lift a heavy object. However, many hernias do not cause pain.
An inguinal hernia isn't necessarily dangerous. It doesn't improve on its own, however, and can lead to life-threatening complications. Your doctor is likely to recommend surgery to fix an inguinal hernia that's painful or enlarging. Inguinal hernia repair is a common surgical procedure.
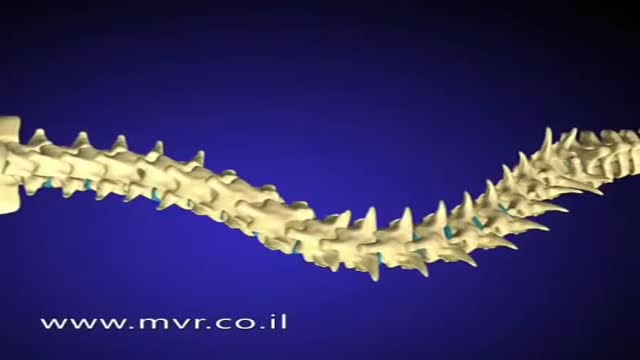
There are several approaches to scoliosis surgery, but all use modern instrumentation systems in which hooks and screws are applied to the spine to anchor long rods. The rods are then used to reduce and hold the spine while bone that is added fuses together with existing bone.

Liposuction is a surgical procedure that is done to remove fat deposits from underneath the skin. Common areas that are treated: the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, upper arms, chest and neck. (use medical graphic of body with labeled parts) The procedure is usually done as an outpatient under some combination of local anesthesia and/or sedation:. This means you are awake but relaxed and pain free. Depending on the number of areas to be treated and the specific technique selected, it may take from one to several hours. A small incision (cut) is made through the skin near the area of the fat deposit. Multiple incisions may be needed if a wide area or multiple areas are being done. A long hollow tube called a cannula will be inserted through this incision. Prior to inserting the cannula, the doctor may inject a solution of salt water that contains an anesthetic (numbing) medication and another medication to decrease bleeding. The cannula is then inserted and moved under the skin in a way to loosen the fat deposits so they may be suctioned out. Because a significant amount of body fluid is removed with the fat, an intravenous (through the veins) fluid line will be kept going during the procedure.
A recent technique called “ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty” uses a special cannula that liquefies the fat cells with ultrasonic energy. You should ask your doctor which technique he/she will use and how it will affect the type of anesthesia you will need and the length of the procedure.
Why is this procedure performed?
Liposuction is done to restore a more normal contour to the body. The procedure is sometimes described as body sculpting. It should be limited to fat deposits that are not responsive to diet and exercise. It is suggested that you should be within 20of your ideal body weight at the time of surgery. If you are planning to lose weight you should delay this procedure. This is not obesity surgery. The maximum amount of fat that can be removed is usually less than 10 pounds. The best results are achieved in people who still have firm and elastic skin. Although rare, there are risks and complications that can occur with liposuction. You should be aware that all the complications are increased if you are a smoker. You will need to quit smoking or at least avoid smoking for a month before and after surgery. If you have had prior surgeries near any of the areas to be treated, this may increase the risk of complications and you should discuss this with your doctor. Any history of heart disease, diabetes, bleeding problems or blood clots in your legs may make you more prone to post-operative problems and you should discuss these with your doctor. Finally, as with any cosmetic procedure it is important to have realistic expectations. The goals, limitations, and expectations of the procedure should be discussed openly and in detail with your doctor. Most insurance companies do not cover cosmetic surgery.
What should I expect during the post-operative period?
After surgery you should be able to go home but you will need someone to drive you. In the first few days after surgery it is common for the incisions to drain fluid and you will have to change dressings frequently. Fresh blood is not usual and if you have any bleeding you should call your doctor immediately. In some cases a small tube may have been placed through the skin to allow drainage. You will be limited to sponge baths until the drains and dressings are removed. After that you may take showers but no baths for 2 weeks. You may experience pain, burning, and numbness for a few days. Take pain medicine as prescribed by your doctor. You may notice a certain amount of bruising and swelling. The bruising will disappear gradually over 1 to 2 weeks. Some swelling may last for up to 6 months. If you have skin sutures they will be removed in 7 to 10 days. You should be able to be up and moving around the house the day after surgery but avoid any strenuous activity for about 1

