Top videos

Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to another organ system, often the kidneys. Preeclampsia usually begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy in a woman whose blood pressure had been normal. Even a slight rise in blood pressure may be a sign of preeclampsia. Left untreated, preeclampsia can lead to serious — even fatal — complications for both you and your baby. If you have preeclampsia, the only cure is delivery of your baby. If you're diagnosed with preeclampsia too early in your pregnancy to deliver your baby, you and your doctor face a challenging task. Your baby needs more time to mature, but you need to avoid putting yourself or your baby at risk of serious complications.

The Combitube is a twin lumen device designed for use in emergency situations and difficult airways. It can be inserted without the need for visualization into the oropharynx, and usually enters the esophagus. It has a low volume inflatable distal cuff and a much larger proximal cuff designed to occlude the oro- and nasopharynx.
If the tube has entered the trachea, ventilation is achieved through the distal lumen as with a standard ETT. More commonly the device enters the esophagus and ventilation is achieved through multiple proximal apertures situated above the distal cuff. In the latter case the proximal and distal cuffs have to be inflated to prevent air from escaping through the esophagus or back out of the oro- and nasopharynx.

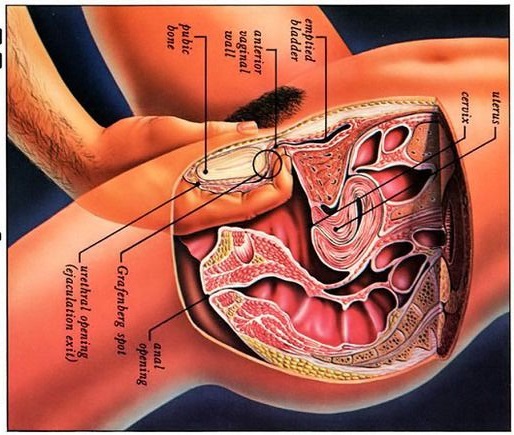
The fuel for the process leading to orgasm is testosterone, a hormone produced in steady supply by the testicles. The testicles also make millions of sperm each day, which mature and then are mixed with whitish, protein-rich fluids. These fluids nourish and support the sperm so they can live after ejaculation for a limited time. This mixture of fluid and sperm, known as semen, is what is moved through the urethra and out the penis during orgasm.

Como Aumentar Los Gluteos, Como Aumentar Las Pompas, Masajes Para Aumentar Gluteos--- http://aumente-gluteos.plus101.com/ --- Para conseguir un cuerpo perfecto hay que tomar en cuenta todo lo que consumimos día a día, razón por la cual te mencionaremos a continuación los mejores alimentos que debes comer frecuentemente para levantar los glúteos y piernas rápidamente: 1. Las Proteínas Las proteínas deben estar presentes dentro de tu dieta de manera constante, ya que ellas son las responsables del aumento del volumen de la masa muscular, te ayudarán a aumentar rápidamente los glúteos y piernas, para luego darle la firmeza y tonificación adecuada con los ejercicios. Proteínas de origen animal: Pollo sin piel, carne de res, pescado y ternera, considerando siempre que sean bajas en grasas, puedes encontrar proteínas además en los huevos y en los productos lácteos descremados. Proteínas de origen vegetal: Las puedes encontrar en las legumbres como lentejas, frijoles o garbanzos, en las semillas, las verduras y los cereales. 2. Carbohidratos Las mayorías de las personas cometen el error de eliminar de su dieta de manera completa los carbohidratos, los cuales son necesarios para el normal funcionamiento del organismo. Te recomendamos comer carbohidratos luego de una fuerte rutina de ejercicio, ya que es el momento ideal para que sean absorbidos completamente por las células musculares aumentando por lo tanto el tamaño de los glúteos y las piernas, entre los carbohidratos fundamentales para una buena alimentación tenemos: avena, granola, pan, arroz y pastas siempre que sean integrales. 3. Grasas Saludables No todas las grasas son malas para nuestra salud, existen algunas que son incluso indispensables para nuestros cuerpos, entre ellas tenemos: aceite de oliva, aceite de canola, nueces, aguacate, omega 3, aceite de almendra y de girasol. 4. Frutas y vegetales Las frutas y vegetales te ayudarán a hacer crecer los glúteos y piernas rápidamente gracias a sus altos contenidos en vitaminas y minerales que favorecen la regeneración de los músculos, dándote la energía y resistencia necesaria al momento de realizar tu rutina de ejercicios, así que inclúyelas dentro de tu dieta saludable para conseguir óptimos resultados. Alguna vez has deseado tener una cola más atractiva, pero sin invertir demasiado tiempo ni trabajo, Ingresa aqui: http://aumente-gluteos.plus101.com/

