Top videos
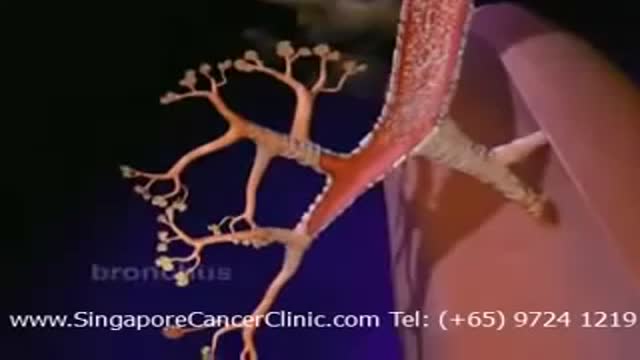
Screening is looking for cancer before a person has any symptoms. This can help find cancer at an early stage when it may be easier to treat. Lung cancer may have spread by the time a person has symptoms. One reason lung cancer is so serious is because it usually is not found until it has spread and is more difficult to treat. Screening may provide new hope for early detection and treatment of lung cancer. Scientists study screening tests to find those with the fewest risks and most benefits. They look at results over time to see if finding the cancer early decreases a person's chance of dying from the disease.

What Causes Ulcers? No single cause has been found for ulcers. However, it is now clear that an ulcer is the end result of an imbalance between digestive fluids in the stomach and duodenum. Most ulcers are caused by an infection with a type of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). Factors that can increase your risk for ulcers include: Use of painkillers called nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin, naproxen (Aleve, Anaprox, Naprosyn, and others), ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, some types of Midol, and others), and many others available by prescription; even safety-coated aspirin and aspirin in powered form can frequently cause ulcers. Excess acid production from gastrinomas, tumors of the acid producing cells of the stomach that increases acid output (seen in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome) Excessive drinking of alcohol Smoking or chewing tobacco Serious illness Radiation treatment to the area What Are the Symptoms of an Ulcer? An ulcer may or may not have symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may include: A gnawing or burning pain in the middle or upper stomach between meals or at night Bloating Heartburn Nausea or vomiting In severe cases, symptoms can include: Dark or black stool (due to bleeding) Vomiting blood (that can look like "coffee-grounds") Weight loss Severe pain in the mid to upper abdomen

This video contains five segments with best practices on how to prevent infection in patients with catheters, fistulas or grafts. It also includes segments on hand hygiene and glove use and dialysis station disinfection. The video is intended to be used by outpatient hemodialysis facilities as an educational tool to help remind their frontline staff, including technicians and nurses, about infection prevention measures. It can be used as an orientation video for new staff and as an annual in-service training tool to remind staff of proper protocols.
See the Spanish captioned version at: http://youtu.be/L5ypnOvOFMQ
Comments on this video are allowed in accordance with our comment policy: http://www.cdc.gov/SocialMedia..../Tools/CommentPolicy
This video can also be viewed at http://streaming.cdc.gov/vod.p....hp?id=dc66d96228817d
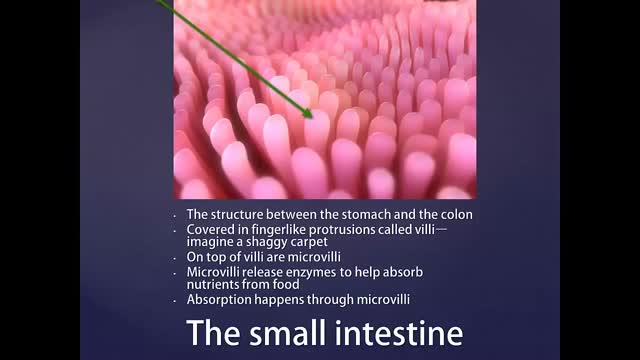
The symptoms of bacterial overgrowth include nausea, flatus, constipation, bloating, abdominal distension, abdominal pain or discomfort, diarrhea, fatigue, and weakness. SIBO also causes an increased permeability of the small intestine. Some patients may lose weight.
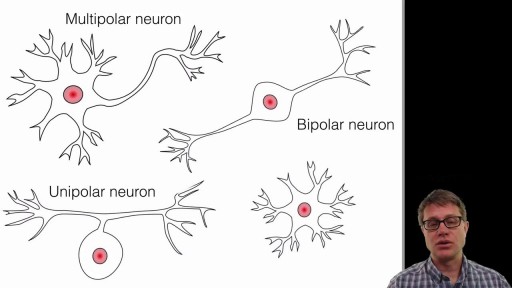
A neuron, also known as a neurone (British spelling) and nerve cell, is an electrically excitable cell that receives, processes, and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals. These signals between neurons occur via specialized connections called synapses.