Genital warts are growths on the skin of the genital area and around the anus. They are caused by certain types of the human papilloma virus (HPV). There are more than 100 types of HPV. Some types of HPV produce warts on different parts of the body, like plantar warts on the feet and common hand warts. There is no specific treatment for HPV, but there are treatments for health problems caused by HPV. Genital warts can be treated by your healthcare provider, or with prescription medication. HPV-related cancers are more treatable when diagnosed and treated promptly. For more information, visit www.cancer.org.
Initial treatment of a deviated septum may be directed at managing the symptoms of the tissues lining the nose, which may then contribute to symptoms of nasal obstruction and drainage. Your doctor may prescribe: Decongestants. Decongestants are medications that reduce nasal tissue swelling, helping to keep the airways on both sides of your nose open. Decongestants are available as a pill or as a nasal spray. Use nasal sprays with caution, however. Frequent and continued use can create dependency and cause symptoms to be worse (rebound) after you stop using them. Decongestants have a stimulant effect and may cause you to be jittery as well as elevate your blood pressure and heart rate. Antihistamines. Antihistamines are medications that help prevent allergy symptoms, including obstruction and runny nose. They can also sometimes help nonallergic conditions such as those occurring with a cold. Some antihistamines cause drowsiness and can affect your ability to perform tasks that require physical coordination, such as driving. Nasal steroid sprays. Prescription nasal corticosteroid sprays can reduce inflammation in your nasal passage and help with obstruction or drainage. It usually takes from one to three weeks for steroid sprays to reach their maximal effect, so it is important to follow your doctor's directions in using them. Medications only treat the swollen mucus membranes and won't correct a deviated septum.

This video shows Prof Dan Reinstein, MD MA(Cantab) FRCSC DABO FRCOphth FEBO performing a ReLEx SMILE keyhole LASIK procedure using the latest surgical instrument that he helped to develop (Malosa MMSU1297 - Reinstein Lenticule Separator: http://www.malosa.com/en/reinstein-le...). This instrument enables the procedure to be performed with one instrument, through one 2mm incision, using only one sweep per plane, and taking about 30 seconds to separate and withdraw the lenticule, improving day 1 uncorrected vision over other lenticule extraction techniques that require more corneal manipulation.

Nasal polyps are soft, painless, noncancerous growths on the lining of your nasal passages or sinuses. They hang down like teardrops or grapes. They result from chronic inflammation due to asthma, recurring infection, allergies, drug sensitivity or certain immune disorders. Nasal polyps are polypoidal masses arising mainly from the mucous membranes of the nose and paranasal sinuses. They are overgrowths of the mucosa that frequently accompany allergic rhinitis, and are freely movable and nontender.

Most intact aortic aneurysms do not produce symptoms. As they enlarge, symptoms such as abdominal pain and back pain may develop. Compression of nerve roots may cause leg pain or numbness. Untreated, aneurysms tend to become progressively larger, although the rate of enlargement is unpredictable for any individual. Rarely, clotted blood which lines most aortic aneurysms can break off and result in an embolus. They may be found on physical examination. Medical imaging is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Symptoms may include: anxiety or feeling of stress; nausea and vomiting; clammy skin; rapid heart rate. In patients presenting with aneurysm of the arch of the aorta, a common symptom is a hoarse voice as the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (a branch of the vagus nerve) is stretched. This is due to the recurrent laryngeal nerve winding around the arch of the aorta. If an aneurysm occurs in this location, the arch of the aorta will swell, hence stretching the left recurrent laryngeal nerve. The patient therefore has a hoarse voice as the recurrent laryngeal nerve allows function and sensation in the voicebox. Abdominal aortic aneurysms, hereafter referred to as AAAs, are the most common type of aortic aneurysm. One reason for this is that elastin, the principal load-bearing protein present in the wall of the aorta, is reduced in the abdominal aorta as compared to the thoracic aorta (nearer the heart). Another is that the abdominal aorta does not possess vasa vasorum, hindering repair. Most are true aneurysms that involve all three layers (tunica intima, tunica media and tunica adventitia), and are generally asymptomatic before rupture. The most common sign for the aortic aneuysm is the Erythema nodosum also known as leg lesions typically found near the ankle area. The prevalence of AAAs increases with age, with an average age of 65–70 at the time of diagnosis. AAAs have been attributed to atherosclerosis, though other factors are involved in their formation. An AAA may remain asymptomatic indefinitely. There is a large risk of rupture once the size has reached 5 cm, though some AAAs may swell to over 15 cm in diameter before rupturing. Before rupture, an AAA may present as a large, pulsatile mass above the umbilicus. A bruit may be heard from the turbulent flow in a severe atherosclerotic aneurysm or if thrombosis occurs. Unfortunately, however, rupture is usually the first hint of AAA. Once an aneurysm has ruptured, it presents with a classic pain-hypotension-mass triad. The pain is classically reported in the abdomen, back or flank. It is usually acute, severe and constant, and may radiate through the abdomen to the back. The diagnosis of an abdominal aortic aneurysm can be confirmed at the bedside by the use of ultrasound. Rupture could be indicated by the presence of free fluid in potential abdominal spaces, such as Morison's pouch, the splenorenal space (between the spleen and left kidney), subdiaphragmatic spaces (underneath the diaphragm) and peri-vesical spaces. A contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan is needed for confirmation. Only 10–25% of patients survive rupture due to large pre- and post-operative mortality. Annual mortality from ruptured abdominal aneurysms in the United States alone is about 15,000. Another important complication of AAA is formation of a thrombus in the aneurysm.