Eric knew he needed help when an old knee injury began worsening over the course of time and was significantly affecting his quality of life. That’s when he turned to his hometown orthopedic experts at Mayo Clinic Health System in Mankato, who recommended a total knee replacement. After overcoming some initial fears, Eric decided it was time to have the operation — a fuller and more active life with his family depended on it.
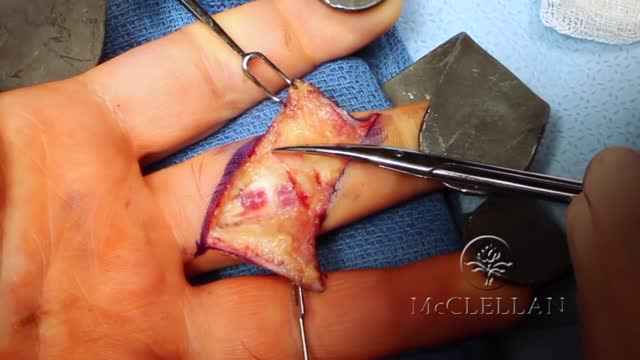
A deep cut on the palm side of your fingers, hand, wrist, or forearm can damage your flexor tendons, which are the tissues that help control movement in your hand. A flexor tendon injury can make it impossible to bend your fingers or thumb.

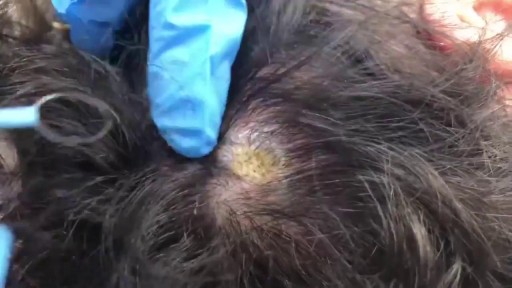
http://hidradenitis-suppurativa-cure.plus101.com --- What Is Hs, How To Get Rid Of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment Options. What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa? Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a non-contagious skin disease that is also known as Acne Inversa. This condition affects areas of the body where there is skin to skin contact and where sweat or oil glands are present; common areas are the underarms, breasts, buttocks, anal region, and groin. It affects between 1 to 4% of the world's population, and is more likely to occur in females. Symptoms Hidradenitis Suppurativa is characterized by persistent abscesses, cysts (epidermoid, sebaceous, and pilonidal) and infections. The condition is chronic and often goes through alternating periods of remission and flare-ups. During flare-ups, the inflammation tends to be severe and patients may develop fever and be very fatigued. The pain can be unbearable and the person's movements will be very limited. The abscesses often drain pus and leave open wounds that may not heal. Eventually, abscesses may become interconnected through tunnels under skin and this makes the condition harder to treat. Causes The immediate cause of Hidradenitis Suppurativa is clogging of the apocrine glands, due to dead skin cells become trapped in the gland, over production of oil, or bacterial accumulation. This will cause the plug to swell with pus formation. What causes this simple blockage to progress into a full blow Hidradenitis Suppurativa case is still debated, however, possible theories include an auto-immune reaction, hormone imbalances and genetic disorders. It is also known that excessive sweating and being overweight will increase the risk of developing the condition. Furthermore, wearing tight clothing, excessive shaving, using lithium medications and hot humid climates have been identified as triggering factors. For a complete guide on curing Hidradenitis Suppurativa through a natural and holistic approach, visit http://hidradenitis-suppurativa-cure.plus101.com