Dialysis lecture 1. Dialysis Study: EXPERT NOTES for DHA, Bonent, CHT, B.Sc in Dialysis, Diploma in Dialysis https://amzn.eu/d/35Ui1kT
2. Dialysis Study : Q & A: MCQs, Fill in the blanks, True or False https://amzn.eu/d/gGn8u73
1. Dialysis Study :EXPERT NOTES for DHA, Bonent, CHT, B.Sc in Dialysis, Diploma in Dialysis, Naseha Helal.
https://play.google.com/store/....books/details?id=D_7
2. Dialysis Study: Q & A MCQ https://play.google.com/store/....books/details?id=T_3
Whatsapp
https://chat.whatsapp.com/DKCHbgsNwXS1wd7xI31tpr
Telegram
https://t.me/dialysislife PRINCIPLE OF dialysis
https://youtu.be/cfOm0aFmbe8
Dialysis machine alarms
https://youtu.be/-1A1INyDEOg
DDS dialysis disequilibrium syndrome
https://youtu.be/8AqVFiBOkIc
Peritoneal Dialysis
https://youtu.be/iHPPadGmsv0
Itching
https://youtu.be/T83Wm3HHU4M
What is CRRT
https://youtu.be/jPgFnoSEBMU
LVH
https://youtu.be/ZhFL3Z6LHeA
Sorbent dialysis
https://youtu.be/-rie5dC_FkY
RO Water
https://youtu.be/3jlEsK4Lg_I
Carbon filter RO water
https://youtu.be/mJrgtjNafQw
Hemoperfusion
https://youtu.be/UkbBm8rm9Ww
AV fistula or Dialysis fistula
https://youtu.be/uDbyfqCkCbo
Dialysis MCQ
https://youtu.be/zmOj0BL6jVY
AVF cannulation
https://youtu.be/PyqMcHA07zY
Complications of AV fistula
https://youtu.be/a_CXIvuOO_s
Blood clotting during Dialysis
https://youtu.be/9hYNepiO2o8
Muscle crapms
https://youtu.be/09s07Eiqr2k
Hepatitis C
https://youtu.be/qdNj_GhmnSE
Dialysis procedure
https://youtu.be/u1mGqXO5pzQ
Hypotension
https://youtu.be/4EVPmWTSyN8
Heparin free dialysis
https://youtu.be/rFqAn7HcWwM
Plasmapheresis
https://youtu.be/kbgsjjs9krg
Isolated ultrafiltration
https://youtu.be/xp5I5--uWb0
High flux dialyzer
https://youtu.be/gCNsErn1HHM
Urea and Creatinine
https://youtu.be/Id9AIySMQ6c
Practical RO water demo
https://youtu.be/2pXKGMDNS84
Sodium profiling
https://youtu.be/bE_DcBXNB5g
Peritoneal Dialysis
https://youtu.be/vtK6VZsi8AY
Air embolism
https://youtu.be/WJE-xqnQfd8
Dialysate
https://youtu.be/z_nb43bcWsM
How to stop Bleed from fistula
https://youtu.be/N_inLKPhPUc
Dialysis short form
https://youtu.be/3BqB-gODb5o
Dialyzer reprocessing
https://youtu.be/XelfkKsndlc
Dialysis catheter
https://youtu.be/V7y90m4xlv8
How to set KT/V
https://youtu.be/hWXjU8VTQdk
Mircera injection
https://youtu.be/STtd3I3EijA
Dialysis procedure
https://youtu.be/MIdhIgcKRZ8
Dialysis in snake bite poison
https://youtu.be/niA9RI38jyY
Uf profiling
https://youtu.be/wyjpFjD5Hi0
Heparin dose
https://youtu.be/kB56MkzHIQ0
Hyperkalemia
https://youtu.be/1rWWNlcAuio
Change bandages of leaking fistula
https://youtu.be/_0cebWWdjM8
AvF needle
https://youtu.be/GvUxbXxftTk
Polycystic kidney disease
https://youtu.be/IhsMbHFXZG8
Nephrotic syndrome
https://youtu.be/FEEOsIrXxV8
Diabetic nephropathy
https://youtu.be/v-FBIQ7MA4k
Hemodialysis permanent access
https://youtu.be/_YrwxwiR0f8
Sex and dialysis
https://youtu.be/vvl8UT8lK4k
Albumin and dialysis
https://youtu.be/yzG7yD45Nwg

