Herpes Simplex
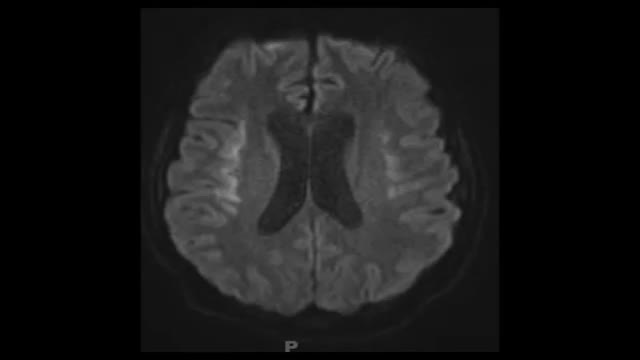
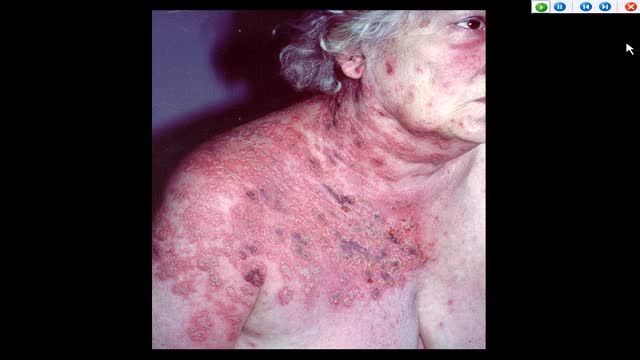
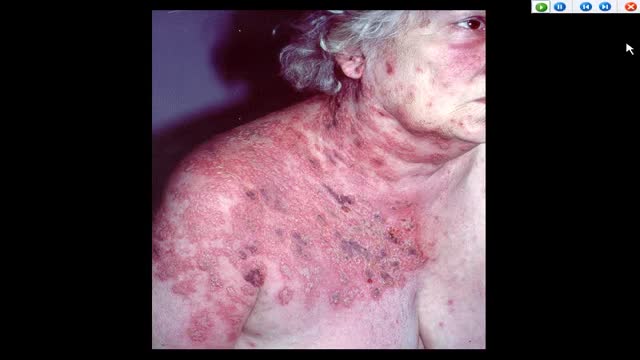
Primary infection with herpes simplex viruses (HSVs) is clinically more severe than recurrent outbreaks. However, most primary HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections are subclinical and may never be clinically diagnosed. Orolabial herpes Herpes labialis (eg, cold sores, fever blisters) is most commonly associated with HSV-1 infection. Oral lesions caused by HSV-2 have been identified, usually secondary to orogenital contact. Primary HSV-1 infection often occurs in childhood and is usually asymptomatic. Primary infection Symptoms of primary herpes labialis may include a prodrome of fever, followed by a sore throat and mouth and submandibular or cervical lymphadenopathy. In children, gingivostomatitis and odynophagia are also observed. Painful vesicles develop on the lips, the gingiva, the palate, or the tongue and are often associated with erythema and edema. The lesions ulcerate and heal within 2-3 weeks. Recurrences The disease remains dormant for a variable amount of time. HSV-1 reactivation in the trigeminal sensory ganglia leads to recurrences in the face and the oral, labial, and ocular mucosae. Pain, burning, itching, or paresthesia usually precedes recurrent vesicular lesions that eventually ulcerate or form a crust. The lesions most commonly occur in the vermillion border, and symptoms of untreated recurrences last approximately 1 week. Recurrent erythema multiforme lesions have been associated with orolabial HSV-1 recurrences. A recent study reported that HSV-1 viral shedding had a median duration of 48-60 hours from the onset of herpes labialis symptoms. They did not detect any virus beyond 96 hours of symptom onset.[7] Genital herpes HSV-2 is identified as the most common cause of herpes genitalis. However, HSV-1 has been increasingly identified as the causative agent in as many as 30% of cases of primary genital herpes infections likely secondary to orogenital contact. Recurrent genital herpes infections are almost exclusively caused by HSV-2. Primary infection Primary herpes genitalis occurs within 2 days to 2 weeks after exposure to the virus and has the most severe clinical manifestations. Symptoms of the primary episode typically last 2-3 weeks. In men, painful, erythematous, vesicular lesions that ulcerate most commonly occur on the penis, but they can also occur on the anus and the perineum. In women, primary herpes genitalis presents as vesicular/ulcerated lesions on the cervix and as painful vesicles on the external genitalia bilaterally. They can also occur on the vagina, the perineum, the buttocks, and, at times, the legs in a sacral nerve distribution. Associated symptoms include fever, malaise, edema, inguinal lymphadenopathy, dysuria, and vaginal or penile discharge. Females may also have lumbosacral radiculopathy, and as many as 25% of women with primary HSV-2 infections may have associated aseptic meningitis. Recurrences After primary infection, the virus may be latent for months to years until a recurrence is triggered. Reactivation of HSV-2 in the lumbosacral ganglia leads to recurrences below the waist. Recurrent clinical outbreaks are milder and often preceded by a prodrome of pain, itching, tingling, burning, or paresthesia. Individuals who are exposed to HSV and have asymptomatic primary infections may experience an initial clinical episode of genital herpes months to years after becoming infected. Such an episode is not as severe as a true primary outbreak. More than one half of individuals who are HSV-2 seropositive do not experience clinically apparent outbreaks. However, these individuals still have episodes of viral shedding and can transmit the virus to their sexual partners. Other HSV infections Localized or disseminated eczema herpeticum is also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption. Caused by HSV-1, eczema herpeticum is a variant of HSV infection that commonly develops in patients with atopic dermatitis, burns, or other inflammatory skin conditions. Children are most commonly affected. Herpes whitlow, vesicular outbreaks on the hands and the digits, was most commonly due to infection with HSV-1. It usually occurred in children who sucked their thumbs and, prior to the widespread use of gloves, in dental and medical health care workers. The occurrence of herpes whitlow due to HSV-2 is increasingly recognized, probably due to digital-genital contact. Herpes gladiatorum is caused by HSV-1 and is seen as papular or vesicular eruptions on the face, arms, or torsos of athletes in sports involving close physical contact (classically wrestling). Disseminated HSV infection can occur in females who are pregnant and in individuals who are immunocompromised. These patients may present with atypical signs and symptoms of HSV, and the condition may be difficult to diagnose. Herpetic sycosis, a follicular infection with HSV, may present as a vesiculopustular eruption on the beard area. This infection often results from autoinoculation after shaving through a recurrent herpetic outbreak. Classically caused by HSV-1, there have been rare reports of relapsing beard folliculitis caused by type 2 HSV.[8] Neonatal HSV HSV-2 infection in pregnancy can have devastating effects on the fetus. Neonatal HSV usually manifests within the first 2 weeks of life and clinically ranges from localized skin, mucosal, or eye infections to encephalitis, pneumonitis, disseminated infection, and demise. Most women who deliver infants with neonatal HSV had no prior history, signs, or symptoms of HSV infection. Risk of transmission is highest in pregnant women who are seronegative for both HSV-1 and HSV-2 and acquire a new HSV infection in the third trimester of pregnancy. Factors that increase the risk of transmission from mother to baby include the type of genital infection at the time of delivery (higher risk with active primary infection), active lesions, prolonged rupture of membranes, vaginal delivery, and an absence of transplacental antibodies. The mortality rate for neonates is extremely high (>80%) if untreated.









SORT BY-
Top Comments
-
Latest comments