- Physical Examination
- Surgical Examination
- Ophthalmology
- Clinical Skills
- Orthopedics
- Surgery Videos
- Laparoscopy
- Pediatrics
- Funny Videos
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Nursing Videos
- Plastic Surgery
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Histology and Histopathology
- Neurosurgery
- Dermatology
- Pediatric Surgery
- Urology
- Dentistry
- Oncology and Cancers
- Anatomy Videos
- Health and Fitness
- Radiology
- Anaesthesia
- Physical Therapy
- Pharmacology
- Interventional Radiology
- Cardiology
- Endocrinology
- Gynecology
- Emergency Medicine
- Psychiatry and Psychology
- Childbirth Videos
- General Medical Videos
- Nephrology
- Physiology
- Diet and Food Health
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Neurology
- Women Health
- Osteoporosis
- Gastroenterology
- Pulmonology
- Hematology
- Rheumatology
- Toxicology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Vascular Disease
- Reproductive Health
- Burns and Wound Healing
- Other
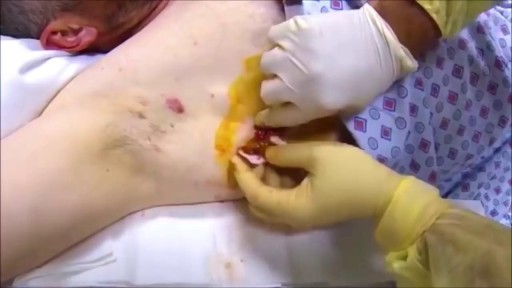
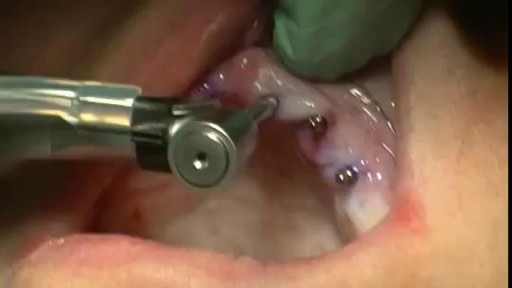
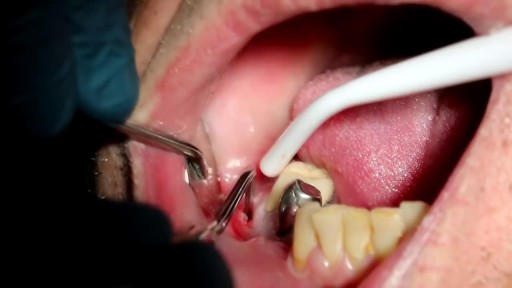
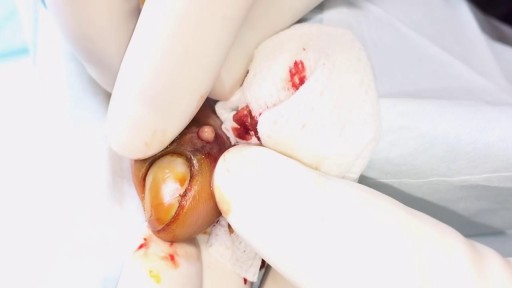
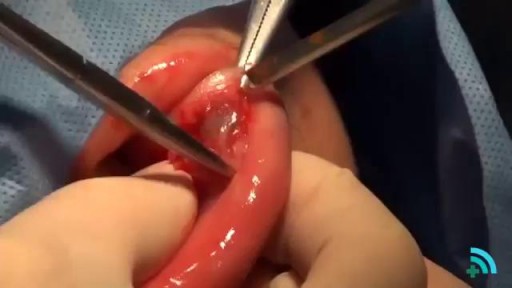
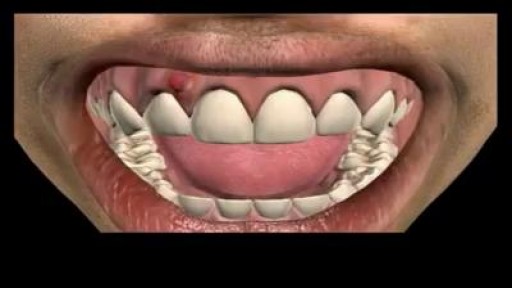
Dental Abscess extending into Submandibular space
If a patient comes to you with a painful, throbbing, swollen, red face (a ''fat face'), perhaps with fever, trismus and lymphadenitis, he is probably suffering from an acute dental or oral infection, most probably an alveolar abscess. He may have: (1) An alveolar abscess begins as an infection in the bone around a non-vital infected tooth. He has severe pain, which becomes less as pus is released into more superficial tissues and his face starts to swell. After 36 hours of cellulitis he usually has a fluctuant abscess which needs draining. If drainage is delayed, the pus in his abscess discharges spontaneously through a sinus (26-8) in his gum or face, which may become chronic. First, control infection with antibiotics, and then drain the abscess, either by incising it where it is pointing, or by removing the infected tooth, which acts as a cork to prevent the pus escaping, or by doing both these things. If you remove a tooth before you have controlled the infection with antibiotics, and while his face is still severely swollen, you may spread the infection; your task will also be more difficult. (2) A periodontal abscess at the side of a tooth, caused by spread from an infected gum. (3) A pericoronal abscess caused by infection of the gum over the crown of an unerupted and impacted tooth, usually a lower third molar (''an infected wisdom tooth'). Often, an abscess does not form, and the gum round the tooth is merely inflamed.