Perdre Du Ventre, Comment Maigrir Des Cuisses, Regime Soupe, Prendre Du Muscle, Maigrir Des Hanches ---- http://perte-poids-rapide.info-pro.co --- Comment maigrir pour un homme ? Les régimes ne sont pas une exclusivité féminine et les hommes ont eux aussi des comptes à rendre à leur balance. Pour séduire, pour se sentir mieux dans leur corps, pour leur travail, ils ont eux aussi des raisons pour se délester de quelques kilos. Hommes et femmes : différentes face aux kilos Les hommes et les femmes ne réagissent pas de la même manière face au poids. Le corps non plus. La première différence est au niveau de la silhouette. La gente féminine va accumuler les kilos en trop au niveau des fesses et des cuisses alors que pour les hommes, la prise de poids se situe surtout au niveau du visage, du cou et du ventre. L’autre différence entre les hommes et les femmes est la faculté à perdre du poids. Si vous avez décidé de suivre un régime en couple, sachez Mesdames que les hommes maigrissent plus vite ! Cette « injustice » est expliquée par le fait que les hommes ou plutôt leur organisme, va brûler plus de calories au repos et à l’effort que les femmes grâce à leur masse corporelle plus importante. Par contre, ces dames sont plus motivées à tenir un régime sur la longueur. Les hommes et les régimes, c’est toute une histoire ! C’est pourquoi ils doivent faire un régime qui leur corresponde et qui est adapté à leur vie au quotidien ! Maigrir lorsque l’on est un homme Les hommes sont de plus en plus nombreux à vouloir perdre du poids. Surtout entre 40 et 45 ans. Mais même s’ils maigrissent plus vite que les femmes, la partie est loin d’être gagnée. Pourquoi ? Parce qu’il est plus compliqué pour eux de modifier leurs habitudes alimentaires. En effet, ce sont les vrais champions d’une alimentation riche en matières grasses, peu variée et très déséquilibrée. Il faut donc qu’ils adoptent de nouvelles habitudes alimentaires tout en conservant une certaines notion de plaisir et qu’ils combattent certaines mauvaises habitudes, souvent responsable de leurs kilos en trop. "Découvrez comment jean-jacques a réussi à perdre 3,2 kilos et 7 cm de tour de taille en 2 semaines, sans peser les aliments ni compter les calories." Cliquez ici: http://perte-poids-rapide.info-pro.co

Following Dr. Eric Skarsgard on his grueling 19-hour day at BC Children's Hospital, we meet several of his patients -- some of who need surgery that day, and some who have chronic conditions and need regular check-ups with him -- and learn how he works with medical students and on research projects as time allows.

How to improve your eyesight at home? Exercising your eyes is one of those simple things that very few people do. However, it can help you maintain excellent vision. Here are 10 exercises that will take you no more than ten minutes to do. You can give them a try right now while watching this video – we are going to do all of them with you! Exercise #1. Blink for a minute. Exercise #2. Rotate your head while staring ahead. Exercise #3. Look to your right and left. Exercise #4. Close your eyes and relax. Exercise #5. Move your gaze in different directions. Exercise #6. Close and open your eyes. Exercise #7. Push against your temples with your fingers. Exercise #8. Draw geometric figures with your gaze. Exercise #9. Move your eyeballs up and down. Exercise #10. Strengthen your eyes’ near and far focusing.

An enlarged spleen may cause: No symptoms in some cases. Pain or fullness in the left upper abdomen that may spread to the left shoulder. Feeling full without eating or after eating only a small amount from the enlarged spleen pressing on your stomach. Anemia. Fatigue. Frequent infections. Easy bleeding.

How to use a Gonorrhea rapid test kit for self-diagnosis of Gonorrhea (swab test). Convenient, Easy to Use, and over 99% Accurate. Certified GMP and ISO13485. Test yourself at home with Complete Privacy. Buy online today at: http://www.stdrapidtest.com

Ten percent of all pregnancies are complicated by hypertension. Eclampsia and preeclampsia account for about half of these cases worldwide, and these conditions have been recognized and described for years despite the general lack of understanding of the disease. [1] In the fifth century, Hippocrates noted that headaches, convulsions, and drowsiness were ominous signs associated with pregnancy. In 1619, Varandaeus coined the term eclampsia in a treatise on gynecology. [2, 3]