- Physical Examination
- Surgical Examination
- Ophthalmology
- Clinical Skills
- Orthopedics
- Surgery Videos
- Laparoscopy
- Pediatrics
- Funny Videos
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Nursing Videos
- Plastic Surgery
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Histology and Histopathology
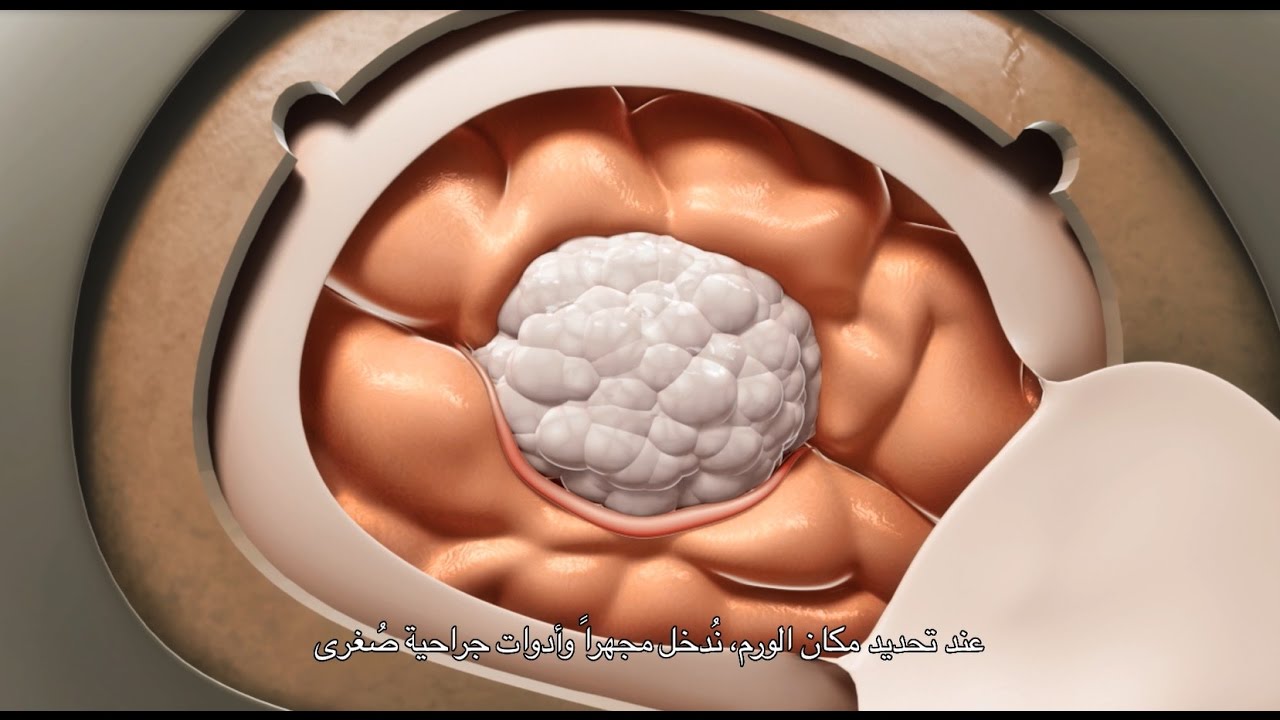
- Neurosurgery
- Dermatology
- Pediatric Surgery
- Urology
- Dentistry
- Oncology and Cancers
- Anatomy Videos
- Health and Fitness
- Radiology
- Anaesthesia
- Physical Therapy
- Pharmacology
- Interventional Radiology
- Cardiology
- Endocrinology
- Gynecology
- Emergency Medicine
- Psychiatry and Psychology
- Childbirth Videos
- General Medical Videos
- Nephrology
- Physiology
- Diet and Food Health
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Neurology
- Women Health
- Osteoporosis
- Gastroenterology
- Pulmonology
- Hematology
- Rheumatology
- Toxicology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Vascular Disease
- Reproductive Health
- Burns and Wound Healing
- Other
Brain Injury
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) TBI is defined as an alteration in brain function, or other evidence of brain pathology, caused by an external force. Adopted by the Brain Injury Association Board of Directors in 2011. This definition is not intended as an exclusive statement of the population served by the Brain Injury Association of America. Acquired Brain Injury An acquired brain injury is an injury to the brain, which is not hereditary, congenital, degenerative, or induced by birth trauma. An acquired brain injury is an injury to the brain that has occurred after birth. There is sometimes confusion about what is considered an acquired brain injury. By definition, any traumatic brain injury (e.g. from a motor vehicle accident or assault) could be considered an acquired brain injury. In the field of brain injury, acquired brain injuries are typically considered any injury that is non traumatic. Examples of acquired brain injury include stroke, near drowning, hypoxic or anoxic brain injury, tumor, neurotoxins, electric shock or lightning strike.