- Physical Examination
- Surgical Examination
- Ophthalmology
- Clinical Skills
- Orthopedics
- Surgery Videos
- Laparoscopy
- Pediatrics
- Funny Videos
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Nursing Videos
- Plastic Surgery
- Otorhinolaryngology
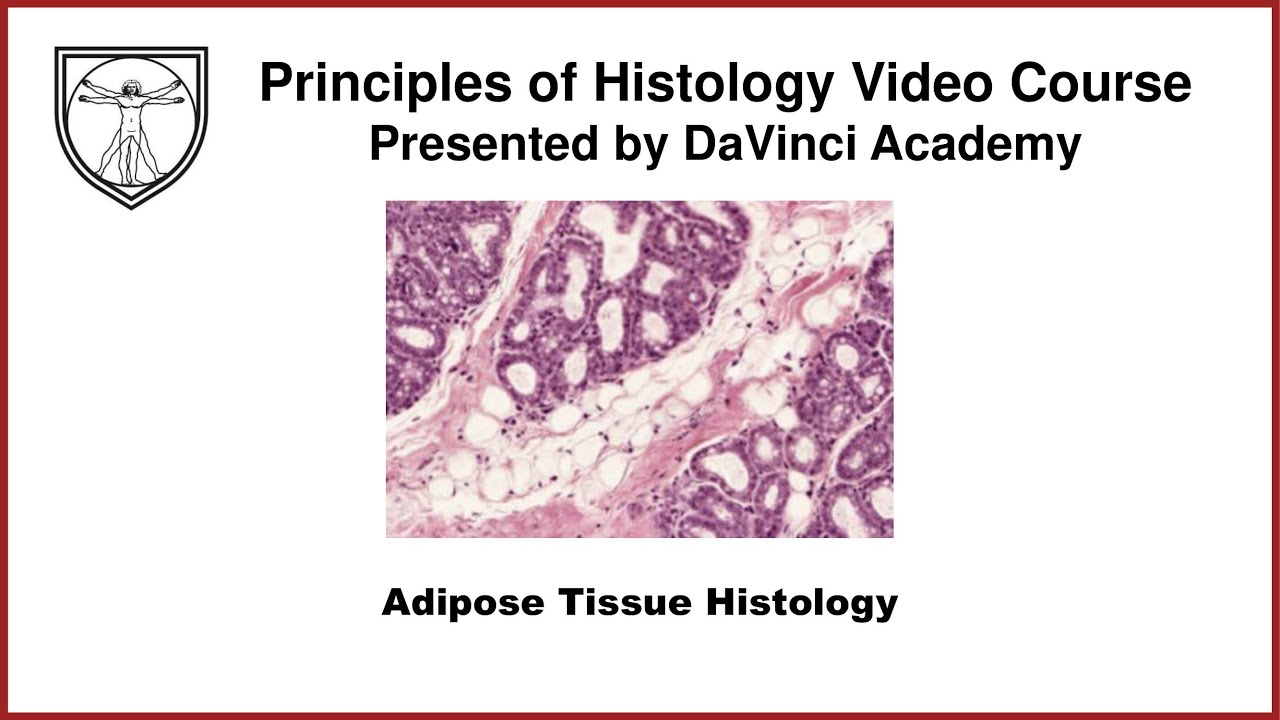
- Histology and Histopathology
- Neurosurgery
- Dermatology
- Pediatric Surgery
- Urology
- Dentistry
- Oncology and Cancers
- Anatomy Videos
- Health and Fitness
- Radiology
- Anaesthesia
- Physical Therapy
- Pharmacology
- Interventional Radiology
- Cardiology
- Endocrinology
- Gynecology
- Emergency Medicine
- Psychiatry and Psychology
- Childbirth Videos
- General Medical Videos
- Nephrology
- Physiology
- Diet and Food Health
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Neurology
- Women Health
- Osteoporosis
- Gastroenterology
- Pulmonology
- Hematology
- Rheumatology
- Toxicology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Vascular Disease
- Reproductive Health
- Burns and Wound Healing
- Other
Help with Histology
How to approach histology for Human Anatomy students. Using a key will help get you through it! Add some penguin fairy dust will help too!
Please note: I mis-spoke and said "striated" instead of "stratified epithelium" a couple of times... apologies!
There are lots of histology keys out there, but the one I showed in the video is here: http://www.penguinprof.com/upl....oads/8/4/3/1/8431323
Want more?
Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/user/ThePenguinProf
FB Page: https://www.facebook.com/ThePenguinProf
Twitter: https://twitter.com/penguinprof
Web: http://www.penguinprof.com/
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Details:
Tissue in the human body:
Epithelial: Is made of cells arranged in a continuous sheet with one or more layers, has apical & basal surfaces.
A basement membrane is the attachment between the basal surface of the cell & the underlying connective tissue.
Two types of epithelial tissues: (1) Covering & lining epithelia and (2) Glandular Epithelium.
The number of cell layers & the shape of the cells in the top layer can classify epithelium.
Simple Epithelium - one cell layer
Stratified epithelium - two or more cell layers
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium - When cells of an epithelial tissue are all anchored to the basement Membrane but not all cells reach the apical surface.
Glandular Epithelium -- (1) Endocrine: Release hormones directly into the blood stream and (2) Exocrine - Secrete into ducts.
Connective: contains many different cell types including: fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and adipocytes. Connective Tissue Matrix is made of two materials: ground substance - proteins and polysaccharides, fiber -- reticular, collagen and elastic.
Classification of Connective Tissue:
Loose Connective - fibers & many cell types in gelatinous matrix, found in skin, & surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs.
Dense Connective - Bundles of parallel collagen fibers& fibroblasts, found in tendons& ligaments.
Cartilage - Cartilage is made of collagen & elastin fibers embedded in a matrix glycoprotein & cells called chondrocytes, which was found in small spaces.
Cartilage has three subtypes:
Hyaline cartilage -- Weakest, most abundant type, Found at end of long bones, & structures like the ear and nose,
Elastic cartilage- maintains shape, branching elastic fibers distinguish it from hyaline and
Fibrous Cartilage - Strongest type, has dense collagen & little matrix, found in pelvis, skull & vertebral discs.
Muscle: is divided into 3 categories, skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
Skeletal Muscle -- voluntary, striated, striations perpendicular to the muscle fibers and it is mainly found attached to bones.
Cardiac Muscle -- involuntary, striated, branched and has intercalated discs
Smooth Muscle -- involuntary, nonstriated, spindle shaped and is found in blood vessels & the GI tract.
Nervous: Consists of only two cell types in the central nervous system (CNS) & peripheral nervous system (PNS):
Neurons - Cells that convert stimuli into electrical impulses to the brain, and Neuroglia -- supportive cells.
Neurons -- are made up of cell body, axon and dendrites. There are 3 types of neurons:
Motor Neuron -- carry impulses from CNS to muscles and glands,
Interneuron - interpret input from sensory neurons and end responses to motor neurons
Sensory Neuron -- receive information from environment and transmit to CNS.
Neuroglia -- is made up of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia in the CNS, and schwann cells and satellite cells in the PNS.

![Histology of Exocrine Gland [Epithelium 7 of 7]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/NkU7YJ7eYd0/maxresdefault.jpg)